Мао Цзэдун
Мао Цзэдун | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Мао Цзэдун | |||
 Mao in 1959 | |||
| Chairman of the Communist Party of China | |||
| In office 20 March 1943 – 9 September 1976 | |||
| Deputy |
| ||
| Preceded by | Zhang Wentian (as General Secretary) | ||
| Succeeded by | Hua Guofeng | ||
| 1st Chairman of the People's Republic of China | |||
| In office 27 September 1954 – 27 April 1959 | |||
| Premier | Zhou Enlai | ||
| Deputy | Zhu De | ||
| Succeeded by | Liu Shaoqi | ||
| Chairman of the Central Military Commission | |||
| In office 8 September 1954 – 9 September 1976 | |||
| Deputy |
| ||
| Succeeded by | Hua Guofeng | ||
| Chairman of the Central People's Government | |||
| In office 1 October 1949 – 27 September 1954 | |||
| Premier | Zhou Enlai | ||
| Preceded by | Office established Li Zongren (as President of the Republic of China) | ||
| Chairman of the Chinese People's Political Consultative Conference | |||
| In office 9 October 1949 – 25 December 1954 | |||
| Preceded by | Office established | ||
| Succeeded by | Zhou Enlai | ||
| Personal details | |||
| Born | 26 December 1893 Shaoshan, Hunan, Qing China | ||
| Died | 9 September 1976 (aged 82) Beijing, China | ||
| Resting place | Chairman Mao Memorial Hall, Beijing | ||
| Political party | Chinese Communist Party (from 1921) | ||
| Other political affiliations | Kuomintang (1925–1926) | ||
| Spouses | |||
| Children | 10, including: | ||
| Parents |
| ||
| Alma mater | Hunan First Normal University | ||
| Signature | |||
| Chinese name | |||
| Simplified Chinese | 毛泽东 | ||
| Traditional Chinese | 毛澤東 | ||
| |||
| Courtesy name | |||
| Simplified Chinese | 润之 | ||
| Traditional Chinese | 潤之 | ||
| |||
Central institution membership Other offices held | |||
| |||
Мао Цзэдун [ а ] (26 декабря 1893 — 9 сентября 1976), также известный как Председатель Мао , был китайским политиком, теоретиком марксизма , военным стратегом, поэтом и революционером, который был основателем Китайской Народной Республики (КНР). Он руководил страной с момента ее создания в 1949 году до своей смерти в 1976 году, одновременно занимая пост председателя Коммунистической партии Китая в это время . Его теории, военные стратегии и политика известны как маоизм .
Мао был сыном зажиточного крестьянина в Шаошани , провинция Хунань. Он поддерживал китайский национализм и в начале своей жизни придерживался антиимпериалистических взглядов, на него особенно повлияли события Синьхайской революции 1911 года и Движения четвертого мая 1919 года. Позже он принял марксизм-ленинизм, работая в Пекинском университете в качестве преподавателя. библиотекарь. Он стал одним из основателей Коммунистической партии Китая (КПК), возглавив восстание осеннего урожая в 1927 году. Во время гражданской войны в Китае между Гоминьданом (Гоминьданом) и КПК Мао помог основать Китайскую Красную Армию , возглавил Советский Союз Цзянси. радикальную политику земельной реформы и в конечном итоге стал главой КПК во время Великого похода . Хотя КПК временно объединилась с Гоминьданом в рамках Второго объединенного фронта во время Второй китайско-японской войны (1937–1945), гражданская война в Китае возобновилась после капитуляции Японии . Силы Мао разгромили националистическое правительство , которое ушло на Тайвань в 1949 году.
On 1 October 1949, Mao proclaimed the foundation of the PRC, a Marxist–Leninist single-party state controlled by the CCP. In the following years he solidified his control through the land reform campaign against landlords, the Campaign to Suppress Counterrevolutionaries, the "Three-anti and Five-anti Campaigns", and through a truce in the Korean War, which altogether resulted in the deaths of several million Chinese. From 1953 to 1958, Mao played an important role in enforcing command economy in China, constructing the first Constitution of the PRC, launching an industrialisation program, and initiating military projects such as the "Two Bombs, One Satellite" project and Project 523. His foreign policies during this time were dominated by the Sino-Soviet split which drove a wedge between China and the Soviet Union. In 1955, Mao launched the Sufan movement, and in 1957 he launched the Anti-Rightist Campaign, in which at least 550,000 people, mostly intellectuals and dissidents, were persecuted. In 1958, he launched the Great Leap Forward that aimed to rapidly transform China's economy from agrarian to industrial, which led to the Great Chinese Famine and the deaths of 15–55 million people between 1958 and 1962.
In 1963, Mao launched the Socialist Education Movement, and in 1966 he initiated the Cultural Revolution, a program to remove "counter-revolutionary" elements in Chinese society which lasted 10 years and was marked by violent class struggle, widespread destruction of cultural artifacts, and an unprecedented elevation of Mao's cult of personality. Tens of millions of people were persecuted during the Revolution, while the estimated number of deaths ranges from hundreds of thousands to millions. After years of ill health, Mao suffered a series of heart attacks in 1976 and died at the age of 82. During the Mao era, China's population grew from around 550 million to over 900 million while the government did not strictly enforce its family planning policy. During his leadership tenure, China was heavily involved with other Asian communist conflicts such as the Korean War, the Vietnam War, and the Cambodian Civil War.
Mao is considered one of the most influential figures of the 20th century. Mao's policies were responsible for a vast number of deaths, with estimates ranging from 40 to 80 million victims due to starvation, persecution, prison labour, and mass executions, and his government has been described as totalitarian. He has been also credited with transforming China from a semi-colony to a leading world power by advancing literacy, women's rights, basic healthcare, primary education, and improving life expectancy. Mao is revered as a national hero who liberated the country from foreign occupation and exploitation in China. He became an ideological figurehead and a prominent influence over the international communist movement, being endowed with remembrance, admiration and a cult of personality both during and after his life.
English romanisation of name
During Mao's lifetime, the English-language media universally rendered his name as Mao Tse-tung, using the Wade–Giles system of transliteration for Standard Chinese though with the circumflex accent in the syllable Tsê dropped. Due to its recognizability, the spelling was used widely, even by the PRC's foreign ministry after Hanyu Pinyin became the PRC's official romanisation system for Mandarin Chinese in 1958; the well-known booklet of Mao's political statements, The Little Red Book, was officially entitled Quotations from Chairman Mao Tse-tung in English translations. While the pinyin-derived spelling Mao Zedong is increasingly common, the Wade–Giles-derived spelling Mao Tse-tung continues to be used in modern publications to some extent.[2]
Early life
Youth and the Xinhai Revolution: 1893–1911

Mao Zedong was born on 26 December 1893, near Shaoshan village in Hunan.[3] His father, Mao Yichang, was a formerly impoverished peasant who had become one of the wealthiest farmers in Shaoshan. Growing up in rural Hunan, Mao described his father as a stern disciplinarian, who would beat him and his three siblings, the boys Zemin and Zetan, as well as an adopted sister/cousin, Zejian.[4] Mao's mother, Wen Qimei, was a devout Buddhist who tried to temper her husband's strict attitude.[5] Mao too became a Buddhist, but abandoned this faith in his mid-teenage years.[5] At age 8, Mao was sent to Shaoshan Primary School. Learning the value systems of Confucianism, he later admitted that he did not enjoy the classical Chinese texts preaching Confucian morals, instead favouring classic novels like Romance of the Three Kingdoms and Water Margin.[6] At age 13, Mao finished primary education, and his father united him in an arranged marriage to the 17-year-old Luo Yixiu, thereby uniting their land-owning families. Mao refused to recognise her as his wife, becoming a fierce critic of arranged marriage and temporarily moving away. Luo was locally disgraced and died in 1910 at 20 years old.[7]

While working on his father's farm, Mao read voraciously[8] and developed a "political consciousness" from Zheng Guanying's booklet which lamented the deterioration of Chinese power and argued for the adoption of representative democracy.[9] Mao also read translations of works by Western authors including Adam Smith, Montesquieu, Jean-Jacques Rousseau, Charles Darwin, and Thomas Huxley.[10]: 34 Interested in history, Mao was inspired by the military prowess and nationalistic fervour of George Washington and Napoleon Bonaparte.[11] His political views were shaped by Gelaohui-led protests which erupted following a famine in Changsha, the capital of Hunan; Mao supported the protesters' demands, but the armed forces suppressed the dissenters and executed their leaders.[12] The famine spread to Shaoshan, where starving peasants seized his father's grain. He disapproved of their actions as morally wrong, but claimed sympathy for their situation.[13] At age 16, Mao moved to a higher primary school in nearby Dongshan,[14] where he was bullied for his peasant background.[15]
In 1911, Mao began middle school in Changsha.[16] Revolutionary sentiment was strong in the city, where there was widespread animosity towards Emperor Puyi's absolute monarchy and many were advocating republicanism. The republicans' figurehead was Sun Yat-sen, an American-educated Christian who led the Tongmenghui society.[17] In Changsha, Mao was influenced by Sun's newspaper, The People's Independence (Minli bao),[18] and called for Sun to become president in a school essay.[19] As a symbol of rebellion against the Manchu monarch, Mao and a friend cut off their queue pigtails, a sign of subservience to the emperor.[20]
Inspired by Sun's republicanism, the army rose up across southern China, sparking the Xinhai Revolution. Changsha's governor fled, leaving the city in republican control.[21] Supporting the revolution, Mao joined the rebel army as a private soldier, but was not involved in fighting or combat. The northern provinces remained loyal to the emperor, and hoping to avoid a civil war, Sun—proclaimed "provisional president" by his supporters—compromised with the monarchist general Yuan Shikai. The monarchy was abolished, creating the Republic of China, but the monarchist Yuan became president. The revolution over, Mao resigned from the army in 1912, after six months as a soldier.[22] Around this time, Mao discovered socialism from a newspaper article; proceeding to read pamphlets by Jiang Kanghu, the student founder of the Chinese Socialist Party, Mao remained interested yet unconvinced by the idea.[23]
Fourth Normal School of Changsha: 1912–1919
Over the next few years, Mao Zedong enrolled and dropped out of a police academy, a soap-production school, a law school, an economics school, and the government-run Changsha Middle School.[24] Studying independently, he spent much time in Changsha's library, reading core works of classical liberalism such as Adam Smith's The Wealth of Nations and Montesquieu's The Spirit of the Laws, as well as the works of western scientists and philosophers such as Darwin, Mill, Rousseau, and Spencer.[25] Viewing himself as an intellectual, years later he admitted that at this time he thought himself better than working people.[26] He was inspired by Friedrich Paulsen, a neo-Kantian philosopher and educator whose emphasis on the achievement of a carefully defined goal as the highest value led Mao to believe that strong individuals were not bound by moral codes but should strive for a great goal.[27] His father saw no use in his son's intellectual pursuits, cut off his allowance and forced him to move into a hostel for the destitute.[28]

Mao wanted to become a teacher and enrolled at the Fourth Normal School of Changsha, which soon merged with the First Normal School of Hunan, widely seen as the best in Hunan.[29] Befriending Mao, professor Yang Changji urged him to read a radical newspaper, New Youth (Xin qingnian), the creation of his friend Chen Duxiu, a dean at Peking University. Although he was a supporter of Chinese nationalism, Chen argued that China must look to the west to cleanse itself of superstition and autocracy.[30] In his first school year, Mao befriended an older student, Xiao Zisheng; together they went on a walking tour of Hunan, begging and writing literary couplets to obtain food.[31]
A popular student, in 1915 Mao was elected secretary of the Students Society. He organised the Association for Student Self-Government and led protests against school rules.[32] Mao published his first article in New Youth in April 1917, instructing readers to increase their physical strength to serve the revolution.[33] He joined the Society for the Study of Wang Fuzhi (Chuan-shan Hsüeh-she), a revolutionary group founded by Changsha literati who wished to emulate the philosopher Wang Fuzhi.[34] In spring 1917, he was elected to command the students' volunteer army, set up to defend the school from marauding soldiers.[35] Increasingly interested in the techniques of war, he took a keen interest in World War I, and also began to develop a sense of solidarity with workers.[36] Mao undertook feats of physical endurance with Xiao Zisheng and Cai Hesen, and with other young revolutionaries they formed the Renovation of the People Study Society in April 1918 to debate Chen Duxiu's ideas. Desiring personal and societal transformation, the Society gained 70–80 members, many of whom would later join the Communist Party.[37] Mao graduated in June 1919, ranked third in the year.[38]
Early revolutionary activity
Beijing, anarchism, and Marxism: 1917–1919

Mao moved to Beijing, where his mentor Yang Changji had taken a job at Peking University.[39] Yang thought Mao exceptionally "intelligent and handsome",[40] securing him a job as assistant to the university librarian Li Dazhao, who would become an early Chinese Communist.[41] Li authored a series of New Youth articles on the October Revolution in Russia, during which the Communist Bolshevik Party under the leadership of Vladimir Lenin had seized power. Lenin was an advocate of the socio-political theory of Marxism, first developed by the German sociologists Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels, and Li's articles added Marxism to the doctrines in Chinese revolutionary movement.[42]
Becoming "more and more radical", Mao was initially influenced by Peter Kropotkin's anarchism, which was the most prominent radical doctrine of the day. Chinese anarchists, such as Cai Yuanpei, Chancellor of Peking University, called for complete social revolution in social relations, family structure, and women's equality, rather than the simple change in the form of government called for by earlier revolutionaries. He joined Li's Study Group and "developed rapidly toward Marxism" during the winter of 1919.[43] Paid a low wage, Mao lived in a cramped room with seven other Hunanese students, but believed that Beijing's beauty offered "vivid and living compensation".[44] A number of his friends took advantage of the anarchist-organised Mouvement Travail-Études to study in France, but Mao declined, perhaps because of an inability to learn languages.[45] Mao raised funds for the movement, however.[10]: 35
At the university, Mao was snubbed by other students due to his rural Hunanese accent and lowly position. He joined the university's Philosophy and Journalism Societies and attended lectures and seminars by the likes of Chen Duxiu, Hu Shih, and Qian Xuantong.[46] Mao's time in Beijing ended in the spring of 1919, when he travelled to Shanghai with friends who were preparing to leave for France.[47] He did not return to Shaoshan, where his mother was terminally ill. She died in October 1919 and her husband died in January 1920.[48]
New Culture and political protests: 1919–1920

On 4 May 1919, students in Beijing gathered at Tiananmen to protest the Chinese government's weak resistance to Japanese expansion in China. Patriots were outraged at the influence given to Japan in the Twenty-One Demands in 1915, the complicity of Duan Qirui's Beiyang government, and the betrayal of China in the Treaty of Versailles, wherein Japan was allowed to receive territories in Shandong which had been surrendered by Germany. These demonstrations ignited the nationwide May Fourth Movement and fuelled the New Culture Movement which blamed China's diplomatic defeats on social and cultural backwardness.[49]
In Changsha, Mao had begun teaching history at the Xiuye Primary School[50] and organising protests against the pro-Duan Governor of Hunan Province, Zhang Jingyao, popularly known as "Zhang the Venomous" due to his corrupt and violent rule.[51] In late May, Mao co-founded the Hunanese Student Association with He Shuheng and Deng Zhongxia, organising a student strike for June and in July 1919 began production of a weekly radical magazine, Xiang River Review. Using vernacular language that would be understandable to the majority of China's populace, he advocated the need for a "Great Union of the Popular Masses", and strengthened trade unions able to wage non-violent revolution.[clarification needed] His ideas were not Marxist, but heavily influenced by Kropotkin's concept of mutual aid.[52]

Zhang banned the Student Association, but Mao continued publishing after assuming editorship of the liberal magazine New Hunan (Xin Hunan) and authored articles in popular local newspaper Ta Kung Pao. Several of these advocated feminist views, calling for the liberation of women in Chinese society; Mao was influenced by his forced arranged-marriage.[53] In fall 1919, Mao organized a seminar in Changsha studying economic and political issues, as well as ways to unite the people, the feasibility of socialism, and issues regarding Confucianism.[54] During this period, Mao involved himself in political work with manual laborers, setting up night schools and trade unions.[54] In December 1919, Mao helped organise a general strike in Hunan, securing some concessions, but Mao and other student leaders felt threatened by Zhang, and Mao returned to Beijing, visiting the terminally ill Yang Changji.[55] Mao found that his articles had achieved a level of fame among the revolutionary movement, and set about soliciting support in overthrowing Zhang.[56] Coming across newly translated Marxist literature by Thomas Kirkup, Karl Kautsky, and Marx and Engels—notably The Communist Manifesto—he came under their increasing influence, but was still eclectic in his views.[57]
Mao visited Tianjin, Jinan, and Qufu,[58] before moving to Shanghai, where he worked as a laundryman and met Chen Duxiu, noting that Chen's adoption of Marxism "deeply impressed me at what was probably a critical period in my life". In Shanghai, Mao met an old teacher of his, Yi Peiji, a revolutionary and member of the Kuomintang (KMT), or Chinese Nationalist Party, which was gaining increasing support and influence. Yi introduced Mao to General Tan Yankai, a senior KMT member who held the loyalty of troops stationed along the Hunanese border with Guangdong. Tan was plotting to overthrow Zhang, and Mao aided him by organising the Changsha students. In June 1920, Tan led his troops into Changsha, and Zhang fled. In the subsequent reorganisation of the provincial administration, Mao was appointed headmaster of the junior section of the First Normal School. Now receiving a large income, he married Yang Kaihui, daughter of Yang Changji, in the winter of 1920.[59][60]
Founding the Chinese Communist Party: 1921–1922

The Chinese Communist Party was founded by Chen Duxiu and Li Dazhao in the Shanghai French Concession in 1921 as a study society and informal network. Mao set up a Changsha branch, also establishing a branch of the Socialist Youth Corps and a Cultural Book Society which opened a bookstore to propagate revolutionary literature throughout Hunan.[61] He was involved in the movement for Hunan autonomy, in the hope that a Hunanese constitution would increase civil liberties and make his revolutionary activity easier. When the movement was successful in establishing provincial autonomy under a new warlord, Mao forgot his involvement.[62][clarification needed] By 1921, small Marxist groups existed in Shanghai, Beijing, Changsha, Wuhan, Guangzhou, and Jinan; it was decided to hold a central meeting, which began in Shanghai on 23 July 1921. The first session of the National Congress of the Chinese Communist Party was attended by 13 delegates, Mao included. After the authorities sent a police spy to the congress, the delegates moved to a boat on South Lake near Jiaxing, in Zhejiang, to escape detection. Although Soviet and Comintern delegates attended, the first congress ignored Lenin's advice to accept a temporary alliance between the Communists and the "bourgeois democrats" who also advocated national revolution; instead they stuck to the orthodox Marxist belief that only the urban proletariat could lead a socialist revolution.[63]
Mao was party secretary for Hunan stationed in Changsha, and to build the party there he followed a variety of tactics.[64] In August 1921, he founded the Self-Study University, through which readers could gain access to revolutionary literature, housed in the premises of the Society for the Study of Wang Fuzhi, a Qing dynasty Hunanese philosopher who had resisted the Manchus.[64] He joined the YMCA Mass Education Movement to fight illiteracy, though he edited the textbooks to include radical sentiments.[65] He continued organising workers to strike against the administration of Hunan Governor Zhao Hengti.[66] Yet labour issues remained central. The successful and famous Anyuan coal mines strikes (contrary to later Party historians) depended on both "proletarian" and "bourgeois" strategies. Liu Shaoqi and Li Lisan and Mao not only mobilised the miners, but formed schools and cooperatives and engaged local intellectuals, gentry, military officers, merchants, Red Gang dragon heads and even church clergy.[67] Mao's labour organizing work in the Anyuan mines also involved his wife Yang Kaihui, who worked for women's rights, including literacy and educational issues, in the nearby peasant communities.[68] Although Mao and Yang were not the originators of this political organizing method of combining labor organizing among male workers with a focus on women's rights issues in their communities, they were among the most effective at using this method.[68] Mao's political organizing success in the Anyuan mines resulted in Chen Duxiu inviting him to become a member of the Communist Party's Central Committee.[69]
Mao claimed that he missed the July 1922 Second Congress of the Communist Party in Shanghai because he lost the address. Adopting Lenin's advice, the delegates agreed to an alliance with the "bourgeois democrats" of the KMT for the good of the "national revolution". Communist Party members joined the KMT, hoping to push its politics leftward.[70] Mao enthusiastically agreed with this decision, arguing for an alliance across China's socio-economic classes, and eventually rose to become propaganda chief of the KMT.[60] Mao was a vocal anti-imperialist and in his writings he lambasted the governments of Japan, the UK and US, describing the latter as "the most murderous of hangmen".[71]
Collaboration with the Kuomintang: 1922–1927
At the Third Congress of the Communist Party in Shanghai in June 1923, the delegates reaffirmed their commitment to working with the KMT. Supporting this position, Mao was elected to the Party Committee, taking up residence in Shanghai.[72] At the First KMT Congress, held in Guangzhou in early 1924, Mao was elected an alternate member of the KMT Central Executive Committee, and put forward four resolutions to decentralise power to urban and rural bureaus. His enthusiastic support for the KMT earned him the suspicion of Li Li-san, his Hunan comrade.[73]
In late 1924, Mao returned to Shaoshan, perhaps to recuperate from an illness. He found that the peasantry were increasingly restless and some had seized land from wealthy landowners to found communes. This convinced him of the revolutionary potential of the peasantry, an idea advocated by the KMT leftists but not the Communists.[74] Mao and many of his colleagues also proposed the end of cooperation with the KMT, which was rejected by the Comintern representative Mikhail Borodin.[75] In the winter of 1925, Mao fled to Guangzhou after his revolutionary activities attracted the attention of Zhao's regional authorities.[76] There, he ran the 6th term of the KMT's Peasant Movement Training Institute from May to September 1926.[77][78] The Peasant Movement Training Institute under Mao trained cadre and prepared them for militant activity, taking them through military training exercises and getting them to study basic left-wing texts.[79]

When party leader Sun Yat-sen died in May 1925, he was succeeded by Chiang Kai-shek, who moved to marginalise the left-KMT and the Communists.[80] Mao nevertheless supported Chiang's National Revolutionary Army, who embarked on the Northern Expedition attack in 1926 on warlords.[81] In the wake of this expedition, peasants rose up, appropriating the land of the wealthy landowners, who were in many cases killed. Such uprisings angered senior KMT figures, who were themselves landowners, emphasising the growing class and ideological divide within the revolutionary movement.[82]

In March 1927, Mao appeared at the Third Plenum of the KMT Central Executive Committee in Wuhan, which sought to strip General Chiang of his power by appointing Wang Jingwei leader. There, Mao played an active role in the discussions regarding the peasant issue, defending a set of "Regulations for the Repression of Local Bullies and Bad Gentry", which advocated the death penalty or life imprisonment for anyone found guilty of counter-revolutionary activity, arguing that in a revolutionary situation, "peaceful methods cannot suffice".[83][84] In April 1927, Mao was appointed to the KMT's five-member Central Land Committee, urging peasants to refuse to pay rent. Mao led another group to put together a "Draft Resolution on the Land Question", which called for the confiscation of land belonging to "local bullies and bad gentry, corrupt officials, militarists and all counter-revolutionary elements in the villages". Proceeding to carry out a "Land Survey", he stated that anyone owning over 30 mou (four and a half acres), constituting 13% of the population, were uniformly counter-revolutionary. He accepted that there was great variation in revolutionary enthusiasm across the country, and that a flexible policy of land redistribution was necessary.[85] Presenting his conclusions at the Enlarged Land Committee meeting, many expressed reservations, some believing that it went too far, and others not far enough. Ultimately, his suggestions were only partially implemented.[86]
Civil War
Nanchang and Autumn Harvest Uprisings: 1927

Fresh from the success of the Northern Expedition against the warlords, Chiang turned on the Communists, who by now numbered in the tens of thousands across China. Chiang ignored the orders of the Wuhan-based left KMT government and marched on Shanghai, a city controlled by Communist militias. As the Communists awaited Chiang's arrival, he loosed the White Terror, massacring 5,000 with the aid of the Green Gang.[84][87] In Beijing, 19 leading Communists were killed by Zhang Zuolin.[88][89] That May, tens of thousands of Communists and those suspected of being communists were killed, and the CCP lost approximately 15,000 of its 25,000 members.[89]
The CCP continued supporting the Wuhan KMT government, a position Mao initially supported,[89] but by the time of the CCP's Fifth Congress he had changed his mind, deciding to stake all hope on the peasant militia.[90] The question was rendered moot when the Wuhan government expelled all Communists from the KMT on 15 July.[90] The CCP founded the Workers' and Peasants' Red Army of China, better known as the "Red Army", to battle Chiang. A battalion led by General Zhu De was ordered to take the city of Nanchang on 1 August 1927, in what became known as the Nanchang Uprising. They were initially successful, but were forced into retreat after five days, marching south to Shantou, and from there they were driven into the wilderness of Fujian.[90] Mao was appointed commander-in-chief of the Red Army and led four regiments against Changsha in the Autumn Harvest Uprising, in the hope of sparking peasant uprisings across Hunan. On the eve of the attack, Mao composed a poem—the earliest of his to survive—titled "Changsha". His plan was to attack the KMT-held city from three directions on 9 September, but the Fourth Regiment deserted to the KMT cause, attacking the Third Regiment. Mao's army made it to Changsha, but could not take it; by 15 September, he accepted defeat and with 1000 survivors marched east to the Jinggang Mountains of Jiangxi.[91]
Base in Jinggangshan: 1927–1928

革命不是請客吃飯,不是做文章,不是繪畫繡花,不能那樣雅緻,那樣從容不迫,文質彬彬,那樣溫良恭讓。革命是暴動,是一個階級推翻一個階級的暴烈的行動。
Revolution is not a dinner party, nor an essay, nor a painting, nor a piece of embroidery; it cannot be so refined, so leisurely and gentle, so temperate, kind, courteous, restrained and magnanimous. A revolution is an insurrection, an act of violence by which one class overthrows another.
— Mao, February 1927[92]
The CCP Central Committee, hiding in Shanghai, expelled Mao from their ranks and from the Hunan Provincial Committee, as punishment for his "military opportunism", for his focus on rural activity, and for being too lenient with "bad gentry". The more orthodox Communists especially regarded the peasants as backward and ridiculed Mao's idea of mobilizing them.[60] They nevertheless adopted three policies he had long championed: the immediate formation of workers' councils, the confiscation of all land without exemption, and the rejection of the KMT. Mao's response was to ignore them.[93] He established a base in Jinggangshan City, an area of the Jinggang Mountains, where he united five villages as a self-governing state, and supported the confiscation of land from rich landlords, who were "re-educated" and sometimes executed. He ensured that no massacres took place in the region, and pursued a more lenient approach than that advocated by the Central Committee.[94] In addition to land redistribution, Mao promoted literacy and non-hierarchical organizational relationships in Jinggangshan, transforming the area's social and economic life and attracted many local supporters.[95]
Mao proclaimed that "Even the lame, the deaf and the blind could all come in useful for the revolutionary struggle", he boosted the army's numbers,[96] incorporating two groups of bandits into his army, building a force of around 1,800 troops.[97] He laid down rules for his soldiers: prompt obedience to orders, all confiscations were to be turned over to the government, and nothing was to be confiscated from poorer peasants. In doing so, he moulded his men into a disciplined, efficient fighting force.[96]
敵進我退,
敵駐我騷,
敵疲我打,
敵退我追。
When the enemy advances, we retreat.
When the enemy rests, we harass him.
When the enemy avoids a battle, we attack.
When the enemy retreats, we advance.

In spring 1928, the Central Committee ordered Mao's troops to southern Hunan, hoping to spark peasant uprisings. Mao was skeptical, but complied. They reached Hunan, where they were attacked by the KMT and fled after heavy losses. Meanwhile, KMT troops had invaded Jinggangshan, leaving them without a base.[100] Wandering the countryside, Mao's forces came across a CCP regiment led by General Zhu De and Lin Biao; they united, and attempted to retake Jinggangshan. They were initially successful, but the KMT counter-attacked, and pushed the CCP back; over the next few weeks, they fought an entrenched guerrilla war in the mountains.[98][101] The Central Committee again ordered Mao to march to south Hunan, but he refused, and remained at his base. Contrastingly, Zhu complied, and led his armies away. Mao's troops fended the KMT off for 25 days while he left the camp at night to find reinforcements. He reunited with the decimated Zhu's army, and together they returned to Jinggangshan and retook the base. There they were joined by a defecting KMT regiment and Peng Dehuai's Fifth Red Army. In the mountainous area they were unable to grow enough crops to feed everyone, leading to food shortages throughout the winter.[102]
In 1928, Mao met and married He Zizhen, an 18-year-old revolutionary who would bear him six children.[103][104]
Jiangxi Soviet Republic of China: 1929–1934

In January 1929, Mao and Zhu evacuated the base with 2,000 men and a further 800 provided by Peng, and took their armies south, to the area around Tonggu and Xinfeng in Jiangxi.[105] The evacuation led to a drop in morale, and many troops became disobedient and began thieving; this worried Li Lisan and the Central Committee, who saw Mao's army as lumpenproletariat, that were unable to share in proletariat class consciousness.[106][107] In keeping with orthodox Marxist thought, Li believed that only the urban proletariat could lead a successful revolution, and saw little need for Mao's peasant guerrillas; he ordered Mao to disband his army into units to be sent out to spread the revolutionary message. Mao replied that while he concurred with Li's theoretical position, he would not disband his army nor abandon his base.[107][108] Both Li and Mao saw the Chinese revolution as the key to world revolution, believing that a CCP victory would spark the overthrow of global imperialism and capitalism. In this, they disagreed with the official line of the Soviet government and Comintern. Officials in Moscow desired greater control over the CCP and removed Li from power by calling him to Russia for an inquest into his errors.[109] They replaced him with Soviet-educated Chinese Communists, known as the "28 Bolsheviks", two of whom, Bo Gu and Zhang Wentian, took control of the Central Committee. Mao disagreed with the new leadership, believing they grasped little of the Chinese situation, and he soon emerged as their key rival.[110][111]

In February 1930, Mao created the Southwest Jiangxi Provincial Soviet Government in the region under his control.[112] In November, he suffered emotional trauma after his second wife Yang Kaihui and sister were captured and beheaded by KMT general He Jian.[113] Facing internal problems, members of the Jiangxi Soviet accused him of being too moderate, and hence anti-revolutionary. In December, they tried to overthrow Mao, resulting in the Futian incident, during which Mao's loyalists tortured many and executed between 2000 and 3000 dissenters.[114] The CCP Central Committee moved to Jiangxi which it saw as a secure area. In November, it proclaimed Jiangxi to be the Soviet Republic of China, an independent Communist-governed state. Although he was proclaimed Chairman of the Council of People's Commissars, Mao's power was diminished, as his control of the Red Army was allocated to Zhou Enlai. Meanwhile, Mao recovered from tuberculosis.[115]
The KMT armies adopted a policy of encirclement and annihilation of the Red armies. Outnumbered, Mao responded with guerrilla tactics influenced by the works of ancient military strategists like Sun Tzu, but Zhou and the new leadership followed a policy of open confrontation and conventional warfare. In doing so, the Red Army successfully defeated the first and second encirclements.[116][117] Angered at his armies' failure, Chiang Kai-shek personally arrived to lead the operation. He too faced setbacks and retreated to deal with the further Japanese incursions into China.[118] As a result of the KMT's change of focus to the defence of China against Japanese expansionism, the Red Army was able to expand its area of control, eventually encompassing a population of 3 million.[117] Mao proceeded with his land reform program. In November 1931 he announced the start of a "land verification project" which was expanded in June 1933. He also orchestrated education programs and implemented measures to increase female political participation.[119] Chiang viewed the Communists as a greater threat than the Japanese and returned to Jiangxi, where he initiated the fifth encirclement campaign, which involved the construction of a concrete and barbed wire "wall of fire" around the state, which was accompanied by aerial bombardment, to which Zhou's tactics proved ineffective. Trapped inside, morale among the Red Army dropped as food and medicine became scarce. The leadership decided to evacuate.[120]
Long March: 1934–1935
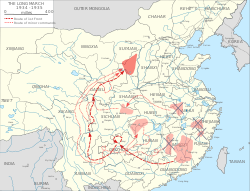
On 14 October 1934, the Red Army broke through the KMT line on the Jiangxi Soviet's south-west corner at Xinfeng with 85,000 soldiers and 15,000 party cadres and embarked on the "Long March". In order to make the escape, many of the wounded and the ill, as well as women and children, were left behind, defended by a group of guerrilla fighters whom the KMT massacred.[121] The 100,000 who escaped headed to southern Hunan, first crossing the Xiang River after heavy fighting,[122] and then the Wu River, in Guizhou where they took Zunyi in January 1935. Temporarily resting in the city, they held a conference; here, Mao was elected to a position of leadership, becoming Chairman of the Politburo, and de facto leader of both Party and Red Army, in part because his candidacy was supported by Soviet Premier Joseph Stalin. Insisting that they operate as a guerrilla force, he laid out a destination: the Shenshi Soviet in Shaanxi, Northern China, from where the Communists could focus on fighting the Japanese. Mao believed that in focusing on the anti-imperialist struggle, the Communists would earn the trust of the Chinese people, who in turn would renounce the KMT.[123]
From Zunyi, Mao led his troops to Loushan Pass, where they faced armed opposition but successfully crossed the river. Chiang flew into the area to lead his armies against Mao, but the Communists outmanoeuvred him and crossed the Jinsha River.[124] Faced with the more difficult task of crossing the Tatu River, they managed it by fighting a battle over the Luding Bridge in May, taking Luding.[125] In Moukung, Western Sichuan, they encountered the 50,000-strong CCP Fourth Front Army of Zhang Guotao (who had marched from the mountain ranges around Ma'anshan[126]), and together proceeded to Maoerhkai and then Gansu. Zhang and Mao disagreed over what to do; the latter wished to proceed to Shaanxi, while Zhang wanted to retreat west to Tibet or Sikkim, far from the KMT threat. It was agreed that they would go their separate ways, with Zhu De joining Zhang.[127] Mao's forces proceeded north, through hundreds of kilometres of grasslands, an area of quagmire where they were attacked by Manchu tribesman and where many soldiers succumbed to famine and disease.[128] Finally reaching Shaanxi, they fought off both the KMT and an Islamic cavalry militia before crossing the Min Mountains and Mount Liupan and reaching the Shenshi Soviet; only 7,000–8,000 had survived.[129] The Long March cemented Mao's status as the dominant figure in the party. In November 1935, he was named chairman of the Military Commission. From this point onward, Mao was the Communist Party's undisputed leader, even though he would not become party chairman until 1943.[130]
World War II

Mao's troops arrived at the Yan'an Soviet during October 1935 and settled in Bao'an, until spring 1936. While there, they developed links with local communities, redistributed and farmed the land, offered medical treatment, and began literacy programs.[131] Mao now commanded 15,000 soldiers, boosted by the arrival of He Long's men from Hunan and the armies of Zhu De and Zhang Guotao returned from Tibet.[132] In February 1936, they established the North West Anti-Japanese Red Army University in Yan'an, through which they trained increasing numbers of new recruits.[133] In January 1937, they began the "anti-Japanese expedition", that sent groups of guerrilla fighters into Japanese-controlled territory to undertake sporadic attacks.[134] In May 1937, a Communist Conference was held in Yan'an to discuss the situation.[135] Western reporters also arrived in the "Border Region" (as the Soviet had been renamed); most notable were Edgar Snow, who used his experiences as a basis for Red Star Over China, and Agnes Smedley, whose accounts brought international attention to Mao's cause.[136]


On the Long March, Mao's wife He Zizhen had been injured by a shrapnel wound to the head. She travelled to Moscow for medical treatment; Mao proceeded to divorce her and marry an actress, Jiang Qing.[137][138] He Zizhen was reportedly "dispatched to a mental asylum in Moscow to make room" for Qing.[139] Mao moved into a cave-house and spent much of his time reading, tending his garden and theorising.[140] He came to believe that the Red Army alone was unable to defeat the Japanese, and that a Communist-led "government of national defence" should be formed with the KMT and other "bourgeois nationalist" elements to achieve this goal.[141] Although despising Chiang Kai-shek as a "traitor to the nation",[142] on 5 May, he telegrammed the Military Council of the Nanjing National Government proposing a military alliance, a course of action advocated by Stalin.[143] Although Chiang intended to ignore Mao's message and continue the civil war, he was arrested by one of his own generals, Zhang Xueliang, in Xi'an, leading to the Xi'an Incident; Zhang forced Chiang to discuss the issue with the Communists, resulting in the formation of a United Front with concessions on both sides on 25 December 1937.[144]
The Japanese had taken both Shanghai and Nanjing—resulting in the Nanjing Massacre, an atrocity Mao never spoke of all his life—and was pushing the Kuomintang government inland to Chongqing.[145] The Japanese's brutality led to increasing numbers of Chinese joining the fight, and the Red Army grew from 50,000 to 500,000.[146][147] In August 1938, the Red Army formed the New Fourth Army and the Eighth Route Army, which were nominally under the command of Chiang's National Revolutionary Army.[148] In August 1940, the Red Army initiated the Hundred Regiments Offensive, in which 400,000 troops attacked the Japanese simultaneously in five provinces. It was a military success that resulted in the death of 20,000 Japanese, the disruption of railways and the loss of a coal mine.[147][149] From his base in Yan'an, Mao authored several texts for his troops, including Philosophy of Revolution, which offered an introduction to the Marxist theory of knowledge; Protracted Warfare, which dealt with guerrilla and mobile military tactics; and On New Democracy, which laid forward ideas for China's future.[150]

In 1944, the U.S. sent a special diplomatic envoy, called the Dixie Mission, to the Chinese Communist Party. The American soldiers who were sent to the mission were favourably impressed. The party seemed less corrupt, more unified, and more vigorous in its resistance to Japan than the Kuomintang. The soldiers confirmed to their superiors that the party was both strong and popular over a broad area.[151] In the end of the mission, the contacts which the U.S. developed with the Chinese Communist Party led to very little.[151] After the end of World War II, the U.S. continued their diplomatic and military assistance to Chiang Kai-shek and his KMT government forces against the People's Liberation Army (PLA) led by Mao Zedong during the civil war and abandoned the idea of a coalition government which would include the CCP.[152] Likewise, the Soviet Union gave support to Mao by occupying north-eastern China, and secretly giving it to the Chinese communists in March 1946.[153]
Leadership of China
Establishment of the People's Republic of China

In 1948, under direct orders from Mao, the People's Liberation Army starved out the Kuomintang forces occupying the city of Changchun. At least 160,000 civilians are believed to have perished during the siege, which lasted from June until October. PLA lieutenant colonel Zhang Zhenglu, who documented the siege in his book White Snow, Red Blood, compared it to Hiroshima: "The casualties were about the same. Hiroshima took nine seconds; Changchun took five months."[154] On 21 January 1949, Kuomintang forces suffered great losses in decisive battles against Mao's forces.[155] In the early morning of 10 December 1949, PLA troops laid siege to Chongqing and Chengdu on mainland China, and Chiang Kai-shek fled from the mainland to Taiwan.[155][156]

Mao proclaimed the establishment of the People's Republic of China from the Gate of Heavenly Peace (Tian'anmen) on 1 October 1949, and later that week declared "The Chinese people have stood up" (中国人民从此站起来了).[157] Mao went to Moscow for long talks in the winter of 1949–50. Mao initiated the talks which focused on the political and economic revolution in China, foreign policy, railways, naval bases, and Soviet economic and technical aid. The resulting treaty reflected Stalin's dominance and his willingness to help Mao.[158][159]
Mao's views as a Marxist were strongly influenced by Lenin, particularly with regard to the vanguardism.[160] Mao believed that only the correct leadership of the Communist Party could advance China into socialism.[160] Conversely, Mao also believed that mass movements and mass criticism were necessary in order to check the bureaucracy.[160]

Korean War
Mao pushed the Party to organise campaigns to reform society and extend control. These campaigns were given urgency in October 1950, when Mao made the decision to send the People's Volunteer Army, a special unit of the People's Liberation Army, into the Korean War and fight as well as to reinforce the armed forces of North Korea, the Korean People's Army, which had been in full retreat. The United States placed a trade embargo on the People's Republic as a result of its involvement in the Korean War, lasting until Richard Nixon's improvements of relations. At least 180,000 Chinese troops died during the war.[161]
Mao directed operations to the minutest detail. As the Chairman of the Central Military Commission (CMC), he was also the Supreme Commander in Chief of the PLA and the People's Republic and Chairman of the Party. Chinese troops in Korea were under the overall command of then newly installed Premier Zhou Enlai, with General Peng Dehuai as field commander and political commissar.[162]
Social reform
During the land reform campaigns, large numbers of landlords and rich peasants were beaten to death at mass meetings organised by the Communist Party as land was taken from them and given to poorer peasants, which significantly reduced economic inequality.[163][164] The Campaign to Suppress Counter-revolutionaries[165] targeted bureaucratic bourgeoisie, such as compradors, merchants and Kuomintang officials who were seen by the party as economic parasites or political enemies.[166] In 1976, the U.S. State Department estimated as many as a million were killed in the land reform, and 800,000 killed in the counter-revolutionary campaign.[167]
Mao himself claimed that a total of 700,000 people were killed in attacks on "counter-revolutionaries" during the years 1950–1952.[168] Because there was a policy to select "at least one landlord, and usually several, in virtually every village for public execution",[169] the number of deaths range between 2 million[169][170][165] and 5 million.[171][172] In addition, at least 1.5 million people,[173] perhaps as many as 4 to 6 million,[174] were sent to "reform through labour" camps where many perished.[174] Mao played a personal role in organising the mass repressions and established a system of execution quotas,[175] which were often exceeded.[165] He defended these killings as necessary for the securing of power.[176]

The Mao government is credited with eradicating both consumption and production of opium during the 1950s using unrestrained repression and social reform.[177][178] Ten million addicts were forced into compulsory treatment, dealers were executed, and opium-producing regions were planted with new crops. Remaining opium production shifted south of the Chinese border into the Golden Triangle region.[178]
Three-anti and Five-anti Campaigns
Starting in 1951, Mao initiated two successive movements in an effort to rid urban areas of corruption by targeting wealthy capitalists and political opponents, known as the Three-anti and Five-anti Campaigns. Whereas the three-anti campaign was a focused purge of government, industrial and party officials, the five-anti campaign set its sights slightly broader, targeting capitalist elements in general.[179] Workers denounced their bosses, spouses turned on their spouses, and children informed on their parents; the victims were often humiliated at struggle sessions, where a targeted person would be verbally and physically abused until they confessed to crimes. Mao insisted that minor offenders be criticised and reformed or sent to labour camps, "while the worst among them should be shot". These campaigns took several hundred thousand additional lives, the vast majority via suicide.[180]

In Shanghai, suicide by jumping from tall buildings became so commonplace that residents avoided walking on the pavement near skyscrapers for fear that suicides might land on them.[181] Some biographers have pointed out that driving those perceived as enemies to suicide was a common tactic during the Mao-era. In his biography of Mao, Philip Short notes that Mao gave explicit instructions in the Yan'an Rectification Movement that "no cadre is to be killed" but in practice allowed security chief Kang Sheng to drive opponents to suicide and that "this pattern was repeated throughout his leadership of the People's Republic".[182]

Five-year plans
Following the consolidation of power, Mao launched the first five-year plan (1953–1958), which emphasised rapid industrial development. Within industry, iron and steel, electric power, coal, heavy engineering, building materials, and basic chemicals were prioritised with the aim of constructing large and highly capital-intensive plants. Many of these plants were built with Soviet assistance and heavy industry grew rapidly.[183] Agriculture, industry and trade was organised as worker cooperatives.[184] This period marked the beginning of China's rapid industrialisation and it resulted in an enormous success.[185]
Despite being initially sympathetic towards the reformist government of Imre Nagy, Mao feared the "reactionary restoration" in Hungary as the Hungarian Revolution of 1956 continued and became more hardline. Mao opposed the withdrawal of Soviet troops by asking Liu Shaoqi to inform the Soviet representatives to use military intervention against "Western imperialist-backed" protestors and Nagy's government. However, it was unclear to what degree Mao's stance played a role in Nikita Khrushchev's decision to invade Hungary. It was also unclear if China was forced to conform to the Soviet position due to economic concerns and China's poor power projections compared to the USSR. Despite his disagreements with Moscow's hegemony in the Eastern Bloc, Mao viewed the integrity of the international communist movement as more important than the national autonomy of the countries in the Soviet sphere of influence. The Hungarian crisis also influenced Mao's Hundred Flowers Campaign. Mao decided to soften his stance on Chinese intelligentsia and allow them to express their social dissatisfaction and criticisms of the errors of the government. Mao wanted to use this movement to prevent a similar uprising in China. However, as people in China began to criticize the CCP's policies and Mao's leadership following the Hundred Flowers Campaign, Mao cracked down the movement he initiated and compared it to the "counter-revolutionary" Hungarian Revolution.[186]
During the Hundred Flowers Campaign, Mao indicated his supposed willingness to consider different opinions about how China should be governed. Given the freedom to express themselves, liberal and intellectual Chinese began opposing the Communist Party and questioning its leadership. This was initially tolerated and encouraged. After a few months, Mao's government reversed its policy and persecuted those who had criticised the party, totalling perhaps 500,000,[187] as well as those who were merely alleged to have been critical, in what is called the Anti-Rightist Movement. The movement led to the persecution of at least 550,000 people, mostly intellectuals and dissidents.[188] Li Zhisui, Mao's physician, suggested that Mao had initially seen the policy as a way of weakening opposition to him within the party and that he was surprised by the extent of criticism and the fact that it came to be directed at his own leadership.[189]
Military projects
United States President Dwight D. Eisenhower's threats during the First Taiwan Strait Crisis to use nuclear weapons against military targets in Fujian province prompted Mao to begin China's nuclear program.[190]: 89–90 Under Mao's Two Bombs, One Satellite program, China developed the atomic and hydrogen bombs in record time[quantify] and launched a satellite a few years after the Soviet Union launched Sputnik.[191]: 218
Project 523 (Chinese: 523项目)[192] is a code name for a 1967 secret military project of the People's Republic of China to find antimalarial medications.[193] Named after the date the project launched, 23 May, it addressed malaria, an important threat in the Vietnam War. At the behest of Ho Chi Minh, Prime Minister of North Vietnam, Zhou Enlai convinced Mao Zedong to start the mass project "to keep [the] allies' troops combat-ready", as the meeting minutes put it. More than 500 Chinese scientists were recruited. The project was divided into three streams.[194] The one for investigating traditional Chinese medicine discovered and led to the development of a class of new antimalarial drugs called artemisinins.[194][195] Launched during and lasting throughout the Cultural Revolution, Project 523 was officially terminated in 1981.
Great Leap Forward

In January 1958, Mao launched the Great Leap Forward, a plan intended to turn China from an agrarian nation to an industrialised one[196] and as an alternative model for economic growth to the Soviet model. Under this economic program, the relatively small agricultural collectives that had been formed to date were rapidly merged into far larger people's communes, and many of the peasants were ordered to work on massive infrastructure projects and on the production of iron and steel. Some private food production was banned, and livestock and farm implements were brought under collective ownership.[197]
The combined effect of the diversion of labour to steel production and infrastructure projects, and cyclical natural disasters led to an approximately 15% drop in grain production in 1959 followed by a further 10% decline in 1960 and no recovery in 1961.[198]
To win favour with their superiors and avoid being purged, each layer in the party exaggerated the amount of grain produced under them. Based upon the falsely reported success, party cadres were ordered to requisition a high amount of that fictitious harvest. The result, compounded in some areas by drought and in others by floods, was that farmers were left with little food for themselves and many millions starved to death in the Great Chinese Famine. The people of urban areas in China were given food stamps each month, but the people of rural areas were expected to grow their own crops and give some of the crops back to the government. The death count in rural parts of China surpassed the deaths in the urban centers. The Chinese government continued to export food that could have been allocated to the country's starving citizens.[199] The famine was a direct cause of the death of some 30 million Chinese peasants between 1959 and 1962.[200] Furthermore, many children who became malnourished during years of hardship died after the Great Leap Forward came to an end in 1962.[198]
In late autumn 1958, Mao condemned the practices used during Great Leap Forward such as forcing peasants to do exhausting labour without enough food or rest which resulted in epidemics and starvation. He also acknowledged that anti-rightist campaigns were a major cause of "production at the expense of livelihood." He refused to abandon the Great Leap Forward, but he did demand that they be confronted. After the July 1959 clash at Lushan Conference with Peng Dehuai, Mao launched a new anti-rightist campaign along with the radical policies that he previously abandoned. It wasn't until the spring of 1960, that Mao would again express concern about abnormal deaths and other abuses, but he did not move to stop them. Bernstein concludes that the Chairman "wilfully ignored the lessons of the first radical phase for the sake of achieving extreme ideological and developmental goals".[201]

Mao stepped down as President of China on 27 April 1959; he retained other top positions such as Chairman of the Communist Party and of the Central Military Commission.[202] The Presidency was transferred to Liu Shaoqi.[202] Mao eventually abandon the policy in 1962.[203]
At the Lushan Conference in July/August 1959, several ministers expressed concern that the Great Leap Forward had not proved as successful as planned. The most direct of these was Minister of Defence Peng Dehuai. Following Peng's criticism of the Great Leap Forward, Mao orchestrated a purge of Peng and his supporters, stifling criticism of the Great Leap policies. Senior officials who reported the truth of the famine to Mao were branded as "right opportunists."[204] A campaign against right-wing opportunism was launched and resulted in party members and ordinary peasants being sent to prison labour camps where many would subsequently die in the famine. Years later the CCP would conclude that as many as six million people were wrongly punished in the campaign.[205]
At a conference in Beijing in January 1962, dubbed the "Seven Thousand Cadres Conference", Liu Shaoqi denounced the Great Leap Forward, attributing the project to widespread famine in China.[206] The overwhelming majority of delegates expressed agreement, but Defense Minister Lin Biao staunchly defended Mao.[206] A brief period of liberalisation followed while Mao and Lin plotted a comeback.[206] Liu Shaoqi and Deng Xiaoping rescued the economy by disbanding the people's communes, introducing elements of private control of peasant smallholdings and importing grain from Canada and Australia to mitigate the worst effects of famine.[207]
Split from Soviet Union

On the international front, the period was dominated by the further isolation of China. The Sino-Soviet split resulted in Nikita Khrushchev's withdrawal of all Soviet technical experts and aid from the country. The split concerned the leadership of world communism. The USSR had a network of Communist parties it supported; China now created its own rival network to battle it out for local control of the left in numerous countries.[208] Lorenz M. Lüthi writes: "The Sino-Soviet split was one of the key events of the Cold War, equal in importance to the construction of the Berlin Wall, the Cuban Missile Crisis, the Second Vietnam War, and Sino-American rapprochement. The split helped to determine the framework of the Second Cold War in general, and influenced the course of the Second Vietnam War in particular."[209]
The split resulted from Khrushchev's more moderate Soviet leadership after the death of Stalin in March 1953. Only Albania openly sided with China, thereby forming an alliance between the two countries which would last until after Mao's death in 1976. Warned that the Soviets had nuclear weapons, Mao minimised the threat. Becker says that "Mao believed that the bomb was a 'paper tiger', declaring to Khrushchev that it would not matter if China lost 300 million people in a nuclear war: the other half of the population would survive to ensure victory".[210] Struggle against Soviet revisionism and U.S. imperialism was an important aspect of Mao's attempt to direct the revolution in the right direction.[211]
In the late 1950s, Mao wrote reading notes responding to the Soviet Book Political Economy: A Textbook and essays (A Critique of Soviet Economics) responding to Stalin's Economic Problems of Socialism in the USSR.[212]: 51 These texts reflect Mao's views that the USSR was becoming alienated from the masses and distorting socialist development.[212]: 51
According to historian Mingjiang Li, Mao deliberately escalated Sino-Soviet diplomatic tensions as part of his attempt to reassert his domestic political power and limit that of his rivals by showcasing his commitment to revolution and his hardline stance against what he deemed Soviet revisionism.[213]
Third Front


After the failure of the Great Leap Forward, China's leadership slowed the pace of industrialization.[214]: 3 It invested more on in China's coastal regions and focused on the production of consumer goods.[214]: 3 Preliminary drafts of the Third Five Year Plan contained no provision for developing large scale industry in China's interior.[214]: 29 After an April 1964 General Staff report concluded that the concentration of China's industry in its major coastal cities made it vulnerable to attack by foreign powers, Mao argued for the development of basic industry and national defense industry in protected locations in China's interior.[214]: 4, 54 Although other key leaders did not initially support the idea, the 2 August 1964 Gulf of Tonkin incident increased fears of a potential invasion by the United States and crystallized support for Mao's industrialization proposal, which came to be known as the Third Front.[214]: 7 Following the Gulf of Tonkin incident, Mao's own concerns of invasion by the United States increased.[215]: 100 He wrote to central cadres, "A war is going to break out. I need to reconsider my actions" and pushed even harder for the creation of the Third Front.[215]: 100
The secretive Third Front construction involved massive projects including extensive railroad infrastructure like the Chengdu–Kunming line,[214]: 153–164 aerospace industry including satellite launch facilities,[214]: 218–219 and steel production industry including Panzhihua Iron and Steel.[214]: 9
Development of the Third Front slowed in 1966 during the Cultural Revolution, but accelerated again after the Sino-Soviet border conflict at Zhenbao Island, which increased the perceived risk of Soviet Invasion.[214]: 12, 150 Third Front construction again decreased after United States President Richard Nixon's 1972 visit to China and the resulting rapprochement between the United States and China.[214]: 225–229 When Reform and Opening up began after Mao's death, China began to gradually wind down Third Front projects.[216]: 180 The Third Front distributed physical and human capital around the country, ultimately decreased regional disparities and created favorable conditions for later market development.[216]: 177–182
Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution

During the early 1960s, Mao became concerned with the nature of post-1959 China. He saw that the revolution and Great Leap Forward had replaced the old ruling elite with a new one. He was concerned that those in power were becoming estranged from the people they were to serve. Mao believed that a revolution of culture would unseat and unsettle the "ruling class" and keep China in a state of "continuous revolution" that, theoretically, would serve the interests of the majority, rather than a tiny and privileged elite.[217] State Chairman Liu Shaoqi and General Secretary Deng Xiaoping favoured the idea that Mao be removed from actual power as China's head of state and government but maintain his ceremonial and symbolic role as Chairman of the Chinese Communist Party, with the party upholding all of his positive contributions to the revolution. They attempted to marginalise Mao by taking control of economic policy and asserting themselves politically as well. Many claim that Mao responded to Liu and Deng's movements by launching the Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution in 1966. Some scholars, such as Mobo Gao, claim the case for this is overstated.[218] Others, such as Frank Dikötter, hold that Mao launched the Cultural Revolution to wreak revenge on those who had dared to challenge him over the Great Leap Forward.[219]
The Cultural Revolution led to the destruction of much of China's traditional cultural heritage and the imprisonment of a huge number of Chinese citizens, as well as the creation of general economic and social chaos in the country. Millions of lives were ruined during this period, as the Cultural Revolution pierced into every part of Chinese life, depicted by such Chinese films as To Live, The Blue Kite and Farewell My Concubine. It is estimated that hundreds of thousands of people, perhaps millions, perished in the violence of the Cultural Revolution.[220] This included prominent figures such as Liu Shaoqi.[221][222][223]
When Mao was informed of such losses, particularly that people had been driven to suicide, he is alleged to have commented: "People who try to commit suicide—don't attempt to save them! ... China is such a populous nation, it is not as if we cannot do without a few people."[224] The authorities allowed the Red Guards to abuse and kill opponents of the regime. Said Xie Fuzhi, national police chief: "Don't say it is wrong of them to beat up bad persons: if in anger they beat someone to death, then so be it."[225] In August and September 1966, there were a reported 1,772 people murdered by the Red Guards in Beijing alone.[226]
It was during this period that Mao chose Lin Biao, who seemed to echo all of Mao's ideas, to become his successor. Lin was later officially named as Mao's successor. By 1971, a divide between the two men had become apparent. Official history in China states that Lin was planning a military coup or an assassination attempt on Mao. Lin Biao died on 13 September 1971, in a plane crash over the air space of Mongolia, presumably as he fled China, probably anticipating his arrest. The CCP declared that Lin was planning to depose Mao and posthumously expelled Lin from the party. At this time, Mao lost trust in many of the top CCP figures. The highest-ranking Soviet Bloc intelligence defector, Lt. Gen. Ion Mihai Pacepa claimed he had a conversation with Nicolae Ceaușescu, who told him about a plot to kill Mao with the help of Lin Biao organised by the KGB.[227]
In 1969, Mao declared the Cultural Revolution to be over, although various historians in and outside of China mark the end of the Cultural Revolution—as a whole or in part—in 1976, following Mao's death and the arrest of the Gang of Four.[228] The Central Committee in 1981 officially declared the Cultural Revolution a "severe setback" for the PRC.[229] It is often looked at in all scholarly circles as a greatly disruptive period for China.[230] Despite the pro-poor rhetoric of Mao's regime, his economic policies led to substantial poverty.[231]
Estimates of the death toll during the Cultural Revolution, including civilians and Red Guards, vary greatly. An estimate of around 400,000 deaths is a widely accepted minimum figure, according to Maurice Meisner.[232] MacFarquhar and Schoenhals assert that in rural China alone some 36 million people were persecuted, of whom between 750,000 and 1.5 million were killed, with roughly the same number permanently injured.[233]
Historian Daniel Leese writes that in the 1950s, Mao's personality was hardening: "The impression of Mao's personality that emerges from the literature is disturbing. It reveals a certain temporal development from a down-to-earth leader, who was amicable when uncontested and occasionally reflected on the limits of his power, to an increasingly ruthless and self-indulgent dictator. Mao's preparedness to accept criticism decreased continuously."[234]
State visits
| Country | Date | Host |
|---|---|---|
| 16 December 1949 | Joseph Stalin | |
| 2–19 November 1957 | Nikita Khrushchev |
During his leadership, Mao traveled outside China on only two occasions, both of which were state visits to the Soviet Union. His first visit abroad was in December 1949 to celebrate the 70th birthday of Soviet leader Joseph Stalin in Moscow, which was also attended by East German Deputy Chairman of the Council of Ministers Walter Ulbricht and Mongolian communist General Secretary Yumjaagiin Tsedenbal.[235] The second visit to Moscow in November 1957 was a two-week state visit of which the highlights included Mao's attendance at the 40th anniversary (Ruby Jubilee) celebrations of the October Revolution (he attended the annual military parade of the Moscow Garrison on Red Square as well as a banquet in the Moscow Kremlin) and the International Meeting of Communist and Workers Parties, where he met with other communist leaders such as North Korea's Kim Il Sung[236] and Albania's Enver Hoxha. When Mao stepped down as head of state on 27 April 1959, further diplomatic state visits and travels abroad to the Soviet Union and other countries were undertaken by either President Liu Shaoqi, Premier Zhou Enlai or Deputy Premier Deng Xiaoping rather than Mao personally.[citation needed]
Death and aftermath
| External videos | |
|---|---|


Mao's health declined in his last years, probably aggravated by his chain-smoking.[237] It became a state secret that he suffered from multiple lung and heart ailments during his later years.[238] There are unconfirmed reports that he possibly had Parkinson's disease[239][240] in addition to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, also known as Lou Gehrig's disease.[241] His final public appearance—and the last known photograph of him alive—had been on 27 May 1976, when he met the visiting Pakistani Prime Minister Zulfikar Ali Bhutto.[242] He suffered two major heart attacks, one in March and another in July, then a third on 5 September, rendering him an invalid. He died nearly four days later, at 00:10 on 9 September 1976, at the age of 82. The Communist Party delayed the announcement of his death until 16:00, when a national radio broadcast announced the news and appealed for party unity.[240]
Mao's embalmed body, draped in the CCP flag, lay in state at the Great Hall of the People for one week.[243] One million Chinese filed past to pay their final respects, many crying openly or displaying sadness, while foreigners watched on television.[244][245] Mao's official portrait hung on the wall with a banner reading: "Carry on the cause left by Chairman Mao and carry on the cause of proletarian revolution to the end".[243] On 17 September, the body was taken in a minibus to the 305 Hospital, where his internal organs were preserved in formaldehyde.[243]
On 18 September, guns, sirens, whistles and horns across China were simultaneously blown and a mandatory three-minute silence was observed.[246] Tiananmen Square was packed with millions of people and a military band played "The Internationale". Hua Guofeng concluded the service with a 20-minute-long eulogy atop Tiananmen Gate.[247] Despite Mao's request to be cremated, his body was later permanently put on display in the Mausoleum of Mao Zedong, in order for the Chinese nation to pay its respects.[248]
On 27 June 1981, the communist party's Central Committee adopted the Resolution on Certain Questions in the History of Our Party since the Founding of the People's Republic of China, which assessed the legacy of the Mao era and the party's priorities going forward.[249]: 166 The Resolution describes setbacks during the period 1957 to 1964 (although it generally affirms this period) and major mistakes beginning in 1965, attributing Mao's errors to individualist tendencies which arose when he departed from the collective view of the leadership.[249]: 167 Regarding Mao's legacy, the Resolution concludes Mao's contributions to the Chinese Revolution far outweigh his mistakes.[250]: 445
Legacy

There is little agreement over Mao's legacy both in China and abroad. He is regarded as one of the most important and influential individuals in the 20th century.[251][252] He is also known as a political intellect, theorist, military strategist, poet, and visionary.[253] He was credited and praised for driving imperialism out of China,[254] having unified China and for ending the previous decades of civil war. He is also credited with having improved the status of women in China and for improving literacy and education.[177][255][256][257] In December 2013, a poll from the state-run Global Times indicated that roughly 85% of the 1,045 respondents surveyed felt that Mao's achievements outweighed his mistakes.[258] It is said in China that Mao was 70 percent right and 30 percent wrong.[10]: 55 [250]: 445
His policies resulted in the deaths of tens of millions of people in China during his 27-year reign,[259][260][261] done through starvation, persecution, prison labour in laogai, and mass executions.[182][259] Mao rarely gave direct instruction for peoples' physical elimination.[262] According to Philip Short, the overwhelming majority of those killed by Mao's policies were unintended casualties of famine, while the other three or four million, in Mao's view, were necessary victims in the struggle to transform China.[263] Mao's China is described as an autocratic and totalitarian regime responsible for mass repression.[264][265][266][267][268]
China's population grew from around 550 million to over 900 million under his rule.[269][270] Mao's revolutionary tactics continue to be used by insurgents, and his political ideology continues to be embraced by many Communist organisations around the world.[271]

In China
In mainland China, Mao is respected by a great number of the general population. Mao is credited for raising the average life expectancy from 35 in 1949 to 63 by 1975, bringing "unity and stability to a country that had been plagued by civil wars and foreign invasions", and laying the foundation for China to "become the equal of the great global powers".[272] He is lauded for carrying out massive land reform, promoting the status of women, improving popular literacy, and positively "transform(ing) Chinese society beyond recognition."[272] Mao is credited for boosting literacy (only 20% of the population could read in 1949, compared to 65.5% thirty years later), doubling life expectancy, a near doubling of the population, and developing China's industry and infrastructure, paving the way for its position as a world power.[273][256][257]
Opposition to Mao can lead to censorship or professional repercussions in mainland China,[274] and is often done in private settings such as the Internet.[275] When a video of Bi Fujian, a television host, insulting Mao at a private dinner in 2015 went viral, Bi garnered the support of Weibo users, with 80% of them saying in a poll that Bi should not apologize amidst backlash from state affiliates.[276][277] In the West, Mao has a bad reputation. He is known for the deaths during the Great Leap Forward and for persecutions during the Cultural Revolution. Chinese citizens are aware of Mao's mistakes, but many see Mao as a national hero. He is seen as someone who successfully liberated the country from Japanese occupation and from Western imperialist exploitation dating back to the Opium Wars.[278] Between 2015 and 2018, 70 interviewees in China were asked about the Maoist era. Their responses mixed nostalgia with trauma. Life used to be simpler and had clear meaning; people trusted and helped one another, and inequality was minimal. They also acknowledged the negative experiences, however, and said their "material life" was poor.[278]

On 25 December 2008, China opened the Mao Zedong Square to visitors in his home town of central Hunan Province to mark the 115th anniversary of his birth.[279]
Former party official Su Shachi has opined that "he was a great historical criminal, but he was also a great force for good."[280] In a similar vein, journalist Liu Binyan has described Mao as "both monster and a genius."[280] Li Rui, Mao's personal secretary and Communist Party comrade, opined that "Mao's way of thinking and governing was terrifying. He put no value on human life. The deaths of others meant nothing to him."[281]
Chen Yun remarked "Had Mao died in 1956, his achievements would have been immortal. Had he died in 1966, he would still have been a great man but flawed. But he died in 1976. Alas, what can one say?"[282] Deng Xiaoping said "I should remind you that Chairman Mao dedicated most of his life to China, that he saved the party and the revolution in their most critical moments, that, in short, his contribution was so great that, without him, the Chinese people would have had a much harder time finding the right path out of the darkness. We also shouldn't forget that it was Chairman Mao who combined the teachings of Marx and Lenin with the realities of Chinese history—that it was he who applied those principles, creatively, not only to politics but to philosophy, art, literature, and military strategy."[283]
Outside China
| External videos | |
|---|---|
Alexander V. Pantsov and Steven I. Levine, in their biography, asserted that Mao was both "a successful creator and ultimately an evil destroyer" but also argued that he was a complicated figure who should not be lionised as a saint or reduced to a demon, as he "indeed tried his best to bring about prosperity and gain international respect for his country."[284] They also remarked on Mao's legacy: "A talented Chinese politician, an historian, a poet and philosopher, an all-powerful dictator and energetic organizer, a skillful diplomat and utopian socialist, the head of the most populous state, resting on his laurels, but at the same time an indefatigable revolutionary who sincerely attempted to refashion the way of life and consciousness of millions of people, a hero of national revolution and a bloody social reformer—this is how Mao goes down in history. The scale of his life was too grand to be reduced to a single meaning."
Mao's English interpreter Sidney Rittenberg wrote in his memoir that whilst Mao "was a great leader in history", he was also "a great criminal because, not that he wanted to, not that he intended to, but in fact, his wild fantasies led to the deaths of tens of millions of people."[285] Dikötter argues that CCP leaders "glorified violence and were inured to massive loss of life. And all of them shared an ideology in which the end justified the means. In 1962, having lost millions of people in his province, Li Jingquan compared the Great Leap Forward to the Long March in which only one in ten had made it to the end: 'We are not weak, we are stronger, we have kept the backbone.'"[286] Regarding the large-scale irrigation projects, Dikötter stresses that they continued unabated for several years, and ultimately claimed the lives of hundreds of thousands of exhausted villagers.[287]
Mao was accused as "one of the great tyrants of the twentieth century",[288][289][182][259] Mao was frequently likened to the First Emperor of a unified China, Qin Shi Huang, and personally enjoyed the comparison.[290] During a speech to party cadre in 1958, Mao said he had far outdone Qin Shi Huang in his policy against intellectuals.[291][292][289][b] Philip Short said that the overwhelming majority of the deaths under Mao were unintended consequences of famine.[263] Short stated that landlord class were not exterminated as a people due to Mao's belief in redemption through thought reform,[263] and compared Mao with 19th-century Chinese reformers who challenged China's traditional beliefs in the era of China's clashes with Western colonial powers. Short writes that "Mao's tragedy and his grandeur were that he remained to the end in thrall to his own revolutionary dreams. ... He freed China from the straitjacket of its Confucian past, but the bright Red future he promised turned out to be a sterile purgatory."[263]

The United States placed a trade embargo on the People's Republic as a result of its involvement in the Korean War, until Richard Nixon decided that developing relations with the PRC would be useful.[293] The television series Biography stated: "[Mao] turned China from a feudal backwater into one of the most powerful countries in the World. ... The Chinese system he overthrew was backward and corrupt; few would argue the fact that he dragged China into the 20th century. But at a cost in human lives that is staggering."[280] Professor Jeffrey Wasserstrom of the University of California, Irvine compares China's relationship to Mao to Americans' remembrance of Andrew Jackson; both countries regard the leaders in a positive light, despite their respective roles in devastating policies. Jackson forcibly moved Native Americans through the Trail of Tears, resulting in thousands of deaths, while Mao was at the helm during the violent years of the Cultural Revolution and the Great Leap Forward.[294][c]

John King Fairbank remarked, "The simple facts of Mao's career seem incredible: in a vast land of 400 million people, at age 28, with a dozen others, to found a party and in the next fifty years to win power, organize, and remold the people and reshape the land—history records no greater achievement. Alexander, Caesar, Charlemagne, all the kings of Europe, Napoleon, Bismarck, Lenin—no predecessor can equal Mao Tse-tung's scope of accomplishment, for no other country was ever so ancient and so big as China."[295] In China: A New History, Fairbank and Goldman assessed Mao's legacy: "Future historians may conclude that Mao's role was to try to destroy the age-old bifurcation of China between a small educated ruling stratum and the vast mass of common people. We do not yet know how far he succeeded. The economy was developing, but it was left to his successors to create a new political structure."[296]
Stuart R. Schram said "Eternal rebel, refusing to be bound by the laws of God or man, nature or Marxism, he led his people for three decades in pursuit of a vision initially noble, which turned increasingly into a mirage, and then into a nightmare. Was he a Faust or Prometheus, attempting the impossible for the sake of humanity, or a despot of unbridled ambition, drunk with his own power and his own cleverness?"[297] Schram also said "I agree with the current Chinese view that Mao's merits outweighed his faults, but it is not easy to put a figure on the positive and negative aspects. How does one weigh, for example, the good fortune of hundreds of millions of peasants in getting land against the execution, in the course of land reform and the 'Campaign against Counter-Revolutionaries,' or in other contexts, of millions, some of whom certainly deserved to die, but others of whom undoubtedly did not? How does one balance the achievements in economic development during the first Five-Year Plan, or during the whole twenty-seven years of Mao's leadership after 1949, against the starvation which came in the wake of the misguided enthusiasm of the Great Leap Forward, or the bloody shambles of the Cultural Revolution?" Schram added, "In the last analysis, however, I am more interested in the potential future impact of his thought than in sending Mao as an individual to Heaven or to Hell."[298]
Maurice Meisner assessed Mao's legacy: "It is the blots on the Maoist record, especially the Great Leap and the Cultural Revolution, that are now most deeply imprinted on our political and historical consciousness. That these adventures were failures colossal in scope, and that they took an enormous human toll, cannot and should not be forgotten. But future historians, without ignoring the failures and the crimes, will surely record the Maoist era in the history of the People's Republic (however else they may judge it) as one of the great modernizing epochs in world history, and one that brought great social and human benefits to the Chinese people."[299]
Delia Davin remarked: "The consequences of Mao's actions were inevitably in proportion to the prodigious power he exercised, and the enormous population he ruled over. As a unifier and modernizer his achievements were immense, but his errors caused appalling suffering on a scale that is difficult to grasp. His utopian dreams, his periodic refusal to engage with reality, his ruthlessness, and his determination to win imposed terrible suffering on the Chinese people and cost millions of them their lives. He was ready to accept huge costs because he believed that suffering and death were inevitable in the pursuit of his cause. Mao's revolution improved life for those who survived it, bringing the economic development, education, and modernization on which subsequent progress was built. It also reunified China and made the country a force to be reckoned with in the world. He left an indelible mark on history."[300]
Third World
The ideology of Maoism has influenced many Communists, mainly in the Third World, including revolutionary movements such as Cambodia's Khmer Rouge,[301] Peru's Shining Path, and the Nepalese revolutionary movement. Under the influence of Mao's agrarian socialism and Cultural Revolution, Pol Pot and the Khmer Rouge conceived of his disastrous Year Zero policies which purged the nation of its teachers, artists and intellectuals and emptied its cities, resulting in the Cambodian genocide.[302] The Revolutionary Communist Party, USA, also claims Marxism–Leninism-Maoism as its ideology, as do other Communist Parties around the world which are part of the Revolutionary Internationalist Movement. China itself has moved sharply away from Maoism since Mao's death, and most people outside of China who describe themselves as Maoist regard the Deng Xiaoping reforms to be a betrayal of Maoism, in line with Mao's view of "capitalist roaders" within the Communist Party.[303] As the Chinese government instituted market economic reforms starting in the late 1970s and as later Chinese leaders took power, less recognition was given to the status of Mao. This accompanied a decline in state recognition of Mao in later years in contrast to previous years when the state organised numerous events and seminars commemorating Mao's 100th birthday. Nevertheless, the Chinese government has never officially repudiated the tactics of Mao. Deng Xiaoping, who was opposed to the Great Leap Forward and the Cultural Revolution, stated that "when we write about his mistakes we should not exaggerate, for otherwise we shall be discrediting Chairman Mao Zedong and this would mean discrediting our party and state."[304]
The July 1963 Limited Nuclear Test Ban Treaty increased Chinese concerns over a US-Soviet re-alignment against China and prompted Mao's articulation of the "Two Intermediate Zones" concept.[190]: 96–97 Mao viewed Africa and Latin America as the "First Intermediate Zone," in which China's status as a non-white power might enable it to compete with and supersede both United States and Soviet Union influence.[190]: 48 The other intermediate zone was the USA's wealthier allies in Europe.[190]: 97
Military strategy
Mao's military writings continue to have a large amount of influence both among those who seek to create an insurgency and those who seek to crush one, especially in manners of guerrilla warfare, at which Mao is popularly regarded as a genius.[305] The Nepali Maoists were highly influenced by Mao's views on protracted war, new democracy, support of masses, permanency of revolution and the Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution.[306] Mao's major contribution to the military science is his theory of People's War, with not only guerrilla warfare but more importantly, Mobile Warfare methodologies. Mao had successfully applied Mobile Warfare in the Korean War, and was able to encircle, push back and then halt the UN forces in Korea, despite the clear superiority of UN firepower.[307] In 1957, Mao also gave the impression that he might even welcome a nuclear war.[308][d]
Literature
Mao's poems and writings are frequently cited by both Chinese and non-Chinese. The official Chinese translation of President Barack Obama's inauguration speech used a famous line from one of Mao's poems.[312] In the mid-1990s, Mao's picture began to appear on all new renminbi currency from the People's Republic of China. This was officially instituted as an anti-counterfeiting measure as Mao's face is widely recognised in contrast to the generic figures that appear in older currency. On 13 March 2006, the People's Daily reported that a member of the Chinese People's Political Consultative Conference proposed to include the portraits of Sun Yat-sen and Deng Xiaoping in the renminbi.[313]
Public image
Mao gave contradicting statements on the subject of personality cults. In 1956, as a response to the Khrushchev Report that criticised Joseph Stalin, Mao stated that personality cults are "poisonous ideological survivals of the old society", and reaffirmed China's commitment to collective leadership.[314] At the 1958 party congress in Chengdu, Mao expressed support for the personality cults of people whom he labelled as genuinely worthy figures, not those that expressed "blind worship".[315]
In 1962, Mao proposed the Socialist Education Movement (SEM) in an attempt to educate the peasants to resist the "temptations" of feudalism and the sprouts of capitalism that he saw re-emerging in the countryside from Liu's economic reforms.[316] Large quantities of politicised art were produced and circulated—with Mao at the centre. Numerous posters, badges, and musical compositions referenced Mao in the phrase "Chairman Mao is the red sun in our hearts" (毛主席是我們心中的紅太陽; Máo Zhǔxí Shì Wǒmen Xīnzhōng De Hóng Tàiyáng)[317] and a "Savior of the people" (人民的大救星; Rénmín De Dà Jiùxīng).[317]
In October 1966, Mao's Quotations from Chairman Mao Tse-tung, known as the Little Red Book, was published. Party members were encouraged to carry a copy with them, and possession was almost mandatory as a criterion for membership. According to Mao: The Unknown Story by Jun Yang, the mass publication and sale of this text contributed to making Mao the only millionaire created in 1950s China (332). Over the years, Mao's image became displayed almost everywhere, present in homes, offices and shops. His quotations were typographically emphasised by putting them in boldface or red type in even the most obscure writings. Music from the period emphasised Mao's stature, as did children's rhymes. The phrase "Long Live Chairman Mao for ten thousand years" was commonly heard during the era.[318]

Mao also has a presence in China and around the world in popular culture, where his face adorns everything from T-shirts to coffee cups. Mao's granddaughter, Kong Dongmei, defended the phenomenon, stating that "it shows his influence, that he exists in people's consciousness and has influenced several generations of Chinese people's way of life. Just like Che Guevara's image, his has become a symbol of revolutionary culture."[285] Since 1950, over 40 million people have visited Mao's birthplace in Shaoshan, Hunan.[319]
A 2016 survey by YouGov survey found that 42% of American millennials have never heard of Mao.[320][321] According to the CIS poll, in 2019 only 21% of Australian millennials were familiar with Mao Zedong.[322] In 2020s China, members of Generation Z are embracing Mao's revolutionary ideas, including violence against the capitalist class, amid rising social inequality, long working hours, and decreasing economic opportunities.[323] As of the early 2020s, surveys conducted on Zhihu frequently rank Mao as one of the greatest and most influential figures in Chinese history.[10]: 58
Genealogy
Ancestors
Mao's ancestors were:
- Máo Yíchāng (毛貽昌, born Xiangtan 1870, died Shaoshan 1920), father, courtesy name Máo Shùnshēng (毛順生) or also known as Mao Jen-sheng
- Wén Qīmèi (文七妹, born Xiangxiang 1867, died 1919), mother. She was illiterate and a devout Buddhist. She was a descendant of Wen Tianxiang.
- Máo Ēnpǔ (毛恩普, born 1846, died 1904), paternal grandfather
- Liú (劉/刘, given name not recorded, born 1847, died 1884),[324] paternal grandmother
- Máo Zǔrén (毛祖人), paternal great-grandfather
Wives

Mao had four wives who gave birth to a total of 10 children, among them:
- Luo Yixiu (1889–1910) of Shaoshan: married 1907 to 1910
- Yang Kaihui (1901–1930) of Changsha: married 1921 to 1927, executed by the KMT in 1930; mother to Mao Anying, Mao Anqing, and Mao Anlong
- He Zizhen (1910–1984) of Jiangxi: married May 1928 to 1937; mother to 6 children
- Jiang Qing (1914–1991), married 1939 until Mao's death; mother to Li Na
Siblings
Mao had several siblings:
- Mao Zemin (1896–1943), younger brother, executed by a warlord
- Mao Zetan (1905–1935), younger brother, executed by the KMT
- Mao Zejian (1905–1929), adopted sister, executed by the KMT
Mao's parents altogether had five sons and two daughters. Two of the sons and both daughters died young, leaving the three brothers Mao Zedong, Mao Zemin, and Mao Zetan. Like all three of Mao Zedong's wives, Mao Zemin and Mao Zetan were communists. Like Yang Kaihui, both Mao Zemin and Mao Zetan were killed in warfare during Mao Zedong's lifetime. Note that the character zé (澤) appears in all of the siblings' given names; this is a common Chinese naming convention.
From the next generation, Mao Zemin's son Mao Yuanxin was raised by Mao Zedong's family, and he became Mao Zedong's liaison with the Politburo in 1975. In Li Zhisui's The Private Life of Chairman Mao, Mao Yuanxin played a role in the final power-struggles.[325]
Children
Mao had a total of ten children,[326] including:
- Mao Anying (1922–1950): son to Yang, married to Liú Sīqí (劉思齊), killed in action during the Korean War
- Mao Anqing (1923–2007): son to Yang, married to Shao Hua, son Mao Xinyu, grandson Mao Dongdong
- Mao Anlong (1927–1931): son to Yang, died during the Chinese Civil War
- Mao Anhong: son to He, left to Mao's younger brother Zetan and then to one of Zetan's guards when he went off to war, was never heard of again
- Li Min (b. 1936): daughter to He, married to Kǒng Lìnghuá (孔令華), son Kǒng Jìníng (孔繼寧), daughter Kong Dongmei (孔冬梅)
- Li Na (b. 1940): daughter to Jiang (whose birth surname was Lǐ, a name also used by Mao while evading the KMT), married to Wáng Jǐngqīng (王景清), son Wáng Xiàozhī (王效芝)
Mao's first and second daughters were left to local villagers because it was too dangerous to raise them while fighting the Kuomintang and later the Japanese. Their youngest daughter (born in early 1938 in Moscow after Mao separated) and one other child (born 1933) died in infancy. Two English researchers who retraced the entire Long March route in 2002–2003[327] located a woman whom they believe might well be one of the missing children abandoned by Mao to peasants in 1935. Ed Jocelyn and Andrew McEwen hope a member of the Mao family will respond to requests for a DNA test.[328]
Through his ten children, Mao became grandfather to twelve grandchildren, many of whom he never knew. He has many great-grandchildren alive today. One of his granddaughters is businesswoman Kong Dongmei, one of the richest people in China.[329] His grandson Mao Xinyu is a general in the Chinese army.[330] Both he and Kong have written books about their grandfather.[331]
Personal life

Mao's private life was kept very secret at the time of his rule. After Mao's death, Li Zhisui, his personal physician, published The Private Life of Chairman Mao, a memoir which mentions some aspects of Mao's private life, such as chain-smoking cigarettes, addiction to powerful sleeping pills and large number of sexual partners.[332] Some scholars and others who knew Mao personally have disputed the accuracy of these accounts and characterisations.[333]
Having grown up in Hunan, Mao spoke Mandarin with a marked Hunanese accent.[334] Ross Terrill wrote Mao was a "son of the soil ... rural and unsophisticated" in origins,[335] while Clare Hollingworth said that Mao was proud of his "peasant ways and manners", having a strong Hunanese accent and providing "earthy" comments on sexual matters.[334] Lee Feigon said that Mao's "earthiness" meant that he remained connected to "everyday Chinese life."[336]
Sinologist Stuart R. Schram emphasised Mao's ruthlessness but also noted that he showed no sign of taking pleasure in torture or killing in the revolutionary cause.[337] Lee Feigon considered Mao "draconian and authoritarian" when threatened but opined that he was not the "kind of villain that his mentor Stalin was".[338] Alexander Pantsov and Steven I. Levine wrote that Mao was a "man of complex moods", who "tried his best to bring about prosperity and gain international respect" for China, being "neither a saint nor a demon."[339] They noted that in early life, he strove to be "a strong, wilful, and purposeful hero, not bound by any moral chains", and that he "passionately desired fame and power".[340]
Mao learned to speak some English, particularly through Zhang Hanzhi, his English teacher, interpreter and diplomat who later married Qiao Guanhua, Minister of Foreign Affairs and the head of China's UN delegation.[341] His spoken English was limited to a few single words, phrases, and some short sentences. He first chose to systematically learn English in the 1950s, which was very unusual as the main foreign language first taught in Chinese schools at that time was Russian.[342]
Writings and calligraphy

鷹擊長空,
魚翔淺底,
萬類霜天競自由。
悵寥廓,
問蒼茫大地,
誰主沉浮
Eagles cleave the air,
Fish glide in the limpid deep;
Under freezing skies a million creatures contend in freedom.
Brooding over this immensity,
I ask, on this boundless land
Who rules over man's destiny?
—Excerpt from Mao's poem "Changsha", September 1927[343]
Mao was a prolific writer of political and philosophical literature.[344] The main repository of his pre-1949 writings is the Selected Works of Mao Zedong, published in four volumes by the People's Publishing House since 1951. A fifth volume, which brought the timeline up to 1957, was briefly issued during the leadership of Hua Guofeng, but subsequently withdrawn from circulation for its perceived ideological errors. There has never been an official "Complete Works of Mao Zedong" collecting all his known publications.[345] Mao is the attributed author of Quotations from Chairman Mao Tse-tung, known in the West as the "Little Red Book" and in Cultural Revolution China as the "Red Treasure Book" (紅寶書). First published in January 1964, this is a collection of short extracts from his many speeches and articles (most found in the Selected Works), edited by Lin Biao, and ordered topically. The Little Red Book contains some of Mao's most widely known quotes.[e]
Mao wrote prolifically on political strategy, commentary, and philosophy both before and after he assumed power.[f] Mao was also a skilled Chinese calligrapher with a highly personal style. In China, Mao was considered a master calligrapher during his lifetime.[346] His calligraphy can be seen today throughout mainland China.[347] His work gave rise to a new form of Chinese calligraphy called "Mao-style" or Maoti, which has gained increasing popularity since his death. There exist various competitions specialising in Mao-style calligraphy.[348]
Literary works
As did most Chinese intellectuals of his generation, Mao's education began with Chinese classical literature. Mao told Edgar Snow in 1936 that he had started the study of the Confucian Analects and the Four Books at a village school when he was eight, but that the books he most enjoyed reading were Water Margin, Journey to the West, the Romance of the Three Kingdoms and Dream of the Red Chamber.[349] Mao published poems in classical forms starting in his youth and his abilities as a poet contributed to his image in China after he came to power in 1949. His style was influenced by the great Tang dynasty poets Li Bai and Li He.[350]
Some of his best known poems are "Changsha" (1925), "The Double Ninth" (October 1929), "Loushan Pass" (1935), "The Long March" (1935), "Snow" (February 1936), "The PLA Captures Nanjing" (1949), "Reply to Li Shuyi" (11 May 1957), and "Ode to the Plum Blossom" (December 1961).
Portrayal in media
Mao has been portrayed in film and television numerous times. Some notable actors include: Han Shi, the first actor ever to have portrayed Mao, in a 1978 drama Dielianhua and later again in a 1980 film Cross the Dadu River;[351] Gu Yue, who had portrayed Mao 84 times on screen throughout his 27-year career and had won the Best Actor title at the Hundred Flowers Awards in 1990 and 1993;[352][353] Liu Ye, who played a young Mao in The Founding of a Party (2011);[354] Tang Guoqiang, who has frequently portrayed Mao in more recent times, in the films The Long March (1996) and The Founding of a Republic (2009), and the television series Huang Yanpei (2010), among others.[355] Mao is a principal character in American composer John Adams' opera Nixon in China (1987). The Beatles' song "Revolution" refers to Mao in the verse "but if you go carrying pictures of Chairman Mao you ain't going to make it with anyone anyhow...";[356] John Lennon expressed regret over including these lines in the song in 1972.[357]
See also
Notes
- ^ /ˈmaʊ (t)səˈtʊŋ/;[1] Chinese: 毛泽东; pinyin: Máo Zédōng pronounced [mǎʊ tsɤ̌.tʊ́ŋ]; traditionally romanised as Mao Tse-tung. In this Chinese name, the family name is Mao and Ze is a generation name.
- ^ "The People's Republic of China under Mao exhibited the oppressive tendencies that were discernible in all the major absolutist regimes of the twentieth century. There are obvious parallels between Mao's China, Nazi Germany and Soviet Russia. Each of these regimes witnessed deliberately ordered mass 'cleansing' and extermination."[289]
- ^ "Though admittedly far from perfect, the comparison is based on the fact that Jackson is remembered both as someone who played a significant role in the development of a political organisation (the Democratic Party) that still has many partisans, and as someone responsible for brutal policies toward Native Americans that are now referred to as genocidal. Both men are thought of as having done terrible things yet this does not necessarily prevent them from being used as positive symbols. And Jackson still appears on $20 bills, even though Americans tend to view as heinous the institution of slavery (of which he was a passionate defender) and the early 19th-century military campaigns against Native Americans (in which he took part). At times Jackson, for all his flaws, is invoked as representing an egalitarian strain within the American democratic tradition, a self-made man of the people who rose to power via straight talk and was not allied with moneyed interests. Mao stands for something roughly similar."[294]
- ^ The often-cited evidence quote as proof is as follows: "Let us imagine how many people would die if war breaks out. There are 2.7 billion people in the world, and a third could be lost. If it is a little higher, it could be half. ... I say that if the worst came to the worst and one-half dies, there will still be one-half left, but imperialism would be razed to the ground and the whole world would become socialist. After a few years there would be 2.7 billion people again."[309][310] Historians dispute the sincerity of Mao's words. Robert Service says that Mao "was deadly serious",[311] while Frank Dikötter claims that Mao "was bluffing ... the sabre-rattling was to show that he, not Khrushchev, was the more determined revolutionary."[309]
- ^ Among them are:
"War is the highest form of struggle for resolving contradictions, when they have developed to a certain stage, between classes, nations, states, or political groups, and it has existed ever since the emergence of private property and of classes."
— "Problems of Strategy in China's Revolutionary War" (December 1936), Selected Works of Mao Tse-tung, I, p. 180."Every communist must grasp the truth, 'Political power grows out of the barrel of a gun.'"
— 1938, Selected Works of Mao Tse-tung, II, pp. 224–225."Taken as a whole, the Chinese revolutionary movement led by the Communist Party embraces two stages, i.e., the democratic and the socialist revolutions, which are two essentially different revolutionary processes, and the second process can be carried through only after the first has been completed. The democratic revolution is the necessary preparation for the socialist revolution, and the socialist revolution is the inevitable sequel to the democratic revolution. The ultimate aim for which all communists strive is to bring about a socialist and communist society."
— "The Chinese Revolution and the Chinese Communist Party" (December 1939), Selected Works of Mao Tse-tung, 'II, pp. 330–331."All reactionaries are paper tigers. In appearance, the reactionaries are terrifying, but in reality they are not so powerful. From a long-term point of view, it is not the reactionaries but the people who are really powerful."
— Mao Zedong (July 1956), "U.S. Imperialism Is a Paper Tiger". - ^ The most influential of these include:
- Report on an Investigation of the Peasant Movement in Hunan (《湖南农民运动考察报告》); March 1927
- On Guerrilla Warfare (《游擊戰》); 1937
- On Practice (《實踐論》); 1937
- On Contradiction (《矛盾論》); 1937
- On Protracted War (《論持久戰》); 1938
- In Memory of Norman Bethune (《紀念白求恩》); 1939
- On New Democracy (《新民主主義論》); 1940
- Talks at the Yan'an Forum on Literature and Art (《在延安文藝座談會上的講話》); 1942
- Serve the People (《為人民服務》); 1944
- The Foolish Old Man Who Removed the Mountains (《愚公移山》); 1945
- On the Correct Handling of the Contradictions Among the People (《正確處理人民內部矛盾問題》); 1957
References
- ^ "Definition of Mao Tse-tung". Dictionary.com. Retrieved 17 November 2021.
- ^ Pottinger, Jesse (26 August 2019). "Explainer: Mao Zedong or Mao Tse-tung? We Have the Answer". That's Online. Retrieved 24 April 2020.
- ^ Schram 1966, p. 19; Hollingworth 1985, p. 15; Pantsov & Levine 2012, p. 11.
- ^ Schram 1966, pp. 19–20; Terrill 1980, pp. 4–5, 15; Feigon 2002, pp. 13–14; Pantsov & Levine 2012, pp. 13–.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Schram 1966, p. 20; Terrill 1980, p. 11; Pantsov & Levine 2012, pp. 14, 17.
- ^ Schram 1966, pp. 20–21; Terrill 1980, p. 8; Pantsov & Levine 2012, pp. 15, 20
- ^ Terrill 1980, p. 12; Feigon 2002, p. 23, Pantsov & Levine 2012, pp. 25–28
- ^ Feigon 2002, p. 15 Terrill 1980, pp. 10–11
- ^ Schram 1966, p. 23; Terrill 1980, pp. 12–13; Pantsov & Levine 2012, p. 21
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Marquis, Christopher; Qiao, Kunyuan (2022). Mao and Markets: The Communist Roots of Chinese Enterprise. New Haven: Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-300-26883-6. OCLC 1348572572.
- ^ Schram 1966, p. 25; Terrill 1980, pp. 20–21; Pantsov & Levine 2012, p. 29
- ^ Schram 1966, p. 22; Terrill 1980, p. 13; Pantsov & Levine 2012, pp. 17–18
- ^ Terrill 1980, p. 14; Pantsov & Levine 2012, p. 18
- ^ Schram 1966, p. 22; Feigon 2002, p. 15; Terrill 1980, p. 18; Pantsov & Levine 2012, p. 28
- ^ Schram 1966, p. 26; Terrill 1980, p. 19; Pantsov & Levine 2012, pp. 28–30
- ^ Schram 1966, p. 26; Terrill 1980, pp. 22–23; Pantsov & Levine 2012, p. 30
- ^ Pantsov & Levine 2012, pp. 32–34
- ^ Schram 1966, p. 27;Terrill 1980, p. 22; Pantsov & Levine 2012, p. 33
- ^ Schram 1966, pp. 26–27; Terrill 1980, pp. 22–24; Pantsov & Levine 2012, p. 33
- ^ Schram 1966, p. 26; Terrill 1980, p. 23; Pantsov & Levine 2012, p. 33
- ^ Schram 1966, pp. 30–32; Pantsov & Levine 2012, pp. 32–35
- ^ Schram 1966, p. 34; Pantsov & Levine 2012, pp. 34–35
- ^ Schram 1966, pp. 34–35; Terrill 1980, pp. 23–24
- ^ Schram 1966, pp. 35–36; Terrill 1980, pp. 22, 25; Pantsov & Levine 2012, p. 35.
- ^ Schram 1966, p. 36; Terrill 1980, p. 26; Pantsov & Levine 2012, pp. 35–36.
- ^ Pantsov & Levine 2012, pp. 36–37.
- ^ Pantsov & Levine 2012, pp. 40–41.
- ^ Pantsov & Levine 2012, p. 36.
- ^ Schram 1966, pp. 36–37; Terrill 1980, p. 27; Pantsov & Levine 2012, p. 37.
- ^ Schram 1966, pp. 38–39.
- ^ Pantsov & Levine 2012, p. 43; see also Yu, Hsiao (1959). Mao Tse-Tung and I Were Beggars. Syracuse, N.Y.: Syracuse University Press.
- ^ Schram 1966, pp. 42–43; Terrill 1980, p. 32; Pantsov & Levine 2012, p. 48.
- ^ Schram 1966, p. 41; Terrill 1980, p. 32; Pantsov & Levine 2012, p. 42.
- ^ Schram 1966, pp. 40–41; Terrill 1980, pp. 30–31.
- ^ Schram 1966, p. 43; Terrill 1980, p. 32; Pantsov & Levine 2012, pp. 49–50.
- ^ Панцов и Левин 2012 , стр. 49–50.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 44; Террилл 1980 , с. 33; Панцов и Левин 2012 , стр. 101-1. 50–52.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 45; Террилл 1980 , с. 34; Панцов и Левин 2012 , с. 52.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 48; Панцов и Левин 2012 , стр. 101-1. 47, 56–57.
- ^ Фейгон 2002 , с. 18; Панцов и Левин 2012 , с. 39.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 48; Панцов и Левин 2012 , с. 59.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 47; Панцов и Левин 2012 , стр. 101-1. 59–62.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 48–49; Панцов и Левин 2012 , стр. 62–64.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 48; Панцов и Левин 2012 , стр. 101-1. 57–58.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 51; Панцов и Левин 2012 , стр. 101-1. 53–55,
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 48; Панцов и Левин 2012 , стр. 101-1. 62, 66.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 50–52; Панцов и Левин 2012 , с. 66.
- ^ Панцов и Левин 2012 , стр. 66–67.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 51–52; Фейгон 2002 , стр. 21–22; Панцов и Левин 2012 , стр. 69–70.
- ^ Панцов и Левин 2012 , с. 68.
- ^ Панцов и Левин 2012 , с. 76.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 53–54; Панцов и Левин 2012 , стр. 71–76.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 55; Панцов и Левин 2012 , стр. 101-1. 76–77.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Хуан, Ибин (2020). Идеологическая история Коммунистической партии Китая . Том. 1. Цянь Чжэн, Гою Ву, Сюэмэй Дин, Ли Сун, Шелли Брайант. Монреаль, Квебек: Издательская группа Royal Collins. п. 16. ISBN 978-1-4878-0425-1 . OCLC 1165409653 .
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 55–56; Панцов и Левин 2012 , с. 79.
- ^ Панцов и Левин 2012 , с. 80.
- ^ Панцов и Левин 2012 , стр. 81–83.
- ^ Панцов и Левин 2012 , с. 84.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , стр. 56–57.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Майр, Виктор Х.; Санпин, Санпин; Вуд, Фрэнсис (2013). Жизни китайцев: Люди, создавшие цивилизацию . Лондон: Темза и Гудзон . п. 211. ИСБН 978-0500251928 .
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 63; Фейгон 2002 , стр. 23, 28.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , стр. 63–64; Фейгон 2002 , стр. 23–24, 28, 30.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , стр. 64–66.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Шрам 1966 , с. 68.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , стр. 68–69.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 69.
- ^ Перри, Элизабет Дж. (14 января 2013 г.). «Аньюань: революционная традиция горнодобывающего Китая» . Азиатско-Тихоокеанский журнал . 11 (1). ISBN 978-0520271890 .
переиздание главы 2 Элизабет Дж. Перри. Аньюань: развитие революционной традиции горнодобывающего Китая. Беркли: Калифорнийский университет Press, 2012.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Карл, Ребекка Э. (2010). Мао Цзэдун и Китай в мире двадцатого века: краткая история . Дарем [Северная Каролина]: Издательство Университета Дьюка . стр. 22–23. ISBN 978-0-8223-4780-4 . OCLC 503828045 .
- ^ Карл, Ребекка Э. (2010). Мао Цзэдун и Китай в мире двадцатого века: краткая история . Дарем [Северная Каролина]: Издательство Университета Дьюка . п. 23. ISBN 978-0-8223-4780-4 . OCLC 503828045 .
- ^ Шрам 1966 , стр. 69–70.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , стр. 73–74; Фейгон 2002 , с. 33
- ^ Шрам 1966 , стр. 74–76.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , стр. 76–82.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 78.
- ^ Уилбур, К. Мартин; Как, Джули Лиен-ин (1989). Миссионеры революции: советские советники и националистический Китай, 1920–1927 гг . Издательство Гарвардского университета . ISBN 978-0674576520 .
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 83.
- ^ Мао Цзэдун (1992), Шрам, Стюарт Рейнольдс; и др. (ред.), Национальная революция и социальная революция, декабрь 1920 г. - июнь 1927 г. , Дорога Мао к власти , Vol. II, М. Е. Шарп , с. 465 .
- ^ Лю Сяоюань (2004), Пограничные переходы: этнополитика и рост китайского коммунизма, 1921–1945 , Стэнфорд: Stanford University Press , стр. 66 , ISBN 978-0804749602 – через Google Книги
- ^ Шрам 1966 , стр. 82, 90–91.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , стр. 84, 89.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , стр. 87, 92–93; Фейгон 2002 , с. 39
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 95.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 98.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Фейгон 2002 , с. 42.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , стр. 99–100.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 100.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 106; Картер 1976 , стр. 61–62.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , стр. 106–109, 112–113.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Картер 1976 , с. 62.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Картер 1976 , с. 63.
- ^ Картер 1976 , с. 64; Шрам 1966 , стр. 122–125; Фейгон 2002 , стр. 46–47.
- ^ «Мао Цзэдун о войне и революции» . Цитаты Мао Цзэдуна о войне и революции . Колумбийский университет . Проверено 12 ноября 2011 г. ; Фейгон 2002 , с. 41
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 125; Картер 1976 , с. 68
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 130; Картер 1976 , стр. 67–68; Фейгон 2002 , с. 48
- ^ Карл, Ребекка Э. (2010). Мао Цзэдун и Китай в мире двадцатого века: краткая история . Дарем [Северная Каролина]: Издательство Университета Дьюка . п. 36. ISBN 978-0-8223-4780-4 . OCLC 503828045 .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Картер 1976 , с. 69
- ^ Шрам 1966 , стр. 126–127; Картер 1976 , стр. 66–67.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Картер 1976 , с. 70
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 159; Фейгон 2002 , с. 47
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 131; Картер 1976 , стр. 68–69.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , стр. 128, 132.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , стр. 133–137; Картер 1976 , стр. 70–71; Фейгон 2002 , с. 50
- ^ «Мемориал открыт в честь второй жены Мао» . www.china.org.cn . 20 ноября 2007 года . Проверено 7 октября 2021 г.
- ^ Да, Цзин-цзин (27 марта 2007 г.). Написано в Пекине. «Смерть освещает нишу жизни Мао » Лос-Анджелес Таймс . Лос-Анджелес, Калифорния. Архивировано 11 октября. из оригинала Получено 7 октября.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 138; Картер 1976 , стр. 71–72.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , стр. 138, 141.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Картер 1976 , с. 72
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 139.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , стр. 146–149; Картер 1976 , с. 75; Фейгон 2002 , с. 51
- ^ Картер 1976 , с. 75.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , стр. 149–151.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 149.
- ^ Фейгон 2002 , с. 50; Картер 1976 , с. 75; Шрам 1966 , с. 153
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 152; Картер 1976 , с. 76; Фейгон 2002 , стр. 51–53.
- ^ Картер 1976 , с. 77; Шрам 1966 , стр. 154–155; Фейгон 2002 , стр. 54–55.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , стр. 155–161.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Картер 1976 , с. 78
- ^ Картер 1976 , с. 77; Шрам 1966 , стр. 161–165; Фейгон 2002 , стр. 53–54.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , стр. 166–168; Фейгон 2002 , с. 55
- ^ Шрам 1966 , стр. 175–177; Картер 1976 , стр. 80–81; Фейгон 2002 , стр. 56–57.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 180; Картер 1976 , стр. 81–82; Фейгон 2002 , с. 57
- ^ Фейгон 2002 , с. 57; Шрам 1966 , стр. 180–181; Картер 1976 , с. 83
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 181; Картер 1976 , стр. 84–86; Фейгон 2002 , с. 58
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 183; Картер 1976 , стр. 86–87.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , стр. 184–186; Картер 1976 , стр. 88–90; Фейгон 2002 , стр. 59–60.
- ^ Картер 1976 , стр. 90–91.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 186; Картер 1976 , стр. 91–92; Фейгон 2002 , с. 60
- ^ Шрам 1966 , стр. 187–188; Картер 1976 , стр. 92–93; Фейгон 2002 , с. 61
- ^ Фейгон 2002 , с. 61; Шрам 1966 , с. 188; Картер 1976 , с. 93
- ^ Барнуэн, Барбара; Ю, Чангэн (2006). Чжоу Эньлай: его политическая жизнь . Гонконг: Китайский университет Гонконга . п. 62. ИСБН 9629962802 . Проверено 12 марта 2011 г. - через Google Книги .
- ^ Фейгон 2002 , с. 61; Шрам 1966 , с. 193; Картер 1976 , стр. 94–96.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 193.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , стр. 206–207.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 20; Картер 1976 , с. 101
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 202.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , стр. 209–210.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 208
- ^ Картер 1976 , с. 95
- ^ Террилл, Росс (8 марта 1998 г.). «Что Мао променял на секс» . Лос-Анджелес Таймс . Архивировано из оригинала 24 мая 2020 года . Проверено 7 октября 2021 г.
- ^ Картер 1976 , стр. 95–96.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 194
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 196
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 197
- ^ Шрам 1966 , стр. 198–200; Картер 1976 , стр. 98–99; Фейгон 2002 , стр. 64–65.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 211; Картер 1976 , стр. 100–101.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 205
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Картер 1976 , с. 105
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 204; Фейгон 2002 , с. 66
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 217
- ^ Шрам 1966 , стр. 211–216; Картер 1976 , стр. 101–110.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Мойс, Эдвин Э. (2008). Современный Китай, история . Пирсон/Лонгман. п. 105. ИСБН 978-0582772779 – через Google Книги .
- ^ Истман, Ллойд Э.; Чен, Джером; Пеппер, Сюзанна; Слайк, Лайман П. Ван (30 августа 1991 г.). Националистическая эпоха в Китае, 1927–1949 гг . Издательство Кембриджского университета . п. 353. ИСБН 978-0521385916 – через Google Книги .
- ^ Автор: Лю Сяншан (20 апреля 2009 г. ) . «Инцидент Чжан Синьфу» и вывод советской армии из северо-восточного Китая [«Инцидент Чжан Синьфу» и вывод Советской Армии из Северо-Восточного Китая] (на китайском языке). 揚子晚報網. Архивировано из оригинала 1 ноября 2013 года . Проверено 20 апреля 2009 г.
- ^ Джейкобс, Эндрю (2 октября 2009 г.). «Китай молчит о травмах подъема коммунистов» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Проверено 2 октября 2009 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Палестини, Роберт (2011). Возвращение в будущее: путь лидерства для преподавателей . R&L Образование. п. 170. ИСБН 978-1607095866 – через Google Книги .
- ^ Перкинс, Дороти (2013). Энциклопедия Китая: история и культура . Рутледж . п. 79. ИСБН 978-1135935627 – через Google Книги .
- ^ Чик, Т., изд. (2002). Мао Цзэдун и революции в Китае: краткая история с документами . Нью-Йорк: Пэлгрейв Макмиллан . п. 125. ИСБН 978-0312256265 .
Часто ошибочно полагают, что эта фраза была произнесена во время речи у Врат Небесного Мира, но впервые она была использована 21 сентября на первом пленарном заседании Народного политического консультативного совета Китая, а затем повторена несколько раз.
- ^ Вестад, Одд Арне (1996). «Борьба за дружбу: Мао, Сталин и советско-китайский договор 1950 года». Бюллетень проекта международной истории холодной войны . 8 (9): 224–236.
- ^ Норт, Роберт К. (1950). «Советско-китайские соглашения 1950 года». Дальневосточное обследование . 19 (13): 125–130. дои : 10.2307/3024085 . ISSN 0362-8949 . JSTOR 3024085 .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Цай, Сян; Запуск (2016). Революция и ее повествования: социалистические литературные и культурные фантазии Китая (1949-1966) . Ребекка Э. Карл, Сюэпин Чжун, Ченнаи. Дарем: Издательство Университета Дьюка . п. 100. ИСБН 978-0-8223-7461-9 . OCLC 932368688 .
- ^ «180 000 китайских солдат погибли в Корейской войне» . china.org.cn . Проверено 28 ноября 2019 г. .
- ^ Беркитт, Лори; Скобелл, Эндрю; Ворцель, Ларри М. (2003). Уроки истории: Народно-освободительной армии Китая 75 лет (PDF) . Институт стратегических исследований . стр. 340–341. ISBN 978-1584871262 . Архивировано из оригинала (PDF) 5 февраля 2012 года . Проверено 14 июля 2009 г.
- ^ Short 2001 , стр. 436–437.
- ^ Шайдель, Вальтер (2017). Великий уравнитель: насилие и история неравенства от каменного века до XXI века . Издательство Принстонского университета . п. 226. ИСБН 978-0691165028 .
В Чжанчжуанцуне, на более тщательно реформированном севере страны, большинство «помещиков» и «богатых крестьян» потеряли всю свою землю, а зачастую и жизнь, или бежали. Все бывшие безземельные рабочие получили землю, что полностью исключило эту категорию. В результате «середняки», составлявшие теперь 90 процентов населения деревни, владели 90,8 процентами земли, что было настолько близко к полному равенству, насколько можно было надеяться.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Куйсонг 2008 .
- ^ Мошер, Стивен В. (1992). Неверное восприятие Китая: американские иллюзии и китайская реальность . Основные книги . стр. 72–73. ISBN 0465098134 .
- ^ Шалом, Стивен Росскамм (1984). Смертность в Китае из-за коммунизма . Центр азиатских исследований Университета штата Аризона . п. 24. ISBN 0939252112 .
- ^ Спенс 1999 [ нужна страница ] . Эту цифру Мао получил из отчета, представленного заместителем министра общественной безопасности Сюй Цзыжуном, в котором говорилось, что 712 000 контрреволюционеров были казнены, 1 290 000 были заключены в тюрьмы, а еще 1 200 000 были «подвергнуты контролю»: см. Kuisong 2008 .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Твитчетт, Денис; Фэрбанк, Джон К .; Макфаркуар, Родерик (1987). Кембриджская история Китая . Издательство Кембриджского университета . ISBN 978-0521243360 . Проверено 23 августа 2008 г. - через Google Книги .
- ^ Мейснер, Морис (1999). Китай Мао и после: История Народной Республики (Третье изд.). Свободная пресса. п. 72. ИСБН 0684856352 .
... оценка многих относительно беспристрастных наблюдателей о том, что за первые три года существования Народной Республики было казнено 2 миллиона человек, вероятно, является настолько точным предположением, насколько можно сделать на основе скудной информации.
- ^ Мошер, Стивен В. (1992). Неверное восприятие Китая: американские иллюзии и китайская реальность . Основные книги . п. 74. ИСБН 0465098134 .
... цифра, которую Фэрбанк назвал верхним пределом «трезвых» оценок.
- ^ Фейгон 2002 , с. 96: «К 1952 году они распространили земельную реформу на всю сельскую местность, но в ходе этого процесса было убито от двух до пяти миллионов землевладельцев».
- ^ Короткометражка 2001 , с. 436.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Валентино 2004 , стр. 121–122.
- ^ Чангюй, Ли. «Квоты на убийства Мао. Права человека в Китае (HRIC). 26 сентября 2005 г., Шаньдунский университет» (PDF) . Архивировано из оригинала (PDF) 29 июля 2009 года . Проверено 21 июня 2009 г.
- ^ Браун, Джереми. «Ужасный медовый месяц: борьба с проблемой террора в Китае начала 1950-х годов» . Архивировано из оригинала 27 июня 2009 года.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Боттелье, Питер (2018). Разработка экономической политики в Китае (1949–2016): роль экономистов . Рутледж . п. 131. ИСБН 978-1351393812 – через Google Книги .
Однако мы должны помнить, что Мао также сделал замечательные вещи для Китая; Помимо воссоединения страны, он восстановил чувство естественной гордости, значительно улучшил права женщин, базовое здравоохранение и начальное образование, положил конец злоупотреблению опиумом, упростил китайские иероглифы, разработал систему пиньинь и пропагандировал ее использование в учебных целях.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Маккой, Альфред В. «История опиума, 1858–1940 годы» . Архивировано из оригинала 4 апреля 2007 года . Проверено 4 мая 2007 г.
- ^ Фэрбенк, Джон; Гольдман, Мерл (2002). Китай: новая история . Кембридж, Массачусетс: Издательство Belknap Press Гарвардского университета . п. 349.
- ^ Короткометражка 2001 , с. 437.
- ^ «Прилив террора» . Время . 5 марта 1956 года. Архивировано из оригинала 18 марта 2008 года . Проверено 11 мая 2009 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Короткое 2001 , с. 631.
- ^ «Китай – Экономическая политика» . Британская энциклопедия . 1998.
- ^ Ведение бизнеса в Китайской Народной Республике . Прайс, Уотерхаус. 1994. с. 3 – через Google Книги .
В то же время сельское хозяйство было организовано на коллективной основе (социалистическая кооперация), промышленность и торговля.
- ^ «Китай – Переход к социализму, 1953–57» . Британская энциклопедия . 1998.
- ^ Тесзар, Дэвид Тибор (октябрь 2015 г.). «Венгерские связи: Венгерская революция 1956 года и ее влияние на внутреннюю политику Мао Цзэдуна в конце 1950-х годов» (PDF) . Обзор глобальной политики . 1 (1): 18–34.
- ^ Видаль, Кристина (2016). «Антиправая кампания 1957–1958 годов в Китае: история и память (1978–2014)» . Хал-ШС .
- ^ Макфаркуар, Родерик (13 января 1997 г.). Политика Китая: эпохи Мао и Дэна Издательство Кембриджского университета. ISBN 978-0-521-58863-8 – через Google Книги.
- ^ Ли 1994 , стр. 198, 200, 468–469.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д Крин, Джеффри (2024). Страх перед мощью Китая: международная история . Серия «Новые подходы к международной истории». Лондон, Великобритания: Bloomsbury Academic . ISBN 978-1-350-23394-2 .
- ^ Джин, Кейю (2023). Новый учебник Китая: за пределами социализма и капитализма . Нью-Йорк: Викинг. ISBN 978-1-9848-7828-1 .
- ^ Сюй, Элизабет (2006). «Размышления об «открытии» противомалярийного средства цинхао» . Британский журнал клинической фармакологии . 61 (6): 666–670. дои : 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2006.02673.x . ПМК 1885105 . ПМИД 16722826 .
- ^ Сентилингам, Мира. «Химия в своей стихии: соединения: Артемизинин» . Химический мир . Королевское химическое общество . Проверено 27 апреля 2015 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Хао, Синди (29 сентября 2011 г.). «Премия Ласкера возобновила дебаты по поводу открытия Артемизинина» . Наука . Проверено 23 июля 2020 г.
- ^ Ту, Юю (2011). «Открытие артемизинина (цинхаосу) и дары китайской медицины». Природная медицина . 17 (10): 1217–1220. дои : 10.1038/нм.2471 . ПМИД 21989013 . S2CID 10021463 .
- ^ Кинг, Гилберт. «Молчание, предшествовавшее большому прыжку Китая в голод» . Смитсоновский институт . Проверено 28 ноября 2019 г. .
- ^ Слейер, Уилл (20 февраля 2015 г.). Ритмы жизни и смерти капиталистических режимов - долг перед бесчестием: график мирового господства 1400-2100 гг . Издательство Партридж, Сингапур. п. 509. ИСБН 978-1-4828-2961-7 – через Google Книги .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Спенс 1999 г. [ нужна страница ]
- ^ Юши, Мао (22 сентября 2014 г.). «Уроки Великого голода в Китае» . Журнал Катона . 34 (3): 483–491. Гейл А387348115 .
- ^ Смиль, В. (18 декабря 1999 г.). «Великий голод в Китае: 40 лет спустя» . БМЖ . 319 (7225): 1619–1621. дои : 10.1136/bmj.319.7225.1619 . ПМК 1127087 . ПМИД 10600969 .
- ^ Томас П., Бернштейн (июнь 2006 г.). «Мао Цзэдун и голод 1959–1960 годов: исследование своеволия». Китайский ежеквартальный журнал . 186 (186): 421–445. дои : 10.1017/S0305741006000221 . JSTOR 20192620 . S2CID 153728069 .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Ли, Сяобин; Тянь, Сяньшэн (2013). Эволюция власти: борьба, выживание и успех Китая . Лексингтонские книги . п. 41. ИСБН 978-0739184981 – через Google Книги .
- ^ «Три китайских лидера: Мао Цзэдун, Чжоу Эньлай и Дэн Сяопин» . Колумбийский университет . Архивировано из оригинала 11 декабря 2013 года . Проверено 22 апреля 2020 г.
- ^ Беккер 1998 , стр. 92–93.
- ^ Валентино 2004 , с. 127.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Чанг и Холлидей 2005 , стр. 568, 579.
- ^ Тиббетс, Янн (2016). 50 великих военачальников всех времен . Vij Books India Pvt Ltd. ISBN 978-9385505669 – через Google Книги .
- ^ Скалапино, Роберт А. (1964). «Советско-китайское соревнование в Африке». Иностранные дела . 42 (4): 640–654. дои : 10.2307/20029719 . JSTOR 20029719 .
- ^ Люти, Лоренц М. (2010). Советско-китайский раскол: холодная война в коммунистическом мире . Издательство Принстонского университета . п. 1. ISBN 978-1400837625 – через Google Книги .
- ^ Беккер, Джаспер (2002). Китайцы . Издательство Оксфордского университета . п. 271. ИСБН 978-0199727223 – через Google Книги .
- ^ Гарвер, Джон В. (2016). В поисках Китая: история международных отношений Китайской Народной Республики . Издательство Оксфордского университета . п. 132. ИСБН 978-0190261054 – через Google Книги .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Хаммонд, Кен (2023). Китайская революция и поиски социалистического будущего . Нью-Йорк, штат Нью-Йорк: Книги 1804 г. ISBN 9781736850084 .
- ^ Ли, Минцзян (27 октября 2010 г.). «Идеологическая дилемма: Китай Мао и советско-китайский раскол, 1962–63» . История холодной войны . 11 (3): 387–419. дои : 10.1080/14682745.2010.498822 . S2CID 153617754 . Получено 12 февраля.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д и ж г час я дж Мейскенс, Ковелл Ф. (2020). Третий фронт Мао: Милитаризация Китая времен холодной войны . Кембридж, Соединенное Королевство: Издательство Кембриджского университета . дои : 10.1017/9781108784788 . ISBN 978-1-108-78478-8 . OCLC 1145096137 . S2CID 218936313 .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Хоу, Ли (2021). Строительство нефти: Дацин и формирование китайского социалистического государства . Серия монографий Гарвардского института Йенчин . Кембридж, Массачусетс: Азиатский центр Гарвардского университета . ISBN 978-0-674-26022-1 .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Маркиз, Кристофер ; Цяо, Кунюань (2022). Мао и рынки: коммунистические корни китайского предпринимательства . Нью-Хейвен: Издательство Йельского университета . дои : 10.2307/j.ctv3006z6k . ISBN 978-0-300-26883-6 . JSTOR j.ctv3006z6k . OCLC 1348572572 . S2CID 253067190 .
- ^ Фейгон 2002 , с. 140.
- ↑ Полное описание этой идеи см. в Gao 2008.
- ^ Джонатан Мирски. Проблемы средств к существованию. Архивировано 6 сентября 2010 года в Wayback Machine. литературном обозрении
- ^ «Список источников и подробные данные о количестве погибших в результате гемоклизма двадцатого века» . Исторический атлас ХХ века . Проверено 23 августа 2008 г.
- ^ Василогамброс, Мэтт (16 мая 2016 г.). «Наследие культурной революции в Китае» . Атлантика . Проверено 28 ноября 2019 г. .
- ^ «Обсуждение культурной революции в Китае» . Обзоры в истории . Проверено 28 ноября 2019 г. .
- ^ Пай, Люциан В. (1986). «Переоценка культурной революции». Китайский ежеквартальный журнал . 108 (108): 597–612. дои : 10.1017/S0305741000037085 . ISSN 0305-7410 . JSTOR 653530 . S2CID 153730706 .
- ^ MacFarquhar & Schoenhals 2006 , стр. 110.
- ^ MacFarquhar & Schoenhals 2006 , стр. 125.
- ^ MacFarquhar & Schoenhals 2006 , стр. 124.
- ^ Ион Михай Пачепа (28 ноября 2006 г.). «Убийственные методы Кремля» . Национальное обозрение . Архивировано из оригинала 8 августа 2007 года . Проверено 23 августа 2008 г.
- ^ Великая пролетарская культурная революция, продолжавшаяся до 1976 года:
- «Глоссарий Marxists.org: Культурная революция» . Интернет-архив марксистов . Энциклопедия марксизма . Проверено 6 октября 2015 г.
- «Великая пролетарская культурная революция в Китае, 1966–1976» . sjsu.edu . Экономический факультет государственного университета Сан-Хосе. Архивировано из оригинала 24 апреля 2019 года . Проверено 6 октября 2015 г.
- Спенс, Джонатан (2001). «Введение в культурную революцию» (PDF) . iis-db.stanford.edu . Архивировано из оригинала (PDF) 31 января 2016 года . Проверено 6 октября 2015 г. – Адаптировано из книги «В поисках современного Китая».
- ^ «Резолюция по некоторым вопросам истории нашей партии с момента основания Китайской Народной Республики» (принята шестым пленумом Центрального комитета Коммунистической партии Китая одиннадцатого созыва 27 июня 1981 г.) Резолюция об истории КПК (1949–81). (Пекин: Издательство иностранных языков, 1981). п. 32.
- ^ Широт 1996 , с. 198.
- ^ Раваллион, Мартин (25 января 2021 г.). «Бедность в Китае с 1950 года: контрфактическая перспектива» . Национальное бюро экономических исследований . Серия рабочих документов. дои : 10.3386/w28370 . S2CID 234005582 .
- ^ Мейснер, Морис (1999). Китай Мао и после: История Народной Республики (3-е изд.). Свободная пресса. п. 354. ИСБН 978-0684856353 – через Google Книги .
- ^ MacFarquhar & Schoenhals 2006 , стр. 262.
- ^ Дэниел Лиз, «Мао-человек и Мао-икона» в Чик, Тимоти, изд. (2010). Критическое введение в Мао . Издательство Кембриджского университета . п. 233. ИСБН 978-1139789042 – через Google Книги .
- ^ Лев Котюков. Забытый поэт. Archived 28 September 2007 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Пак, Кён Э; Снайдер, Скотт (2012). Северная Корея в переходный период: политика, экономика и общество . Издательство Rowman & Littlefield . п. 214. ИСБН 978-1442218130 .
- ^ Заядлый курильщик:
- Карл, Ребекка Э. (2010). Мао Цзэдун и Китай в мире двадцатого века: краткая история . Издательство Университета Дьюка . п. 79. ИСБН 978-0822393023 . Проверено 28 июля 2015 г.
- Тиммонс, Хизер (30 декабря 2013 г.). «Конец китайской «дипломатии пепельницы» » . Атлантика . Проверено 28 июля 2015 г.
- Нюландер, Йохан (9 февраля 2014 г.). «Тушение дымного наследия Мао» . Аль Джазира . Проверено 28 июля 2015 г.
- Флоркруз, Джейми (7 января 2011 г.). «Китай окутан сигаретным дымом» . CNN . Проверено 28 июля 2015 г.
- ^ «Стенограммы Киссенджера: примечания и выдержки» . nsarchive.gwu.edu . Проверено 28 июля 2015 г.
- ^ Болезнь Паркинсона:
- «Мао Цзэдун» . ПБС . Проверено 28 июля 2015 г.
- «Биография Мао Цзэ-дуна» . биография.com . Проверено 28 июля 2015 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Мао Цзэ-Дун умер в Пекине в возрасте 82 лет; лидер Красной китайской революции; выбор преемника неопределенен» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Проверено 25 октября 2014 г.
- ^ Боковой амиотрофический склероз:
- Ли, Чжисуй (2010). Частная жизнь председателя Мао: Мемуары личного врача Мао (иллюстрировано, переиздание под ред.). Случайный дом . п. 581. ИСБН 978-1407059228 . Проверено 28 июля 2015 г.
- Гриффин, Николас (2014). Пинг-понговая дипломатия: Айвор Монтегю и удивительная история игры, изменившей мир . Саймон и Шустер . п. 163. ИСБН 978-0857207371 . Проверено 28 июля 2015 г.
- Сэдлер-Смит, Юджин (2010). Интуитивный разум: польза от силы шестого чувства . Джон Уайли и сыновья . п. 223. ИСБН 978-0470685389 . Проверено 28 июля 2015 г.
- Триплетт, II, Уильям К. (2004). Государство-изгой: как ядерная Северная Корея угрожает Америке (иллюстрированное издание). Издательство Регнери. п. 224 . ISBN 978-0895260680 . Проверено 28 июля 2015 г.
- ^ Чанг и Холлидей 2005 .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Куигли, Кристина (1998). Современные мумии: сохранение человеческого тела в двадцатом веке (иллюстрировано, переиздание под ред.). МакФарланд. стр. 40–42. ISBN 978-0786428519 . Проверено 28 июля 2015 г. - через Google Книги .
- ^ «Китайцы грустно прощаются с Мао» . УПИ . Проверено 29 марта 2020 г.
- ^ Джеймс, С.Л. «Китай: коммунистическая история через кино» . Интернет-архив . Проверено 28 июля 2015 г.
- ^ «1976: умирает председатель Мао Цзэдун» . Новости Би-би-си . 9 сентября 1976 года . Проверено 28 июля 2015 г.
- ^ «Китайцы прощаются с лидером нации» . Florence Times + Tri-Cities Daily . Юнайтед Пресс Интернешнл. 18 сентября 1976 года . Проверено 8 октября 2015 г.
- ^ Лу, Син (2017). Риторика Мао Цзэдуна: преобразование Китая и его народа . Издательство Университета Южной Каролины . п. 50. ISBN 978-1611177534 – через Google Книги .
В 1956 году Мао подписал предложение о кремации вместе со 151 другим высокопоставленным чиновником. По слухам, Мао написал в своем завещании, что хочет, чтобы его кремировали после смерти. По иронии судьбы его преемники решили выставить его труп на всеобщее обозрение, чтобы нация отдала дань уважения.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Карл, Ребекка Э. (2010). Мао Цзэдун и Китай в мире двадцатого века: краткая история . Азиатско-Тихоокеанский сериал. Дарем, Северная Каролина: Издательство Университета Дьюка . дои : 10.2307/j.ctv11hpp6w . ISBN 978-0-8223-4780-4 . JSTOR j.ctv11hpp6w .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Мейснер, Морис Дж. (1999). Китай Мао и после: история Народной Республики (3-е изд.). Нью-Йорк, штат Нью-Йорк: Свободная пресса. ISBN 978-0-684-85635-3 .
- ^ Уэбли, Кайла (4 февраля 2011 г.). «25 лучших политических икон» . Время .
- ^ «Мао Цзэдун» . Оксфордский справочник по мировой политике . Архивировано из оригинала 21 марта 2006 года . Проверено 23 августа 2008 г.
- ^ Короткометражка 2001 , с. 630 «Мао обладал необычайным сочетанием талантов: он был провидцем, государственным деятелем, политическим и военным стратегом с хитрым интеллектом, философом и поэтом».
- ^ «Китайский лидер Мао Цзэдун / Часть I» . Архивировано из оригинала 12 июля 2015 года . Проверено 2 апреля 2015 г.
- ^ Pantsov, Alexander V.; Levine, Steven I. (2013). Mao: The Real Story . Simon & Schuster . p. 574. ISBN 978-1451654486 .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Галтунг, Марте Кьер; Стенсли, Стиг (2014). 49 Мифов о Китае . Роуман и Литтлфилд . стр. 189. ISBN 978-1442236226 – через Google Книги .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Бабиарз, Кимберли Сингер; Эгглстон, Карен; и др. (2015). «Исследование снижения смертности в Китае при Мао: провинциальный анализ, 1950–80» . Исследования народонаселения . 69 (1): 39–56. дои : 10.1080/00324728.2014.972432 . ПМЦ 4331212 . ПМИД 25495509 .
Рост ожидаемой продолжительности жизни при рождении в Китае с 35–40 лет в 1949 году до 65,5 лет в 1980 году является одним из самых быстрых и устойчивых показателей в документально подтвержденной мировой истории.
- ^ «Достижения Мао «перевешивают» ошибки: опрос» . Аль Джазира . 23 декабря 2013 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Фенби, Дж. (2008). Современный Китай: падение и возвышение великой державы, с 1850 года по настоящее время . Экко Пресс . п. 351 . ISBN 978-0061661167 .
Ответственность Мао за уничтожение от 40 до 70 миллионов жизней клеймит его как массового убийцу, более великого, чем Гитлер или Сталин, его безразличие к страданиям и человеческим потерям захватывает дух.
- ^ Евангелиста, Мэтью (2005). Исследования мира: критические концепции в политической науке . Тейлор и Фрэнсис. п. 96. ИСБН 978-0-415-33923-0 .
По оценкам, в результате политики китайского правительства под руководством Мао Цзэдуна в период с 1950 по 1976 год погибло около 80 миллионов человек.
- ^ Штраус, Валери; Саутерл, Дэниел (17 июля 1994 г.). «Сколько погибло? Новые данные свидетельствуют о гораздо большем количестве жертв эпохи Мао Цзэдуна» . Вашингтон Пост . ISSN 0190-8286 . Проверено 28 ноября 2019 г. .
- ^ Короткометражка 2001 , с. 631–632.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с д Короткое 2001 , с. 632.
- ^ «Культурная революция и история тоталитаризма» . Время . Проверено 14 декабря 2020 г.
- ^ Джонсон, Ян (5 февраля 2018 г.). «Кто убил больше: Гитлер, Сталин или Мао?» . Нью -Йоркское обозрение книг . Архивировано из оригинала 5 февраля 2018 года . Проверено 18 июля 2020 г.
- ^ Фенби, Джонатан (2008). Современный Китай: падение и возвышение великой державы, с 1850 года по настоящее время . Группа Пингвин . п. 351. ИСБН 978-0061661167 .
- ^ Шрам, Стюарт (март 2007 г.). «Мао: Неизвестная история». The China Quarterly (189): 205. doi : 10.1017/s030574100600107x . S2CID 154814055 .
- ^ Евангелиста, Мэтью А. (2005). Исследования мира: критические концепции в политической науке . Тейлор и Фрэнсис . п. 96. ИСБН 978-0415339230 – через Google Книги .
- ^ Аттан, Изабель (2002). «Политика планирования семьи Китая: обзор ее прошлого и будущего». Исследования в области планирования семьи . 33 (1): 103–113. дои : 10.1111/j.1728-4465.2002.00103.x . ISSN 0039-3665 . JSTOR 2696336 . ПМИД 11974414 .
- ^ Ву, Дж. (1994). «Население и планирование семьи в Китае». Слушания – Королевская медицинская академия Бельгии . 56 (5): 383–400, обсуждение 401–402. ISSN 0302-6469 . ПМИД 7892742 .
- ^ Ловелл, Джулия (16 марта 2019 г.). «Маоизм идет вперед: революционная идея, которая до сих пор формирует мир» . Хранитель . ISSN 0261-3077 . Проверено 20 января 2020 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Гао 2008 , стр. 81.
- ^ Эбри, Патрисия Бакли (2010). Кембриджская иллюстрированная история Китая . Издательство Кембриджского университета . п. 327. ИСБН 978-0521124331 – через Google Книги .
- ^ «Китай «увольняет» редакторов за критику Мао, задерживает левого активиста» . Рефмир . Проверено 18 мая 2019 г.
- ^ Татлоу, Диди Кирстен (5 мая 2011 г.). «Наследие Мао все еще разделяет Китай» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . ISSN 0362-4331 . Проверено 18 мая 2019 г.
- ^ "Все являются жертвами Мао, но никто не смеет этого сказать", - говорит телеведущий в Китае, вызывая гнев" . Первый пост . 10 апреля 2015 года . Проверено 18 мая 2019 г.
- ^ «Китайский телеведущий будет наказан за Мао Цзибэ» . Небесные новости . Проверено 18 мая 2019 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Дин, Иза; Джавед, Джеффри (26 мая 2019 г.). «Почему маоизм до сих пор находит отклик в Китае» . Вашингтон Пост .
- ^ «Площадь Председателя Мао открылась в день его 115-летия со дня рождения» . Китайская газета . 25 декабря 2008 года . Проверено 2 января 2013 г. ; «Мао Цзэдун по-прежнему собирает толпы людей в свой 113-й день рождения» . Народная газета . 27 декабря 2006 г. Проверено 2 января 2013 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Биография (сериал) Мао Цзе Дун: Крестьянский император Китая A&E Network 2005, ASIN B000AABKXG [ необходимо время ]
- ^ Уоттс, Джонатан (1 июня 2005 г.). «Китай должен противостоять темному прошлому, — говорит доверенное лицо Мао» . Хранитель . Архивировано из оригинала 17 сентября 2018 года . Проверено 13 августа 2021 г.
- ^ «Большой злой волк» . Экономист . 31 августа 2006 года . Проверено 28 июля 2015 г.
- ^ «Дэн: Исправляя ошибки Мао» . Вашингтон Пост . 1980. Архивировано из оригинала 29 августа 2019 года . Проверено 20 ноября 2021 г.
- ^ Pantsov, Alexander V.; Levine, Steven I. (2013). Mao: The Real Story . Simon & Schuster . pp. 5–6. ISBN 978-1451654486 .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Внучка сохраняет память о Мао в книжном магазине. Архивировано 4 января 2021 года в Wayback Machine Максимом Дунканом, Reuters , 28 сентября 2009 года.
- ^ Дикёттер 2010 , стр. 299.
- ^ Дикёттер 2010 , стр. 33.
- ^ MacFarquhar & Schoenhals 2006 , стр. 471: « Вместе с Иосифом Сталиным и Адольфом Гитлером Мао, похоже, суждено войти в историю как один из величайших тиранов двадцатого века ».
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б с Линч, Майкл (2004). Мао . Исторические биографии Рутледжа. Рутледж . п. 230.
- ^ MacFarquhar & Schoenhals 2006 , стр. 428 .
- ^ Мао Цзэдун шестьян ван суй (1969), стр. 195. См.: Либерталь, Кеннет (2003). Управление Китаем: от революции к реформе (второе изд.). WW Нортон и компания . п. 71. ИСБН 0393924920 .
- ^ Цзэдун, Мао. «Выступления на второй сессии VIII съезда партии» . Интернет-архив марксистов . Проверено 28 июня 2016 г.
- ^ Чен, Синь-чжу Дж. (2006). «Китай и торговое эмбарго США, 1950–1972» . Американский журнал китаеведения . 13 (2): 169–186. ISSN 2166-0042 . JSTOR 44288827 .
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б «Некоторые заметки о китайской книге» . Мэтт Скьявенца.com . Архивировано из оригинала 9 февраля 2015 года . Проверено 8 февраля 2015 г.
- ^ Фэрбанк, Джон Кинг (1983). США и Китай (4-е исправленное и расширенное изд.). Издательство Гарвардского университета . ISBN 9780674036642 .
- ^ Фэрбенк, Джон Кинг; Гольдман, Мерл (2006). Китай: новая история (2-е расширенное изд.). Кембридж (Массачусетс): Belknap Press издательства Гарвардского университета. ISBN 0-674-01828-1 .
- ^ Шрам, Стюарт Р. (1989). Мысль Мао Цзэдуна . Кембридж [Кембриджшир]: Издательство Кембриджского университета . ISBN 978-0521310628 .
- ^ Макфаркуар, Родерик (декабрь 2012 г.). «Стюарт Рейнольдс Шрам, 1924–2012» . Китай Ежеквартальный . 212 (212): 1099–1122. дои : 10.1017/S0305741012001518 .
- ^ Мейснер, Морис Дж. (1999). Китай Мао и после: история Народной Республики (3-е изд.). Нью-Йорк, штат Нью-Йорк: Свободная пресса. ISBN 0684856352 .
- ^ Дэвин, Делия (2013). Мао: очень краткое вступление . Оксфорд: Оксфордский университет. Нажимать. ISBN 978-0199588664 .
- ^ Александр, Роберт Джексон (1999). Международный маоизм в развивающихся странах . Прегер. п. 200. ; Джексон, Карл Д. (1992). Камбоджа, 1975–1978: Встреча со смертью . Издательство Принстонского университета . п. 219. ИСБН 978-0691025414 – через Google Книги .
- ^ Биография (сериал) : Пол Пот; Сеть A&E , 2003.
- ^ Клиссолд, Тим (2014). Китайские правила: собака Мао, кот Дэна и пять вечных уроков с линии фронта в Китае . Нью-Йорк: Харпер. ISBN 978-0062316578 .
- ^ Дирлик, Ариф (4 июня 2012 г.). «Мао Цзэдун в современном китайском официальном дискурсе и истории» . Перспективы Китая . 2012 (2): 17–27. doi : 10.4000/chinaperspectives.5852 . ISSN 2070-3449 .
- ^ Ганди, RKS (1965). «Мао Цзэ-дун: его военные сочинения и философия» . Обзор военно-морского колледжа . 17 (7): 1–27. ISSN 0028-1484 . JSTOR 44635448 – через JSTOR .
- ^ Упрети, Бхуван Чандра (2008). Маоисты в Непале: от повстанческого движения к политическому мейнстриму . Издательство Гян. п. 56. ИСБН 978-8178356877 – через Google Книги .
- ^ «Чжан, Военный романтизм Мао: Китай и Корейская война, 1950-1953, 1995 | Американо-китайский институт» . china.usc.edu . Проверено 19 мая 2023 г.
- ^ Фокс Баттерфилд , « Мао Цзэ-Дун: отец китайской революции ». Нью-Йорк Таймс . 10 сентября 1976 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Дикёттер 2010 , стр. 13.
- ^ Серж Халими (август 2018 г.). «Забытая коммунистическая ссора» . Ле Монд дипломатический . ISSN 0026-9395 . Викиданные Q97657492 . , процитировал этот комментарий, сказав, что он был датирован 1957 годом.
- ^ Роберт Сервис . Товарищи!: История мирового коммунизма. Издательство Гарвардского университета , 2007. стр. 321. ISBN 067402530X
- ^ «Аобаму джиужи йэншуо йэн маозедонг шици» Обама цитирует стихи Мао Цзэдуна в своей инаугурационной речи [Инаугурационная речь Обамы цитирует поэзию Мао Цзэдуна]. People's Daily (на китайском языке). 22 января 2009 года. Архивировано из оригинала 27 августа 2009 года . Проверено 28 июля 2015 г.
- ^ «Портреты Сунь Ятсена Дэн Сяопин предложил добавить к нотам юаней» . Народная газета . 13 марта 2006 г. Архивировано из оригинала 8 марта 2016 г. . Проверено 23 августа 2008 г.
- ^ Мейснер, Морис (2007). Мао Цзэдун: политический и интеллектуальный портрет . Политика. п. 133.
- ^ «Культ Мао» . библиотека.thinkquest.org. Архивировано из оригинала 1 июня 2008 года . Проверено 23 августа 2008 г.
В этом замечании Мао есть доля правды, но оно неверно. Он путает поклонение истине с культом личности, хотя между ними есть существенная разница. Но это замечание сыграло свою роль в распространении культа личности, который постепенно возник в КПК.
- ^ «Стефан Ландсбергер, Раскрась это в красный. Пятьдесят лет китайских пропагандистских плакатов» . chineseposters.net . Проверено 7 ноября 2017 г.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Глава 5: «Значки Мао – визуальные изображения и надписи» в: Хелен Ван : Значки председателя Мао : символы и лозунги культурной революции (Исследовательская публикация Британского музея 169). Попечители Британского музея, 2008. ISBN 978-0861591695 .
- ^ Лу, Син (2004). Риторика китайской культурной революции: влияние на китайскую мысль, культуру и коммуникацию . Издательство Университета Южной Каролины . п. 65. ИСБН 978-1570035432 – через Google Книги .
- ^ «Сёшан шэн ци юнгюан бо луо де хон тайян» Красное солнце, которое никогда не заходит, восходит в Шаошане. [Красное солнце, которое никогда не заходит, восходит в Шаошане] (на китайском языке). Шаошань.gov.cn. Архивировано из оригинала 7 ноября 2014 года . Проверено 25 октября 2014 г.
- ^ «Опрос: Миллениалам крайне необходимо изучить историю коммунизма» . МаркетВотч . 21 октября 2016 г.
- ^ «Опрос показал, что молодые американцы более открыты социалистическим идеям» . Новости «Голоса Америки» . 23 октября 2016 г.
- ^ Свитцер, Том (23 февраля 2019 г.). «Мнение: почему миллениалы принимают социализм» . Сидней Морнинг Геральд .
- ^ Юань, Ли (8 июля 2021 г.). « Кто наши враги?» Горькая молодежь Китая поддерживает Мао» . Нью-Йорк Таймс . Проверено 8 июля 2021 г.
- ^ Панцов и Левин 2012 , стр. 13.
- ^ Ли 1994 , с. 659.
- ^ Спенс 1999 , с. 97.
- ^ «Вход в историю» . Китайская газета . 23 ноября 2003 года . Проверено 23 августа 2008 г.
- ↑ «Долгий поход» , Эд Джоселин и Эндрю МакИвен. Констебль 2006 г.
- ^ Конг Дунмей в списке богатых людей Китая:
- «Кун Дунмэй, внучка Мао Цзэдуна, значится в списке богатых людей Китая» . ХаффПост . Агентство Франс-Пресс . 9 июля 2015 года . Проверено 29 июля 2015 г.
- Малкольм Мур (9 мая 2013 г.). «Внучка Мао обвиняется в списке богатых людей Китая» . «Дейли телеграф» . Пекин. Архивировано из оригинала 10 января 2022 года . Проверено 29 июля 2015 г.
- ^ «Внук Мао, получивший звание генерал-майора, подвергается насмешкам» . Лос-Анджелес Таймс . 4 августа 2010 г. Проверено 29 июля 2015 г.
- ^ «Семья дорожит председателем» . Китайский интернет-информационный центр . 22 декабря 2003 г.
- ^ Ли , 1994.
- ^ ДеБорга и Донг 1996 . п. 4.
- ^ Перейти обратно: а б Холлингворт 1985 , стр. 29–30.
- ^ Террилл 1980 , с. 19.
- ^ Фейгон 2002 , с. 26.
- ^ Шрам 1966 , с. 153.
- ^ Фейгон 2002 , с. 53.
- ^ Панцов и Левин 2012 , стр. 5–6.
- ^ Панцов и Левин 2012 , стр. 42, 66.
- ^ Барбоза, Дэвид (29 января 2008 г.). «Чжан Ханьчжи, наставник Мао по английскому языку, умер в возрасте 72 лет» . Нью-Йорк Таймс .
- ^ "Jiēmìmàozédōng wèishéme xué yingyǔ:"Zhè shì xouzhēng de xūyào" " Рассказываем, почему Мао Цзэдун выучил английский язык: «Это необходимость борьбы» [Разъясняем, почему Мао Цзэдун выучил английский язык: «Это необходимость борьбы»]. People's Daily (на китайском языке (Китай)). 9 июля 2015 г. Архивировано из оригинала 13 января 2018 г. . Проверено 12 января 2018 г.
- ^ Картер 1976 , с. 64.
- ^ «Мысли Мао Цзэдуна – Часть 1» . Проверено 30 апреля 2011 г.
- ^ Уилкинсон, Эндимион (2018). История Китая: новое руководство (5-е изд. в мягкой обложке). Кембридж, Массачусетс: Азиатский центр Гарвардского университета. ISBN 978-0998888309 .
- ^ «100 лет» . Азиатский ветер . Проверено 23 августа 2008 г.
- ^ Йен, Юэпин (2005). Каллиграфия и власть в современном китайском обществе . Рутледж. п. 2.
- ^ «Сюцзиэ мао ту шуфу йаоцингсай цзинпэн фэнчэн» Первый пригласительный конкурс каллиграфии Мао представляет превосходную продукцию [Первый пригласительный конкурс каллиграфии Мао Ди]. Люди (на китайском языке). 11 сентября 2006 г. Архивировано из оригинала 26 ноября 2006 г. Проверено 1 апреля 2007 г.
- ^ Барнстон, Уиллис (1972; руководитель Беркли: University of California Press, 2008). Стихи Мао Цзэдуна . стр. 3–4. ISBN 0520935004 .
- ^ Нг, Ён Сан (1963). «Поэзия Мао Цзэ-дуна». The China Quarterly 13 : 60–73. дои : 10.1017/S0305741000009711 .
- ^ «Быть Мао Цзэдуном» . Глобал Таймс . 4 июля 2011 года . Проверено 15 марта 2013 г.
- ^ «Умер знаменитый актер, игравший Мао Цзэдуна» . Народная газета . 5 июля 2005 г. Проверено 15 марта 2013 г.
- ^ «Актер, известный по роли Мао Цзэдуна, умирает от инфаркта миокарда» . Народная газета . 5 июля 2005 г. Проверено 15 марта 2013 г.
- ^ Лю, Вэй (3 июня 2011 г.). «Катушка Мао» . Китайская ежедневная европейская еженедельная газета . Проверено 15 марта 2013 г.
- ^ Сюн, Цюй (26 ноября 2011 г.). «Артисты ожидают процветания китайской культуры» . Новости видеонаблюдения. Архивировано из оригинала 14 декабря 2013 года . Проверено 15 марта 2013 г.
- ^ Олдридж, Алан; Битлз (1969). Иллюстрированные тексты песен The Beatles . Хоутон Миффлин Харкорт . п. 104. ИСБН 978-0395594261 .
- ^ Спиньези, Стивен Дж.; Льюис, Майкл (2004). Здесь, там и повсюду: 100 лучших песен Битлз . Нью-Йорк: Черный пес . п. 40. ИСБН 978-1579123697 .
Библиография
- Беккер, Джаспер (1998). Голодные призраки: Тайный голод Мао . Холт в мягкой обложке. ISBN 978-0805056686 .
- Картер, Питер (1976). Мао . Лондон: Издательство Оксфордского университета. ISBN 978-0192731401 .
- Чанг, Юнг ; Холлидей, Джон (2005). Мао: Неизвестная история . Лондон: Джонатан Кейп. ISBN 978-0224071260 .
- Широ, Даниэль (1996). Современные тираны: сила и распространенность зла в наш век . Издательство Принстонского университета . ISBN 978-0691027777 .
- Клиссон, Тим (2014). Китайские правила: собака Мао, кот Дэна и пять вечных уроков с линии фронта в Китае . Нью-Йорк: Харпер. ISBN 978-0062316578 .
- Дикёттер, Франк (2010). Великий голод Мао: история самой разрушительной катастрофы Китая, 1958–62 гг . Лондон: Уокер и компания. ISBN 978-0802777683 .
- Фейгон, Ли (2002). Мао: новая интерпретация . Чикаго: Иван Р. Ди. ISBN 978-1566634588 .
- Гао, Мобо (2008). Битва за прошлое Китая: Мао и культурная революция . Лондон: Плутон Пресс . ISBN 978-0745327808 .
- Холлингворт, Клэр (1985). Мао и люди против него . Лондон: Джонатан Кейп. ISBN 978-0224017602 .
- Куйсонг, Ян (март 2008 г.). «Пересмотр кампании по подавлению контрреволюционеров». Китайский ежеквартальный журнал . 193 (193): 102–121. дои : 10.1017/S0305741008000064 . S2CID 154927374 .
- Ли, Чжисуй (1994). Частная жизнь председателя Мао: Мемуары личного врача Мао . Лондон: Рэндом Хаус . ISBN 978-0679764434 .
- Макфаркуар, Родерик ; Шенхалс, Майкл (2006). Последняя революция Мао . Кембридж, Массачусетс: Издательство Гарвардского университета . ISBN 978-0674027480 .
- Панцов Александр Владимирович; Левин, Стивен И. (2012). Мао: Реальная история . Нью-Йорк и Лондон: Саймон и Шустер . ISBN 978-1451654479 .
- Шрам, Стюарт (1966). Мао Цзэдун . Лондон: Саймон и Шустер . ISBN 978-0140208405 .
- Коротко, Филип (2001). Мао: Жизнь . Книги о сове . ISBN 978-0805066388 .
- Спенс, Джонатан (1999). Мао Цзэдун . Пингвин жив. Нью-Йорк: Викинг Пресс . ISBN 978-0670886692 . OCLC 41641238 .
- Бернс, Джон Ф. (6 февраля 2000 г.). «Методы великого лидера» . Нью-Йорк Таймс .
- Террилл, Росс (1980). Мао: Биография . Саймон и Шустер . , который заменяется Террилл, Росс (1999). Мао: Биография . Стэнфорд, Калифорния: Издательство Стэнфордского университета . ISBN 0804729212 .
- Валентино, Бенджамин А. (2004). Окончательные решения: массовые убийства и геноцид в двадцатом веке . Издательство Корнелльского университета . ISBN 978-0801439650 .
Дальнейшее чтение
- Эндрю, Анита М.; Рэпп, Джон А. (2000). Автократия и повстанческие императоры-основатели Китая: сравнение председателя Мао и Мин Тайцзу . Роуман и Литтлфилд . стр. 110–. ISBN 978-0847695805 .
- Дэвин, Делия (2013). Мао: Очень краткое введение . Издательство Оксфордского университета . ISBN 978-0191654039 .
- Кейт, Шоппа Р. (2004). Двадцатый век в Китае: история в документах . Оксфорд: Издательство Оксфордского университета . ISBN 978-0199732005 .
- Шайк, Сэм (2011). Тибет: История . Нью-Хейвен: Публикации прессы Йельского университета . ISBN 978-0300154047 .
Внешние ссылки
Общий
- «Основы китайской внешней политики», онлайн-документы на английском языке из Центра Вильсона в Вашингтоне.
- Азия Источник биография
- ChineseMao.com: обширные ресурсы о Мао Цзэдуне. Архивировано 6 сентября 2013 г. на Wayback Machine.
- Профиль CNN
- Собрание сочинений Мао о маоистском интернационалистическом движении
- Собрание сочинений Мао Цзэ-дуна (1917–1949) Объединенная служба исследований публикаций
- Цитаты Мао
- Справочный архив Мао Цзэдуна на сайте marxists.org
- Оксфордский спутник мировой политики: Мао Цзэдун
- Биография Мао на официальном веб-сайте Коммунистической партии Китая
- Фотография председателя Мао, прогуливающегося возле своей официальной резиденции, 1957 год.
Комментарий
- Обсуждает жизнь, военное влияние и труды председателя Мао Цзэдуна.
- Что внес маоизм. Архивировано 12 августа 2021 г. в Wayback Machine Самиром Амином (21 сентября 2006 г.).
- Китай должен противостоять темному прошлому, говорит доверенное лицо Мао
- Мао был жестоким, но он также заложил основу для сегодняшнего Китая
- «О роли Мао Цзэдуна» Уильям Хинтон . Monthly Review Foundation, 2004 г., том 56, выпуск 04 (сентябрь)
- Пропагандистские картины, изображающие Мао как великого лидера Китая.
- Вспоминая жертв Мао
- Большой скачок Мао к голоду
- Поиск фактов о жертвах Мао
- Вспоминая великого рулевого Китая
- Действительно ли Мао убил миллионы людей во время «большого скачка»? Архивировано 11 октября 2019 года в Wayback Machine.
- Мао Цзэдун: крестьянский император Китая
- Мао Цзэдун
- 1893 рождения
- 1976 смертей
- Семья Мао Цзэдуна
- Атеисты 20-го века
- Главы правительств Китая 20-го века
- Китайские философы XX века
- Китайские поэты 20-го века
- Китайские писатели XX века
- Антиимпериалисты
- Антиревизионисты
- Председатели Национального комитета Народного политического консультативного совета Китая
- Китайские антикапиталисты
- Китайские атеисты
- Политики Коммунистической партии Китая из провинции Хунань
- Китайская коммунистическая революция
- Китайские коммунисты
- Китайские партизаны
- Китайские писатели-мужчины XX века
- Китайские марксисты
- Китайские военные писатели
- Китайские националисты
- Китайцы во Второй мировой войне
- Китайцы Корейской войны
- Китайские политические философы
- Китайские политические писатели
- Китайские революционеры
- Китайские социалистические феминистки
- поэты-коммунисты
- Критики религий
- Обожествленные китайские мужчины
- Делегаты I Всекитайского съезда Коммунистической партии Китая.
- Делегаты III Всекитайского съезда Коммунистической партии Китая.
- Делегаты V Всекитайского съезда Коммунистической партии Китая.
- Бывшие буддисты
- Генеральные секретари и председатели Коммунистической партии Китая
- Теоретики партизанской войны
- Выпускники Первого педагогического университета Хунани
- маоистские теоретики
- Члены VI ЦК Коммунистической партии Китая.
- Члены VII Политбюро Коммунистической партии Китая.
- Члены Постоянного комитета Политбюро Коммунистической партии Китая VIII созыва.
- Члены Постоянного комитета Политбюро Коммунистической партии Китая 9-го созыва.
- Члены Постоянного комитета Политбюро Коммунистической партии Китая 10-го созыва.
- Люди гражданской войны в Китае
- Люди холодной войны
- Люди культурной революции
- Люди с болезнью Паркинсона
- Политики Китайской Народной Республики из провинции Хунань
- Философы из провинции Хунань
- Поэты из провинции Хунань
- Политики из Сянтаня
- Политоубийцы
- Президенты Китайской Народной Республики
- Теоретики революции

