Древний Рим
Рим | |
|---|---|
| 753 г. до н.э. – 476/480 г. 1 ОБЪЯВЛЕНИЕ | |
| Девиз: Римский сенат и народ | |
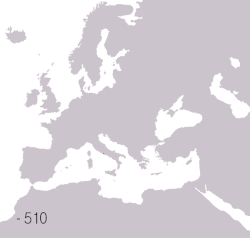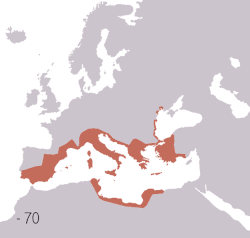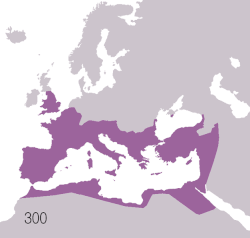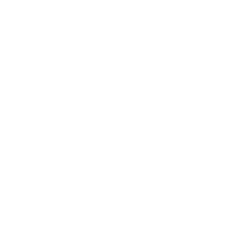 Территории римской цивилизации: | |
| Статус |
|
| Капитал | Рим (и другие страны поздней Империи, особенно Константинополь и Равенна ) |
| Общие языки | латинский |
| Правительство |
|
| Историческая эпоха | Древняя история |
| 753 г. до н. э. | |
| 509 г. до н.э. | |
• Октавиан провозгласил Августом | 27 г. до н.э. |
| 476/480 1 ОБЪЯВЛЕНИЕ | |
| |
В современной Древний историографии Рим — это римская цивилизация от основания итальянского города Рима в 8 веке до нашей эры до распада Западной Римской империи в 5 веке нашей эры. Он включает Римское королевство (753–509 до н. э.), Римскую республику (509–27 до н. э.) и Римскую империю (27 до н. э. – 476 г. н. э.) до падения Западной империи. [1] [а]
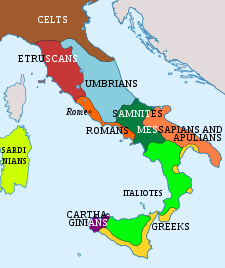
Древний Рим зародился как италийское поселение, традиционно датируемое 753 годом до нашей эры, на берегу реки Тибр на итальянском полуострове . Поселение превратилось в город и государство Рим и стало контролировать своих соседей благодаря сочетанию договоров и военной мощи. В конечном итоге оно контролировало Итальянский полуостров, ассимилируя греческую культуру южной Италии ( Великую Грецию ) и этрусскую культуру, а затем стало доминирующей державой в Средиземноморском регионе и некоторых частях Европы. На пике своего развития он контролировал побережье Северной Африки , Египет , Южную Европу и большую часть Западной Европы, Балканы , Крым и большую часть Ближнего Востока, включая Анатолию , Левант и части Месопотамии и Аравии . Эта империя была одной из крупнейших империй древнего мира, занимая около 5 миллионов квадратных километров (1,9 миллиона квадратных миль) в 117 году нашей эры. [2] с населением от 50 до 90 миллионов человек, что в то время составляло примерно 20% населения мира. [б] Римское государство превратилось из выборной монархии в классическую республику , а затем во все более автократическую военную диктатуру во времена Империи.
Древний Рим часто объединяют в классическую древность вместе с Древней Грецией , а их схожие культуры и общества известны как греко-римский мир . Древнеримская цивилизация внесла свой вклад в современный язык, религию, общество, технологии, право, политику, правительство, войну, искусство, литературу, архитектуру и инженерное дело. Рим повысил профессионализм и расширил свою армию и создал систему правления под названием res publica , вдохновившую современные республики, такие как Соединенные Штаты и Франция . [3] Он достиг впечатляющих технологических и архитектурных достижений, таких как строительство акведуков и дорог по всей империи , а также более грандиозных памятников и сооружений.
История
[ редактировать ]Ранняя Италия и основание Рима
[ редактировать ]Начинают появляться археологические свидетельства поселений вокруг Рима ок. 1000 г. до н.э. [4] Крупномасштабная организация появляется только c. 800 г. до н.э. , первые могилы в некрополе Эсквилинского холма , а также глиняно-деревянная стена у подножия Палатинского холма, датируемая серединой 8 века до н.э. Начиная с ц. В 650 году до нашей эры римляне начали осушать долину между Капитолийским и Палатинским холмами, где сегодня находится Римский форум . [5] К шестому веку до нашей эры римляне строили Храм Юпитера Оптимуса Максимуса на Капитолийском полуострове и расширялись до Бычьего форума, расположенного между Капитолийским и Авентинским холмами . [6]
У самих римлян был основополагающий миф , приписывающий свой город Ромулу и Рему , отпрыскам Марса и принцессе мифического города Альба-Лонга . [7] Сыновья, приговоренные к смертной казни, были спасены волком и вернулись, чтобы восстановить албанского короля и основать город. После спора Ромул убил Рема и стал единственным основателем города. Район его первоначального поселения на Палатинском холме позже стал известен как Roma Quadrata («Квадрат Рима»). Эта история датируется как минимум третьим веком, а более поздний римский антиквар Марк Теренций Варрон отнес основание города к 753 году до нашей эры. [8] Другая легенда, записанная греческим историком Дионисием Галикарнасским , гласит, что царевич Эней возглавил группу троянцев в морском путешествии, чтобы основать новую Трою после Троянской войны . Они высадились на берегу реки Тибр , и путешествующая с ними женщина, Рома, подожгла их корабли, чтобы они не смогли уйти снова. В ее честь назвали поселение. [9] Римский поэт Вергилий изложил эту легенду в своей классической эпической поэме « Энеида» , где троянскому царевичу Энею суждено основать новую Трою.

Королевство
[ редактировать ]
Литературные и археологические свидетельства ясно свидетельствуют о существовании царей в Риме, о чем свидетельствуют фрагментарные тексты VI века до нашей эры. [10] Спустя долгое время после отмены римской монархии рудиментарный rex Sacrorum сохранялся для выполнения прежних священнических функций монарха. Римляне считали, что их монархия была выборной, с семью легендарными королями, которые практически не были связаны кровным родством. [11]
Свидетельства римской экспансии очевидны в шестом веке до нашей эры; к концу Рим контролировал территорию площадью около 780 квадратных километров (300 квадратных миль) с населением, возможно, достигавшим 35 000 человек. [11] Дворец Регия был построен ок. 625 г. до н.э .; [11] римляне относили и создание своих первых народных организаций и Сената . К царственному периоду [12] Рим также начал расширять свой контроль над своими латинскими соседями. В то время как более поздние римские истории, такие как « Энеида», утверждали, что все латиняне произошли от главного героя Энея , [13] общая культура подтверждена археологически. [14] Подтвержденные взаимные права на брак и гражданство между латинскими городами - Jus Latii - наряду с общими религиозными праздниками, еще раз указывают на общую культуру. К концу VI века большая часть этой территории оказалась под властью римлян. [15]
Республика
[ редактировать ]К концу шестого века Рим и многие его итальянские соседи вступили в период турбулентности. Археологические данные свидетельствуют о некоторой степени крупномасштабной войны. [16] Согласно традиции и более поздним писателям, таким как Ливий , Римская республика была основана ок. 509 г. до н.э. , [17] когда последний из семи царей Рима, Тарквиний Гордый , был свергнут система, основанная на ежегодно избираемых магистратах и различных представительных собраниях. и была установлена [18] Конституция разделение устанавливает ряд сдержек и противовесов , а также властей . Самыми важными магистратами были два консула , которые вместе осуществляли исполнительную власть, такую как империум или военное командование. [19] Консулы должны были работать с Сенатом , который первоначально был консультативным советом высокопоставленной знати или патрициев , но рос в размерах и силе. [20]
Другие магистраты Республики включают трибунов , квесторов , эдилов , преторов и цензоров . [21] Первоначально магистратуры были доступны только патрициям , но позже были открыты для простых людей или плебеев . [22] Республиканские избирательные собрания включали comitia centuriata (центуриатное собрание), которое голосовало по вопросам войны и мира и избирало мужчин на наиболее важные должности, и comitia tributa (племенное собрание), которое избирало менее важные должности. [23]
В 4 веке до нашей эры Рим подвергся нападению галлов , которые теперь распространили свою власть на итальянском полуострове за пределы долины реки По и через Этрурию. 16 июля 390 г. до н. э. галльская армия под предводительством вождя племени Бренна разбила римлян в битве при Аллии и двинулась на Рим. Галлы разграбили и сожгли город, а затем в течение семи месяцев осадили Капитолийский холм, где забаррикадировались некоторые римляне. Затем галлы согласились дать римлянам мир в обмен на 1000 фунтов золота. [24] По более поздней легенде, римлянин, наблюдавший за взвешиванием, заметил, что галлы пользуются фальшивыми весами. Затем римляне взяли в руки оружие и разгромили галлов. Их победоносный полководец Камилл заметил: «Рим покупает свою свободу железом, а не золотом». [25]
Римляне постепенно подчинили себе другие народы итальянского полуострова, в том числе этрусков . [26] Последняя угроза римской гегемонии в Италии возникла, когда Тарент , крупная греческая колония, заручился помощью Пирра Эпирского в 281 г. до н. э., но и эта попытка провалилась. [27] [26] Римляне закрепили свои завоевания, основав римские колонии в стратегических районах, установив тем самым стабильный контроль над регионом. [26]
Пунические войны
[ редактировать ]

В III веке до нашей эры Рим столкнулся с новым и грозным противником: Карфагеном , другой крупной державой в Западном Средиземноморье. [29] Первая Пуническая война началась в 264 году до нашей эры, когда город Мессана обратился за помощью к Карфагену в своих конфликтах с Гиероном II Сиракузским . После заступничества карфагенцев Мессана попросил Рим изгнать карфагенян. Рим вступил в эту войну, потому что Сиракузы и Мессана находились слишком близко к недавно завоеванным греческим городам Южной Италии, и Карфаген теперь мог провести наступление через римскую территорию; наряду с этим Рим мог расширить свои владения и на Сицилию . [30]
Carthage was a maritime power, and the Roman lack of ships and naval experience made the path to the victory a long and difficult one for the Roman Republic. Despite this, after more than 20 years of war, Rome defeated Carthage and a peace treaty was signed. Among the reasons for the Second Punic War[31] was the subsequent war reparations Carthage acquiesced to at the end of the First Punic War.[32] Война началась с дерзкого вторжения в Испанию Ганнибала , который прошел через Испанию к итальянским Альпам , вызвав панику среди итальянских союзников Рима. Лучший способ победить цель Ганнибала — заставить итальянцев покинуть Рим — это задержать карфагенян с помощью партизанской войны на истощение — стратегии, предложенной Квинтом Фабием Максимом Веррукозом . Вторжение Ганнибала длилось более 16 лет, опустошая Италию, но в конечном итоге Карфаген потерпел поражение в решающей битве при Заме в октябре 202 г. до н. э.
More than a half century after these events, Carthage was humiliated and the Republic's focus now was only to the Hellenistic kingdoms of Greece and revolts in Hispania. However, Carthage, having paid the war indemnity, felt that its commitments and submission to Rome had ceased, a vision not shared by the Roman Senate. The Third Punic War began when Rome declared war against Carthage in 149 BC. Carthage resisted well at the first strike but could not withstand the attack of Scipio Aemilianus, who entirely destroyed the city, enslaved all the citizens and gained control of that region, which became the province of Africa. All these wars resulted in Rome's first overseas conquests (Sicily, Hispania and Africa) and the rise of Rome as a significant imperial power.[33]
Late Republic
[edit]After defeating the Macedonian and Seleucid Empires in the 2nd century BC, the Romans became the dominant people of the Mediterranean Sea.[34] The conquest of the Hellenistic kingdoms brought the Roman and Greek cultures in closer contact and the Roman elite, once rural, became cosmopolitan. At this time Rome was a consolidated empire—in the military view—and had no major enemies.
Foreign dominance led to internal strife. Senators became rich at the provinces' expense; soldiers, who were mostly small-scale farmers, were away from home longer and could not maintain their land; and the increased reliance on foreign slaves and the growth of latifundia reduced the availability of paid work.[35] Income from war booty, mercantilism in the new provinces, and tax farming created new economic opportunities for the wealthy, forming a new class of merchants, called the equestrians.[36] The lex Claudia forbade members of the Senate from engaging in commerce, so while the equestrians could theoretically join the Senate, they were severely restricted in political power.[36][37] The Senate squabbled perpetually, repeatedly blocked important land reforms and refused to give the equestrian class a larger say in the government.
Violent gangs of the urban unemployed, controlled by rival Senators, intimidated the electorate through violence. The situation came to a head in the late 2nd century BC under the Gracchi brothers, a pair of tribunes who attempted to pass land reform legislation that would redistribute the major patrician landholdings among the plebeians. Both brothers were killed and the Senate passed reforms reversing the Gracchi brother's actions.[38] This led to the growing divide of the plebeian groups (populares) and equestrian classes (optimates).
Gaius Marius soon become a leader of the Republic, holding the first of his seven consulships (an unprecedented number) in 107 BC by arguing that his former patron Quintus Caecilius Metellus Numidicus was not able to defeat and capture the Numidian king Jugurtha. Marius then started his military reform: in his recruitment to fight Jugurtha, he levied the very poor (an innovation), and many landless men entered the army. Marius was elected for five consecutive consulships from 104 to 100 BC, as Rome needed a military leader to defeat the Cimbri and the Teutones, who were threatening Rome. After Marius's retirement, Rome had a brief peace, during which the Italian socii ("allies" in Latin) requested Roman citizenship and voting rights. The reformist Marcus Livius Drusus supported their legal process but was assassinated, and the socii revolted against the Romans in the Social War. At one point both consuls were killed; Marius was appointed to command the army together with Lucius Julius Caesar and Lucius Cornelius Sulla.[39]
By the end of the Social War, Marius and Sulla were the premier military men in Rome and their partisans were in conflict, both sides jostling for power. In 88 BC, Sulla was elected for his first consulship and his first assignment was to defeat Mithridates VI of Pontus, whose intentions were to conquer the Eastern part of the Roman territories. However, Marius's partisans managed his installation to the military command, defying Sulla and the Senate. To consolidate his own power, Sulla conducted a surprising and illegal action: he marched to Rome with his legions, killing all those who showed support to Marius's cause. In the following year, 87 BC, Marius, who had fled at Sulla's march, returned to Rome while Sulla was campaigning in Greece. He seized power along with the consul Lucius Cornelius Cinna and killed the other consul, Gnaeus Octavius, achieving his seventh consulship. Marius and Cinna revenged their partisans by conducting a massacre.[39][40]
Marius died in 86 BC, due to age and poor health, just a few months after seizing power. Cinna exercised absolute power until his death in 84 BC. After returning from his Eastern campaigns, Sulla had a free path to reestablish his own power. In 83 BC he made his second march on Rome and began a time of terror: thousands of nobles, knights and senators were executed. Sulla held two dictatorships and one more consulship, which began the crisis and decline of Roman Republic.[39]
Caesar and the First Triumvirate
[edit]
In the mid-1st century BC, Roman politics were restless. Political divisions in Rome split into one of two groups, populares (who hoped for the support of the people) and optimates (the "best", who wanted to maintain exclusive aristocratic control). Sulla overthrew all populist leaders and his constitutional reforms removed powers (such as those of the tribune of the plebs) that had supported populist approaches. Meanwhile, social and economic stresses continued to build; Rome had become a metropolis with a super-rich aristocracy, debt-ridden aspirants, and a large proletariat often of impoverished farmers. The latter groups supported the Catilinarian conspiracy—a resounding failure since the consul Marcus Tullius Cicero quickly arrested and executed the main leaders.
Gaius Julius Caesar reconciled the two most powerful men in Rome: Marcus Licinius Crassus, who had financed much of his earlier career, and Crassus' rival, Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (anglicised as Pompey), to whom he married his daughter. He formed them into a new informal alliance including himself, the First Triumvirate ("three men"). Caesar's daughter died in childbirth in 54 BC, and in 53 BC, Crassus invaded Parthia and was killed in the Battle of Carrhae; the Triumvirate disintegrated. Caesar conquered Gaul, obtained immense wealth, respect in Rome and the loyalty of battle-hardened legions. He became a threat to Pompey and was loathed by many optimates. Confident that Caesar could be stopped by legal means, Pompey's party tried to strip Caesar of his legions, a prelude to Caesar's trial, impoverishment, and exile.
To avoid this fate, Caesar crossed the Rubicon River and invaded Rome in 49 BC. The Battle of Pharsalus was a brilliant victory for Caesar and in this and other campaigns, he destroyed all of the optimates leaders: Metellus Scipio, Cato the Younger, and Pompey's son, Gnaeus Pompeius. Pompey was murdered in Egypt in 48 BC. Caesar was now pre-eminent over Rome: in five years he held four consulships, two ordinary dictatorships, and two special dictatorships, one for perpetuity. He was murdered in 44 BC, on the Ides of March by the Liberatores.[41]
Octavian and the Second Triumvirate
[edit]Caesar's assassination caused political and social turmoil in Rome; the city was ruled by his friend and colleague, Marcus Antonius. Soon afterward, Octavius, whom Caesar adopted through his will, arrived in Rome. Octavian (historians regard Octavius as Octavian due to the Roman naming conventions) tried to align himself with the Caesarian faction. In 43 BC, along with Antony and Marcus Aemilius Lepidus, Caesar's best friend,[42] he legally established the Second Triumvirate. Upon its formation, 130–300 senators were executed, and their property was confiscated, due to their supposed support for the Liberatores.[43]
In 42 BC, the Senate deified Caesar as Divus Iulius; Octavian thus became Divi filius,[44] the son of the deified. In the same year, Octavian and Antony defeated both Caesar's assassins and the leaders of the Liberatores, Marcus Junius Brutus and Gaius Cassius Longinus, in the Battle of Philippi. The Second Triumvirate was marked by the proscriptions of many senators and equites: after a revolt led by Antony's brother Lucius Antonius, more than 300 senators and equites involved were executed, although Lucius was spared.[45]
The Triumvirate divided the Empire among the triumvirs: Lepidus was given charge of Africa, Antony, the eastern provinces, and Octavian remained in Italia and controlled Hispania and Gaul. The Second Triumvirate expired in 38 BC but was renewed for five more years. However, the relationship between Octavian and Antony had deteriorated, and Lepidus was forced to retire in 36 BC after betraying Octavian in Sicily. By the end of the Triumvirate, Antony was living in Ptolemaic Egypt, ruled by his lover, Cleopatra VII. Antony's affair with Cleopatra was seen as an act of treason, since she was queen of another country. Additionally, Antony adopted a lifestyle considered too extravagant and Hellenistic for a Roman statesman.[46] Following Antony's Donations of Alexandria, which gave to Cleopatra the title of "Queen of Kings", and to Antony's and Cleopatra's children the regal titles to the newly conquered Eastern territories, war between Octavian and Antony broke out. Octavian annihilated Egyptian forces in the Battle of Actium in 31 BC. Antony and Cleopatra committed suicide. Now Egypt was conquered by the Roman Empire.
Empire – the Principate
[edit]
In 27 BC and at the age of 36, Octavian was the sole Roman leader. In that year, he took the name Augustus. That event is usually taken by historians as the beginning of Roman Empire. Officially, the government was republican, but Augustus assumed absolute powers.[47] His reform of the government brought about a two-century period colloquially referred to by Romans as the Pax Romana.
Julio-Claudian dynasty
[edit]The Julio-Claudian dynasty was established by Augustus. The emperors of this dynasty were Augustus, Tiberius, Caligula, Claudius and Nero. The Julio-Claudians started the destruction of republican values, but on the other hand, they boosted Rome's status as the central power in the Mediterranean region.[48] While Caligula and Nero are usually remembered in popular culture as dysfunctional emperors, Augustus and Claudius are remembered as successful in politics and the military. This dynasty instituted imperial tradition in Rome[49] and frustrated any attempt to reestablish a Republic.[50]
Augustus (r. 27 BC – AD 14) gathered almost all the republican powers under his official title, princeps, and diminished the political influence of the senatorial class by boosting the equestrian class. The senators lost their right to rule certain provinces, like Egypt, since the governor of that province was directly nominated by the emperor. The creation of the Praetorian Guard and his reforms in the military, creating a standing army with a fixed size of 28 legions, ensured his total control over the army.[51] Compared with the Second Triumvirate's epoch, Augustus' reign as princeps was very peaceful, which led the people and the nobles of Rome to support Augustus, increasing his strength in political affairs.[52] His generals were responsible for the field command; gaining such commanders as Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa, Nero Claudius Drusus and Germanicus much respect from the populace and the legions. Augustus intended to extend the Roman Empire to the whole known world, and in his reign, Rome conquered Cantabria, Aquitania, Raetia, Dalmatia, Illyricum and Pannonia.[53]Under Augustus' reign, Roman literature grew steadily in what is known as the Golden Age of Latin Literature. Poets like Virgil, Horace, Ovid and Rufus developed a rich literature, and were close friends of Augustus. Along with Maecenas, he sponsored patriotic poems, such as Virgil's epic Aeneid and historiographical works, as well as those of Livy. Augustus continued the changes to the calendar promoted by Caesar, and the month of August is named after him.[54] Augustus brought a peaceful and thriving era to Rome, known as Pax Augusta or Pax Romana. Augustus died in 14 AD, but the empire's glory continued after his era.
The Julio-Claudians continued to rule Rome after Augustus' death and remained in power until the death of Nero in 68 AD.[55] Influenced by his wife, Livia Drusilla, Augustus appointed her son from another marriage, Tiberius, as his heir.[56] The Senate agreed with the succession, and granted to Tiberius the same titles and honours once granted to Augustus: the title of princeps and Pater patriae, and the Civic Crown. However, Tiberius was not an enthusiast for political affairs: after agreement with the Senate, he retired to Capri in 26 AD,[57] and left control of the city of Rome in the hands of the praetorian prefect Sejanus (until 31 AD) and Macro (from 31 to 37 AD).
Tiberius died (or was killed)[58] in 37 AD. The male line of the Julio-Claudians was limited to Tiberius' nephew Claudius, his grandson Tiberius Gemellus and his grand-nephew Caligula. As Gemellus was still a child, Caligula was chosen to rule the empire. He was a popular leader in the first half of his reign, but became a crude and insane tyrant in his years controlling government.[59] The Praetorian Guard murdered Caligula four years after the death of Tiberius,[60] and, with belated support from the senators, proclaimed his uncle Claudius as the new emperor.[61] Claudius was not as authoritarian as Tiberius and Caligula. Claudius conquered Lycia and Thrace; his most important deed was the beginning of the conquest of Britannia.[62] Claudius was poisoned by his wife, Agrippina the Younger in 54 AD.[63] His heir was Nero, son of Agrippina and her former husband, since Claudius' son Britannicus had not reached manhood upon his father's death.
Nero sent his general, Suetonius Paulinus, to invade modern-day Wales, where he encountered stiff resistance. The Celts there were independent, tough, resistant to tax collectors, and fought Paulinus as he battled his way across from east to west. It took him a long time to reach the north west coast, and in 60 AD he finally crossed the Menai Strait to the sacred island of Mona (Anglesey), the last stronghold of the druids.[64] His soldiers attacked the island and massacred the druids: men, women and children,[65] destroyed the shrine and the sacred groves and threw many of the sacred standing stones into the sea. While Paulinus and his troops were massacring druids in Mona, the tribes of modern-day East Anglia staged a revolt led by queen Boadicea of the Iceni.[66] The rebels sacked and burned Camulodunum, Londinium and Verulamium (modern-day Colchester, London and St Albans respectively) before they were crushed by Paulinus.[67] Boadicea, like Cleopatra before her, committed suicide to avoid the disgrace of being paraded in triumph in Rome.[68] Nero is widely known as the first persecutor of Christians and for the Great Fire of Rome, rumoured to have been started by the emperor himself.[69] A conspiracy against Nero in 65 AD under Calpurnius Piso failed, but in 68 AD the armies under Julius Vindex in Gaul and Servius Sulpicius Galba in modern-day Spain revolted. Deserted by the Praetorian Guards and condemned to death by the senate, Nero killed himself.[70]
As Roman provinces were being established throughout the Mediterranean, Italy maintained a special status which made it domina provinciarum ("ruler of the provinces"),[71][72][73] and – especially in relation to the first centuries of imperial stability – rectrix mundi ("governor of the world")[74][75] and omnium terrarum parens ("parent of all lands").[76][77]
Flavian dynasty
[edit]
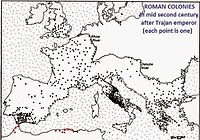
The Flavians were the second dynasty to rule Rome.[78] By 68 AD, the year of Nero's death, there was no chance of a return to the Roman Republic, and so a new emperor had to arise. After the turmoil in the Year of the Four Emperors, Titus Flavius Vespasianus (anglicised as Vespasian) took control of the empire and established a new dynasty. Under the Flavians, Rome continued its expansion, and the state remained secure.[79] Under Trajan, the Roman Empire reached the peak of its territorial expansion.[80] Rome's dominion now spanned 5.0 million square kilometres (1.9 million square miles).[2]
The most significant military campaign undertaken during the Flavian period was the siege and destruction of Jerusalem in 70 AD by Titus. The destruction of the city was the culmination of the Roman campaign in Judea following the Jewish uprising of 66 AD. The Second Temple was completely demolished, after which Titus' soldiers proclaimed him imperator in honour of the victory. Jerusalem was sacked and much of the population killed or dispersed. Josephus claims that 1,100,000 people were killed during the siege, of whom a majority were Jewish.[81] 97,000 were captured and enslaved, including Simon bar Giora and John of Giscala. Many fled to areas around the Mediterranean.
Vespasian was a general under Claudius and Nero and fought as a commander in the First Jewish-Roman War. Following the turmoil of the Year of the Four Emperors, in 69 AD, four emperors were enthroned in turn: Galba, Otho, Vitellius, and, lastly, Vespasian, who crushed Vitellius' forces and became emperor.[82] He reconstructed many buildings which were uncompleted, like a statue of Apollo and the temple of Divus Claudius ("the deified Claudius"), both initiated by Nero. Buildings destroyed by the Great Fire of Rome were rebuilt, and he revitalised the Capitol. Vespasian started the construction of the Flavian Amphitheater, commonly known as the Colosseum.[82] The historians Josephus and Pliny the Elder wrote their works during Vespasian's reign. Vespasian was Josephus' sponsor and Pliny dedicated his Naturalis Historia to Titus, son of Vespasian. Vespasian sent legions to defend the eastern frontier in Cappadocia, extended the occupation in Britannia (modern-day England, Wales and southern Scotland) and reformed the tax system. He died in 79 AD.
Titus became emperor in 79. He finished the Flavian Amphitheater, using war spoils from the First Jewish-Roman War, and hosted victory games that lasted for a hundred days. These games included gladiatorial combats, horse races and a sensational mock naval battle on the flooded grounds of the Colosseum.[83] Titus died of fever in 81 AD, and was succeeded by his brother Domitian. As emperor, Domitian showed the characteristics of a tyrant.[84] He ruled for fifteen years, during which time he acquired a reputation for self-promotion as a living god. He constructed at least two temples in honour of Jupiter, the supreme deity in Roman religion.[85] He was murdered following a plot within his own household.
Nerva–Antonine dynasty
[edit]
Following Domitian's murder, the Senate rapidly appointed Nerva as Emperor. Nerva had noble ancestry, and he had served as an advisor to Nero and the Flavians. His rule restored many of the traditional liberties of Rome's upper classes, which Domitian had over-ridden.[86] The Nerva–Antonine dynasty from 96 AD to 192 AD included the "five good emperors" Nerva, Trajan, Hadrian, Antoninus Pius and Marcus Aurelius. Trajan, Hadrian, Antoninus Pius and Marcus Aurelius were part of Italic families settled in Roman colonies outside of Italy: the families of Trajan and Hadrian had settled in Italica (Hispania Baetica), that of Antoninus Pius in Colonia Agusta Nemausensis (Gallia Narbonensis), and that of Marcus Aurelius in Colonia Claritas Iulia Ucubi (Hispania Baetica). The Nerva-Antonine dynasty came to an end with Commodus, son of Marcus Aurelius.[87]
Nerva abdicated and died in 98 AD, and was succeeded by the general Trajan. Trajan is credited with the restoration of traditional privileges and rights of commoner and senatorial classes, which later Roman historians claim to have been eroded during Domitian's autocracy.[88] Trajan fought three Dacian wars, winning territories roughly equivalent to modern-day Romania and Moldova. He undertook an ambitious public building program in Rome, including Trajan's Forum, Trajan's Market and Trajan's Column, with the architect Apollodorus of Damascus. He remodelled the Pantheon and extended the Circus Maximus.[89] When Parthia appointed a king for Armenia without consulting Rome, Trajan declared war on Parthia and deposed the king of Armenia. In 115 he took the Northern Mesopotamian cities of Nisibis and Batnae, organised a province of Mesopotamia (116), and issued coins that claimed Armenia and Mesopotamia were under the authority of the Roman people.[90] In that same year, he captured Seleucia and the Parthian capital Ctesiphon (near modern Baghdad).[91] After defeating a Parthian revolt and a Jewish revolt, he withdrew due to health issues, and in 117, he died of edema.

Trajan's successor Hadrian withdrew all the troops stationed in Parthia, Armenia and Mesopotamia (modern-day Iraq), abandoning Trajan's conquests. Hadrian's army crushed a revolt in Mauretania and the Bar Kokhba revolt in Judea. This was the last large-scale Jewish revolt against the Romans, and was suppressed with massive repercussions in Judea. Hundreds of thousands of Jews were killed. Hadrian renamed the province of Judea "Provincia Syria Palaestina", after one of Judea's most hated enemies.[92] He constructed fortifications and walls, like the celebrated Hadrian's Wall which separated Roman Britannia and the tribes of modern-day Scotland. Hadrian promoted culture, especially the Greek. He forbade torture and humanised the laws. His many building projects included aqueducts, baths, libraries and theatres; additionally, he travelled nearly every province in the Empire to review military and infrastructural conditions.[93] Following Hadrian's death in 138 AD, his successor Antoninus Pius built temples, theatres, and mausoleums, promoted the arts and sciences, and bestowed honours and financial rewards upon the teachers of rhetoric and philosophy. On becoming emperor, Antoninus made few initial changes, leaving intact as far as possible the arrangements instituted by his predecessor. Antoninus expanded Roman Britannia by invading what is now southern Scotland and building the Antonine Wall.[94] He also continued Hadrian's policy of humanising the laws. He died in 161 AD.

Marcus Aurelius, known as the Philosopher, was the last of the Five Good Emperors. He was a stoic philosopher and wrote the Meditations. He defeated barbarian tribes in the Marcomannic Wars as well as the Parthian Empire.[95] His co-emperor, Lucius Verus, died in 169 AD, probably from the Antonine Plague, a pandemic that killed nearly five million people through the Empire in 165–180 AD.[96]
From Nerva to Marcus Aurelius, the empire achieved an unprecedented status. The powerful influence of laws and manners had gradually cemented the union of the provinces. All the citizens enjoyed and abused the advantages of wealth. The image of a free constitution was preserved with decent reverence. The Roman senate appeared to possess the sovereign authority, and devolved on the emperors all the executive powers of government. Gibbon declared the rule of these "Five Good Emperors" the golden era of the Empire.[97] During this time, Rome reached its greatest territorial extent.[98]
Commodus, son of Marcus Aurelius, became emperor after his father's death. He is not counted as one of the Five Good Emperors, due to his direct kinship with the latter emperor; in addition, he was militarily passive. Cassius Dio identifies his reign as the beginning of Roman decadence: "(Rome has transformed) from a kingdom of gold to one of iron and rust."[95]
Severan dynasty
[edit]Commodus was killed by a conspiracy involving Quintus Aemilius Laetus and his wife Marcia in late 192 AD. The following year is known as the Year of the Five Emperors, during which Helvius Pertinax, Didius Julianus, Pescennius Niger, Clodius Albinus and Septimius Severus held the imperial dignity. Pertinax, a member of the senate who had been one of Marcus Aurelius's right-hand men, was the choice of Laetus, and he ruled vigorously and judiciously. Laetus soon became jealous and instigated Pertinax's murder by the Praetorian Guard, who then auctioned the empire to the highest bidder, Didius Julianus, for 25,000 sesterces per man.[99] The people of Rome were appalled and appealed to the frontier legions to save them. The legions of three frontier provinces—Britannia, Pannonia Superior, and Syria—resented being excluded from the "donative" and replied by declaring their individual generals to be emperor. Lucius Septimius Severus Geta, the Pannonian commander, bribed the opposing forces, pardoned the Praetorian Guards and installed himself as emperor. He and his successors governed with the legions' support. The changes on coinage and military expenditures were the root of the financial crisis that marked the Crisis of the Third Century.

Severus was enthroned after invading Rome and having Didius Julianus killed. Severus attempted to revive totalitarianism and, addressing the Roman people and Senate, praised the severity and cruelty of Marius and Sulla, which worried the senators.[100] When Parthia invaded Roman territory, Severus successfully waged war against that country. Notwithstanding this military success, Severus failed in invading Hatra, a rich Arabian city. Severus killed his legate, who was gaining respect from the legions; and his soldiers fell victim to famine. After this disastrous campaign, he withdrew.[101] Severus also intended to vanquish the whole of Britannia. To achieve this, he waged war against the Caledonians. After many casualties in the army due to the terrain and the barbarians' ambushes, Severus himself went to the field. However, he became ill and died in 211 AD, at the age of 65.

Upon the death of Severus, his sons Caracalla and Geta were made emperors. Caracalla had his brother, a youth, assassinated in his mother's arms, and may have murdered 20,000 of Geta's followers. Like his father, Caracalla was warlike. He continued Severus' policy and gained respect from the legions. Knowing that the citizens of Alexandria disliked him and were denigrating his character, Caracalla served a banquet for its notable citizens, after which his soldiers killed all the guests. From the security of the temple of Sarapis, he then directed an indiscriminate slaughter of Alexandria's people.[102] In 212, he issued the Edict of Caracalla, giving full Roman citizenship to all free men living in the Empire, with the exception of the dediticii, people who had become subject to Rome through surrender in war, and freed slaves.[103]
Mary Beard points to the edict as a fundamental turning point, after which Rome was "effectively a new state masquerading under an old name".[104]
Macrinus conspired to have Caracalla assassinated by one of his soldiers during a pilgrimage to the Temple of the Moon in Carrhae, in 217 AD. Macrinus assumed power, but soon removed himself from Rome to the east and Antioch. His brief reign ended in 218, when the youngster Bassianus, high priest of the temple of the Sun at Emesa, and supposedly illegitimate son of Caracalla, was declared Emperor by the disaffected soldiers of Macrinus. He adopted the name of Antoninus but history has named him after his Sun god Elagabalus, represented on Earth in the form of a large black stone. An incompetent and lascivious ruler,[105] Elagabalus offended all but his favourites. Cassius Dio, Herodian and the Historia Augusta give many accounts of his notorious extravagance. Elagabalus adopted his cousin Severus Alexander, as Caesar, but subsequently grew jealous and attempted to assassinate him. However, the Praetorian guard preferred Alexander, murdered Elagabalus, dragged his mutilated corpse through the streets of Rome, and threw it into the Tiber. Severus Alexander then succeeded him. Alexander waged war against many foes, including the revitalised Persia and also the Germanic peoples, who invaded Gaul. His losses generated dissatisfaction among his soldiers, and some of them murdered him during his Germanic campaign in 235 AD.[106]
Crisis of the Third Century
[edit]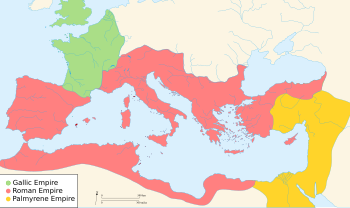
A disastrous scenario emerged after the death of Alexander Severus: the Roman state was plagued by civil wars, external invasions, political chaos, pandemics and economic depression.[107] The old Roman values had fallen, and Mithraism and Christianity had begun to spread through the populace. Emperors were no longer men linked with nobility; they usually were born in lower-classes of distant parts of the Empire. These men rose to prominence through military ranks, and became emperors through civil wars.
There were 26 emperors in a 49-year period, a signal of political instability. Maximinus Thrax was the first ruler of that time, governing for just three years. Others ruled just for a few months, like Gordian I, Gordian II, Balbinus and Hostilian. The population and the frontiers were abandoned, since the emperors were mostly concerned with defeating rivals and establishing their power. The economy also suffered: massive military expenditures from the Severi caused a devaluation of Roman coins. Hyperinflation came at this time as well. The Plague of Cyprian broke out in 250 and killed a huge portion of the population.[108] In 260 AD, the provinces of Syria Palaestina, Asia Minor and Egypt separated from the rest of the Roman state to form the Palmyrene Empire, ruled by Queen Zenobia and centered on Palmyra. In that same year the Gallic Empire was created by Postumus, retaining Britannia and Gaul.[109] These countries separated from Rome after the capture of emperor Valerian by the Sassanids of Persia, the first Roman ruler to be captured by his enemies; it was a humiliating fact for the Romans.[108] The crisis began to recede during the reigns of Claudius Gothicus (268–270), who defeated the Gothic invaders, and Aurelian (271–275), who reconquered both the Gallic and Palmyrene Empires.[110] The crisis was overcome during the reign of Diocletian.
Empire – The Tetrarchy
[edit]Diocletian
[edit]
In 284 AD, Diocletian was hailed as Imperator by the eastern army. Diocletian healed the empire from the crisis, by political and economic shifts. A new form of government was established: the Tetrarchy. The Empire was divided among four emperors, two in the West and two in the East. The first tetrarchs were Diocletian (in the East), Maximian (in the West), and two junior emperors, Galerius (in the East) and Flavius Constantius (in the West). To adjust the economy, Diocletian made several tax reforms.[111]
Diocletian expelled the Persians who plundered Syria and conquered some barbarian tribes with Maximian. He adopted many behaviours of Eastern monarchs. Anyone in the presence of the emperor had now to prostrate himself—a common act in the East, but never practised in Rome before.[112] Diocletian did not use a disguised form of Republic, as the other emperors since Augustus had done.[113] Between 290 and 330, half a dozen new capitals had been established by the members of the Tetrarchy, officially or not: Antioch, Nicomedia, Thessalonike, Sirmium, Milan, and Trier.[114] Diocletian was also responsible for a significant Christian persecution. In 303 he and Galerius started the persecution and ordered the destruction of all the Christian churches and scripts and forbade Christian worship.[115] Diocletian abdicated in 305 AD together with Maximian, thus, he was the first Roman emperor to resign. His reign ended the traditional form of imperial rule, the Principate (from princeps) and started the Tetrarchy.

Constantine and Christianity
[edit]Constantine assumed the empire as a tetrarch in 306. He conducted many wars against the other tetrarchs. Firstly he defeated Maxentius in 312. In 313, he issued the Edict of Milan, which granted liberty for Christians to profess their religion.[116] Constantine was converted to Christianity, enforcing the Christian faith. He began the Christianization of the Empire and of Europe—a process concluded by the Catholic Church in the Middle Ages. He was defeated by the Franks and the Alamanni during 306–308. In 324 he defeated another tetrarch, Licinius, and controlled all the empire, as it was before Diocletian. To celebrate his victories and Christianity's relevance, he rebuilt Byzantium and renamed it Nova Roma ("New Rome"); but the city soon gained the informal name of Constantinople ("City of Constantine").[117]
The reign of Julian, who under the influence of his adviser Mardonius attempted to restore Classical Roman and Hellenistic religion, only briefly interrupted the succession of Christian emperors. Constantinople served as a new capital for the Empire. In fact, Rome had lost its central importance since the Crisis of the Third Century—Mediolanum was the western capital from 286 to 330, until the reign of Honorius, when Ravenna was made capital, in the 5th century.[118] Constantine's administrative and monetary reforms, that reunited the Empire under one emperor, and rebuilt the city of Byzantium, as Constantinopolis Nova Roma, changed the high period of the ancient world.
Fall of the Western Roman Empire
[edit]In the late 4th and 5th centuries the Western Empire entered a critical stage which terminated with the fall of the Western Roman Empire.[119] Under the last emperors of the Constantinian dynasty and the Valentinianic dynasty, Rome lost decisive battles against the Sasanian Empire and Germanic barbarians: in 363, emperor Julian the Apostate was killed in the Battle of Samarra, against the Persians and the Battle of Adrianople cost the life of emperor Valens (364–378); the victorious Goths were never expelled from the Empire nor assimilated.[120] The next emperor, Theodosius I (379–395), gave even more force to the Christian faith, and after his death, the Empire was divided into the Eastern Roman Empire, ruled by Arcadius and the Western Roman Empire, commanded by Honorius, both of which were Theodosius' sons.[121]
The situation became more critical in 408, after the death of Stilicho, a general who tried to reunite the Empire and repel barbarian invasion in the early years of the 5th century. The professional field army collapsed. In 410, the Theodosian dynasty saw the Visigoths sack Rome.[122] During the 5th century, the Western Empire experienced a significant reduction of its territory. The Vandals conquered North Africa, the Visigoths claimed the southern part of Gaul, Gallaecia was taken by the Suebi, Britannia was abandoned by the central government, and the Empire suffered further from the invasions of Attila, chief of the Huns.[123] General Orestes refused to meet the demands of the barbarian "allies" who now formed the army, and tried to expel them from Italy. Unhappy with this, their chieftain Odoacer defeated and killed Orestes, invaded Ravenna and dethroned Romulus Augustus, son of Orestes. This event of 476, usually marks the end of Classical antiquity and beginning of the Middle Ages.[124] The Roman noble and former emperor Julius Nepos continued to rule as emperor from Dalmatia even after the deposition of Romulus Augustus until his death in 480. Some historians consider him to be the last emperor of the Western Empire instead of Romulus Augustus.[125]
After 1200 years of independence and nearly 700 years as a great power, the rule of Rome in the West ended.[126] Various reasons for Rome's fall have been proposed ever since, including loss of Republicanism, moral decay, military tyranny, class war, slavery, economic stagnation, environmental change, disease, the decline of the Roman race, as well as the inevitable ebb and flow that all civilisations experience.The Eastern Empire survived for almost 1000 years after the fall of its Western counterpart and became the most stable Christian realm during the Middle Ages. During the 6th century, Justinian reconquered the Italian peninsula from the Ostrogoths, North Africa from the Vandals, and southern Hispania from the Visigoths. But within a few years of Justinian's death, Eastern Roman (Byzantine) possessions in Italy were greatly reduced by the Lombards who settled in the peninsula.[127] In the east, partially due to the weakening effect of the Plague of Justinian as well as a series of mutually destructive wars against the Persian Sassanian Empire, the Byzantine Romans were threatened by the rise of Islam. Its followers rapidly brought about the conquest of the Levant, the conquest of Armenia and the conquest of Egypt during the Arab–Byzantine wars, and soon presented a direct threat to Constantinople.[128][129] In the following century, the Arabs captured southern Italy and Sicily.[130] In the west, Slavic populations penetrated deep into the Balkans.
The Byzantine Romans, however, managed to stop further Islamic expansion into their lands during the 8th century and, beginning in the 9th century, reclaimed parts of the conquered lands.[128][131] In 1000 AD, the Eastern Empire was at its height: Basil II reconquered Bulgaria and Armenia, and culture and trade flourished.[132] However, soon after, this expansion was abruptly stopped in 1071 with the Byzantine defeat in the Battle of Manzikert. The aftermath of this battle sent the empire into a protracted period of decline. Two decades of internal strife and Turkic invasions ultimately led Emperor Alexios I Komnenos to send a call for help to the Western European kingdoms in 1095.[128] The West responded with the Crusades, eventually resulting in the Sack of Constantinople by participants of the Fourth Crusade. The conquest of Constantinople in 1204 fragmented what remained of the Empire into successor states; the ultimate victor was the Empire of Nicaea.[133] After the recapture of Constantinople by Imperial forces, the Empire was little more than a Greek state confined to the Aegean coast. The Eastern Roman (Byzantine) Empire collapsed when Mehmed the Conqueror conquered Constantinople on 29 May 1453.[134]
Society
[edit]
The imperial city of Rome was the largest urban center in the empire, with a population variously estimated from 450,000 to close to one million.[135] Around 20 per cent of the population under jurisdiction of ancient Rome (25–40%, depending on the standards used, in Roman Italy)[136] lived in innumerable urban centers, with population of 10,000 and more and several military settlements, a very high rate of urbanisation by pre-industrial standards. Most of those centers had a forum, temples, and other buildings similar to Rome's. The average life expectancy in the Middle Empire was about 26–28 years.[137][138]
Law
[edit]The roots of the legal principles and practices of the ancient Romans may be traced to the Law of the Twelve Tables promulgated in 449 BC and to the codification of law issued by order of Emperor Justinian I around 530 AD (see Corpus Juris Civilis). Roman law as preserved in Justinian's codes continued into the Byzantine Roman Empire, and formed the basis of similar codifications in continental Western Europe. Roman law continued, in a broader sense, to be applied throughout most of Europe until the end of the 17th century.
The major divisions of the law of ancient Rome, as contained within the Justinian and Theodosian law codes, consisted of Jus civile, Jus gentium, and Jus naturale. The Jus civile ("Citizen Law") was the body of common laws that applied to Roman citizens.[139] The praetores urbani (sg. Praetor Urbanus) were the people who had jurisdiction over cases involving citizens. The Jus gentium ("Law of nations") was the body of common laws that applied to foreigners, and their dealings with Roman citizens.[140] The praetores peregrini (sg. Praetor Peregrinus) were the people who had jurisdiction over cases involving citizens and foreigners. Jus naturale encompassed natural law, the body of laws that were considered common to all beings.
Class structure
[edit]
Roman society is largely viewed as hierarchical, with slaves (servi) at the bottom, freedmen (liberti) above them, and free-born citizens (cives) at the top. Free citizens were subdivided by class. The broadest, and earliest, division was between the patricians, who could trace their ancestry to one of the 100 patriarchs at the founding of the city, and the plebeians, who could not. This became less important in the later Republic, as some plebeian families became wealthy and entered politics, and some patrician families fell economically. Anyone, patrician or plebeian, who could count a consul as his ancestor was a noble (nobilis); a man who was the first of his family to hold the consulship, such as Marius or Cicero, was known as a novus homo ("new man") and ennobled his descendants. Patrician ancestry, however, still conferred considerable prestige, and many religious offices remained restricted to patricians.
A class division originally based on military service became more important. Membership of these classes was determined periodically by the censors, according to property. The wealthiest were the Senatorial class, who dominated politics and command of the army. Next came the equestrians (equites, sometimes translated "knights"), originally those who could afford a warhorse, and who formed a powerful mercantile class. Several further classes, originally based on the military equipment their members could afford, followed, with the proletarii, citizens who had no property other than their children, at the bottom. Before the reforms of Marius they were ineligible for military service and are often described as being just above freed slaves in wealth and prestige.
Voting power in the Republic depended on class. Citizens were enrolled in voting "tribes", but the tribes of the richer classes had fewer members than the poorer ones, all the proletarii being enrolled in a single tribe. Voting was done in class order, from top down, and stopped as soon as most of the tribes had been reached, so the poorer classes were often unable to cast their votes.
Women in ancient Rome shared some basic rights with their male counterparts, but were not fully regarded as citizens and were thus not allowed to vote or take part in politics. At the same time the limited rights of women were gradually expanded (due to emancipation) and women reached freedom from pater familias, gained property rights and even had more juridical rights than their husbands, but still no voting rights, and were absent from politics.[141]
Allied foreign cities were often given the Latin Rights, an intermediary level between full citizens and foreigners (peregrini), which gave their citizens rights under Roman law and allowed their leading magistrates to become full Roman citizens. While there were varying degrees of Latin rights, the main division was between those cum suffragio ("with vote"; enrolled in a Roman tribe and able to take part in the comitia tributa) and sine suffragio ("without vote"; could not take part in Roman politics). Most of Rome's Italian allies were given full citizenship after the Social War of 91–88 BC, and full Roman citizenship was extended to all free-born men in the Empire by Caracalla in 212, with the exception of the dediticii, people who had become subject to Rome through surrender in war, and freed slaves.[103]
Education
[edit]
In the early Republic, there were no public schools, so boys were taught to read and write by their parents, or by educated slaves, called paedagogi, usually of Greek origin.[142][143][144] The primary aim of education during this period was to train young men in agriculture, warfare, Roman traditions, and public affairs.[142] Young boys learned much about civic life by accompanying their fathers to religious and political functions, including the Senate for the sons of nobles.[143] The sons of nobles were apprenticed to a prominent political figure at the age of 16, and campaigned with the army from the age of 17.[143] Educational practices were modified after the conquest of the Hellenistic kingdoms in the 3rd century BC and the resulting Greek influence, although Roman educational practices were still much different from Greek ones.[143][145] If their parents could afford it, boys and some girls at the age of 7 were sent to a private school outside the home called a ludus, where a teacher (called a litterator or a magister ludi, and often of Greek origin) taught them basic reading, writing, arithmetic, and sometimes Greek, until the age of 11.[143][144][146]
Beginning at age 12, students went to secondary schools, where the teacher (now called a grammaticus) taught them about Greek and Roman literature.[143][146] At the age of 16, some students went on to rhetoric school (where the teacher, usually Greek, was called a rhetor).[143][146] Education at this level prepared students for legal careers, and required that the students memorise the laws of Rome.[143]
Government
[edit]Initially, Rome was ruled by kings, who were elected from each of Rome's major tribes in turn.[147] The exact nature of the king's power is uncertain. He may have held near-absolute power, or may have merely been the chief executive of the Senate and the people. In military matters, the king's authority (Imperium) was likely absolute. He was also the head of the state religion. In addition to the authority of the King, there were three administrative assemblies: the Senate, which acted as an advisory body for the King; the Comitia Curiata, which could endorse and ratify laws suggested by the King; and the Comitia Calata, which was an assembly of the priestly college that could assemble the people to bear witness to certain acts, hear proclamations, and declare the feast and holiday schedule for the next month.

The class struggles of the Roman Republic resulted in an unusual mixture of democracy and oligarchy. The word republic comes from the Latin res publica, which literally translates to "public business". Roman laws traditionally could only be passed by a vote of the Popular assembly (Comitia Tributa). Likewise, candidates for public positions had to run for election by the people. However, the Roman Senate represented an oligarchic institution, which acted as an advisory body.
In the Republic, the Senate held actual authority (auctoritas), but no real legislative power; it was technically only an advisory council. However, as the Senators were individually very influential, it was difficult to accomplish anything against the collective will of the Senate. New senators were chosen from among the most accomplished patricians by censors (Censura), who could also remove a senator from his office if he was found "morally corrupt"; a charge that could include bribery or, as under Cato the Elder, embracing one's wife in public. Later, under the reforms of the dictator Sulla, quaestors were made automatic members of the Senate, though most of his reforms did not survive.
The Republic had no fixed bureaucracy, and collected taxes through the practice of tax farming. Government positions such as quaestor, aedile, or praefect were funded by the office-holder. To prevent any citizen from gaining too much power, new magistrates were elected annually and had to share power with a colleague. For example, under normal conditions, the highest authority was held by two consuls. In an emergency, a temporary dictator could be appointed. Throughout the Republic, the administrative system was revised several times to comply with new demands. In the end, it proved inefficient for controlling the ever-expanding dominion of Rome, contributing to the establishment of the Roman Empire.
In the early Empire, the pretense of a republican form of government was maintained. The Roman Emperor was portrayed as only a princeps, or "first citizen", and the Senate gained legislative power and all legal authority previously held by the popular assemblies. However, the rule of the Emperors became increasingly autocratic, and the Senate was reduced to an advisory body appointed by the Emperor. The Empire did not inherit a set bureaucracy from the Republic, since the Republic did not have any permanent governmental structures apart from the Senate. The Emperor appointed assistants and advisers, but the state lacked many institutions, such as a centrally planned budget. Some historians have cited this as a significant reason for the decline of the Roman Empire.
Military
[edit] |
| Part of a series on the |
| Military of ancient Rome |
|---|


The early Roman army (c. 500 BC) was, like those of other contemporary city-states influenced by Greek civilisation, a citizen militia that practised hoplite tactics. It was small and organised in five classes (in parallel to the comitia centuriata, the body of citizens organised politically), with three providing hoplites and two providing light infantry. The early Roman army was tactically limited and its stance during this period was essentially defensive.[148][149][150]
By the 3rd century BC, the Romans abandoned the hoplite formation in favour of a more flexible system in which smaller groups of 120 (or sometimes 60) men called maniples could manoeuvre more independently on the battlefield. Thirty maniples arranged in three lines with supporting troops constituted a legion, totalling between 4,000 and 5,000 men.[148][149] The early Republican legion consisted of five sections: the three lines of manipular heavy infantry (hastati, principes and triarii), a force of light infantry (velites), and the cavalry (equites). With the new organisation came a new orientation toward the offensive and a much more aggressive posture toward adjoining city-states.[148][149] At nominal full strength, an early Republican legion included 3,600 to 4,800 heavy infantry, several hundred light infantry, and several hundred cavalrymen.[148][151][152]
Until the late Republican period, the typical legionary was a property-owning citizen farmer from a rural area (an adsiduus) who served for particular (often annual) campaigns,[c] and who supplied his own equipment. After 200 BC, economic conditions in rural areas deteriorated as manpower needs increased, so that the property qualifications for compulsory service were gradually reduced. Beginning in the 3rd century BC, legionaries were paid a stipend (stipendium). By the time of Augustus, the ideal of the citizen-soldier had been abandoned and the legions had become fully professional. At the end of the Civil War, Augustus reorganised Roman military forces, discharging soldiers and disbanding legions. He retained 28 legions, distributed through the provinces of the Empire.[154]
During the Principate, the tactical organisation of the Army continued to evolve. The auxilia remained independent cohorts, and legionary troops often operated as groups of cohorts rather than as full legions. A new and versatile type of unit, the cohortes equitatae, combined cavalry and legionaries in a single formation. They could be stationed at garrisons or outposts and could fight on their own as balanced small forces or combine with similar units as a larger, legion-sized force. This increase in organizational flexibility helped ensure the long-term success of Roman military forces.[155] The Emperor Gallienus (253–268 AD) began a reorganisation that created the last military structure of the late Empire. Withdrawing some legionaries from the fixed bases on the border, Gallienus created mobile forces (the comitatenses or field armies) and stationed them behind and at some distance from the borders as a strategic reserve. The border troops (limitanei) stationed at fixed bases continued to be the first line of defence. The basic units of the field army were regimental; legiones or auxilia for infantry and vexillationes for cavalry. Nominal strengths may have been 1,200 men for infantry regiments and 600 for cavalry, but actual troop levels could have been much lower—800 infantry and 400 cavalry.[156] Many infantry and cavalry regiments operated in pairs under the command of a comes. Field armies included regiments recruited from allied tribes and known as foederati. By 400 AD, foederati regiments had become permanently established units of the Roman army, paid and equipped by the Empire, led by a Roman tribune and used just as Roman units were used. The Empire also used groups of barbarians to fight along with the legions as allies without integration into the field armies, under overall command of a Roman general, but led by their own officers.[156]
Military leadership evolved over the course of the history of Rome. Under the monarchy, the hoplite armies were led by the kings. During the early and middle Roman Republic, military forces were under the command of one of the two elected consuls for the year. During the later Republic, members of the Roman Senatorial elite, as part of the normal sequence of elected public offices known as the cursus honorum, would have served first as quaestor (often posted as deputies to field commanders), then as praetor.[157][158] Following the end of a term as praetor or consul, a Senator might be appointed by the Senate as a propraetor or proconsul (depending on the highest office held before) to govern a foreign province. Under Augustus, whose most important political priority was to place the military under a permanent and unitary command, the Emperor was the legal commander of each legion but exercised that command through a legatus (legate) he appointed from the Senatorial elite. In a province with a single legion, the legate commanded the legion (legatus legionis) and served as provincial governor, while in a province with more than one legion, each legion was commanded by a legate and the legates were commanded by the provincial governor (also a legate but of higher rank).[159]
During the later stages of the Imperial period (beginning perhaps with Diocletian), the Augustan model was abandoned. Provincial governors were stripped of military authority, and command of the armies in a group of provinces was given to generals (duces) appointed by the Emperor. These were no longer members of the Roman elite but men who came up through the ranks and had seen much practical soldiering. With increasing frequency, these men attempted (sometimes successfully) to usurp the positions of the Emperors. Decreased resources, increasing political chaos and civil war eventually left the Western Empire vulnerable to attack and takeover by neighbouring barbarian peoples.[160]
Roman navy
[edit]
Less is known about the Roman navy than the Roman army. Prior to the middle of the 3rd century BC, officials known as duumviri navales commanded a fleet of twenty ships used mainly to control piracy. This fleet was given up in 278 AD and replaced by allied forces. The First Punic War required that Rome build large fleets, and it did so largely with the assistance of and financing from allies. This reliance on allies continued to the end of the Roman Republic. The quinquereme was the main warship on both sides of the Punic Wars and remained the mainstay of Roman naval forces until replaced by the time of Caesar Augustus by lighter and more manoeuvrable vessels.[163]
As compared with a trireme, the quinquereme permitted the use of a mix of experienced and inexperienced crewmen (an advantage for a primarily land-based power), and its lesser manoeuvrability permitted the Romans to adopt and perfect boarding tactics using a troop of about 40 marines in lieu of the ram. Ships were commanded by a navarch, a rank equal to a centurion, who was usually not a citizen. Potter suggests that because the fleet was dominated by non-Romans, the navy was considered non-Roman and allowed to atrophy in times of peace.[163]
Information suggests that by the time of the late Empire (350 AD), the Roman navy comprised several fleets including warships and merchant vessels for transportation and supply. Warships were oared sailing galleys with three to five banks of oarsmen. Fleet bases included such ports as Ravenna, Arles, Aquilea, Misenum and the mouth of the Somme River in the West and Alexandria and Rhodes in the East. Flotillas of small river craft (classes) were part of the limitanei (border troops) during this period, based at fortified river harbours along the Rhine and the Danube. That prominent generals commanded both armies and fleets suggests that naval forces were treated as auxiliaries to the army and not as an independent service. The details of command structure and fleet strengths during this period are not well known, although fleets were commanded by prefects.[164]
Economy
[edit]
Ancient Rome commanded a vast area of land, with tremendous natural and human resources. As such, Rome's economy remained focused on farming and trade. Agricultural free trade changed the Italian landscape, and by the 1st century BC, vast grape and olive estates had supplanted the yeoman farmers, who were unable to match the imported grain price. The annexation of Egypt, Sicily and Tunisia in North Africa provided a continuous supply of grains. In turn, olive oil and wine were Italy's main exports. Two-tier crop rotation was practised, but farm productivity was low, around 1 ton per hectare.
Industrial and manufacturing activities were small. The largest such activities were the mining and quarrying of stones, which provided basic construction materials for the buildings of that period. In manufacturing, production was on a relatively small scale, and generally consisted of workshops and small factories that employed at most dozens of workers. However, some brick factories employed hundreds of workers.
The economy of the early Republic was largely based on smallholding and paid labour. However, foreign wars and conquests made slaves increasingly cheap and plentiful, and by the late Republic, the economy was largely dependent on slave labour for both skilled and unskilled work. Slaves are estimated to have constituted around 20% of the Roman Empire's population at this time and 40% in the city of Rome. Only in the Roman Empire, when the conquests stopped and the prices of slaves increased, did hired labour become more economical than slave ownership.

Although barter was used in ancient Rome, and often used in tax collection, Rome had a very developed coinage system, with brass, bronze, and precious metal coins in circulation throughout the Empire and beyond—some have even been discovered in India. Before the 3rd century BC, copper was traded by weight, measured in unmarked lumps, across central Italy. The original copper coins (as) had a face value of one Roman pound of copper, but weighed less. Thus, Roman money's utility as a unit of exchange consistently exceeded its intrinsic value as metal. After Nero began debasing the silver denarius, its legal value was an estimated one-third greater than its intrinsic value.
Horses were expensive and other pack animals were slower. Mass trade on the Roman roads connected military posts, where Roman markets were centered.[165] These roads were designed for wheels.[166] As a result, there was transport of commodities between Roman regions, but increased with the rise of Roman maritime trade in the 2nd century BC. During that period, a trading vessel took less than a month to complete a trip from Gades to Alexandria via Ostia, spanning the entire length of the Mediterranean.[80] Transport by sea was around 60 times cheaper than by land, so the volume for such trips was much larger.
Some economists consider the Roman Empire a market economy, similar in its degree of capitalistic practices to 17th century Netherlands and 18th century England.[167]
Family
[edit]

The basic units of Roman society were households and families.[140] Groups of households connected through the male line formed a family (gens), based on blood ties, a common ancestry or adoption. During the Roman Republic, some powerful families, or Gentes Maiores, came to dominate political life. Families were headed by their oldest male citizen, the pater familias (father of the family), who held lawful authority (patria potestas, "father's power") over wives, sons, daughters, and slaves of the household, and the family's wealth.[140]
The extreme expressions of this power—the selling or killing of family members for moral or civil offences, including simple disobedience—were very rarely exercised, and were forbidden in the Imperial era. A pater familias had moral and legal duties towards all family members. Even the most despotic pater familias was expected to consult senior members of his household and gens over matters that affected the family's well-being and reputation. Traditionally, such matters were regarded as outside the purview of the state and its magistrates; under the emperors, they were increasingly subject to state interference and legislation.[169]
Once accepted into their birth family by their fathers, children were potential heirs. They could not be lawfully given away, or sold into slavery. If parents were unable to care for their child, or if its paternity was in doubt, they could resort to infant exposure (Boswell translates this as being "offered" up to care by the gods or strangers). If a deformed or sickly newborn was patently "unfit to live", killing it was a duty of the pater familias. A citizen father who exposed a healthy freeborn child was not punished, but automatically lost his potestas over that child. Abandoned children were sometimes adopted; some would have been sold into slavery.[170] Slavery was near-ubiquitous and almost universally accepted. In the early Republic, citizens in debt were allowed to sell their labour, and perhaps their sons, to their debtor in a limited form of slavery called nexum, but this was abolished in the middle Republic. Freedom was considered a natural and proper state for citizens; slaves could be lawfully freed, with consent and support of their owners, and still serve their owners' family and financial interests, as freedmen or freed women. This was the basis of the client-patron relationship, one of the most important features of Rome's economy and society.[171]
In law, a pater familias held potestas over his adult sons with their own households. This could give rise to legal anomalies, such as adult sons also having the status of minors. No man could be considered a pater familias, nor could he truly hold property under law, while his own father lived.[172][173] During Rome's early history, married daughters came under the control (manus) of their husbands' pater familias. By the late Republic, most married women retained lawful connection to their birth family, though any children from the marriage belonged to her husband's family.[174] The mother or an elderly relative often raised both boys and girls.[175] Roman moralists held that marriage and child-raising fulfilled a basic duty to family, gens, and the state. Multiple remarriages were not uncommon. Fathers usually began seeking husbands for their daughters when these reached an age between twelve and fourteen, but most commoner-class women stayed single until their twenties, and in general seem to have been far more independent than wives of the elite. Divorce required the consent of one party, along with the return of any dowry. Both parents had power over their children during their minority and adulthood, but husbands had much less control over their wives.[176]
Roman citizen women held a restricted form of citizenship; they could not vote but were protected by law. They ran families, could own and run businesses, own and cultivate land, write their own wills, and plead in court on their own behalf, or on behalf of others, all under dispensation of the courts and the nominal supervision of a senior male relative. Throughout the late Republican and Imperial eras, a declining birthrate among the elite, and a corresponding increase among commoners was cause of concern for many gentes; Augustus tried to address this through state intervention, offering rewards to any woman who gave birth to three or more children, and penalising the childless. The latter was much resented, and the former had seemingly negligible results. Aristocratic women seem to have been increasingly disinclined to childbearing; it carried a high risk of mortality to mothers, and a deal of inconvenience thereafter.[177]
Time and dates
[edit]Roman hours were counted ordinally from dawn to dawn. Thus, if sunrise was at 6 am, then 6 to 7 am was called the "first hour". Midday was called meridies and it is from this word that the terms am (ante meridiem) and pm (post meridiem) stem. The English word "noon" comes from nona ("ninth (hour)"), which referred to 3 pm in ancient Rome.[d] The Romans had clocks (horologia), which included giant public sundials (solaria) and water clocks (clepsydrae).
The ancient Roman week originally had eight days, which were identified by letters A to H, with the eighth day being the nundinum or market day, a kind of weekend when farmers sold their produce on the streets. The seven-day week, first introduced from the East during the early Empire, was officially adopted during the reign of Constantine. Romans named week days after celestial bodies from at least the 1st century AD. Roman months had three important days: the calends (first day of each month, always in plural), the ides (13th or 15th of the month), and the nones (ninth day before the ides, inclusive, i.e. 5th or 7th of the month). Other days were counted backwards from the next one of these days.
The Roman year originally had ten months from Martius (March) to December, with the winter period not included in the calendar. The first four months were named after gods (Martius, Aprilis, Maius, Junius) and the others were numbered (Quintilis, Sextilis, September, October, November, and December). Numa Pompilius, the second king of Rome (716–673 BC), is said to have introduced the months of January and February, both also named after gods, beginning the 12-month calendar still in use today. In 44 BC, the month Quintilis was renamed to Julius (July) after Julius Caesar and in 8 BC, Sextilis was renamed to Augustus (August) after Augustus Caesar.
The Romans had several ways of tracking years. One widespread way was the consular dating, which identified years by the two consuls who ruled each year. Another way, introduced in the late 3rd century AD, was counting years from the indictio, a 15-year period based on the announcement of the delivery of food and other goods to the government. Another way, less popular but more similar to present day, was ab urbe condita, which counted years from the mythical foundation of Rome in 753 BC.
Culture
[edit]
Life in ancient Rome revolved around the city of Rome, located on seven hills. The city had a vast number of monumental structures like the Colosseum, the Trajan's Forum and the Pantheon. It had theatres, gymnasiums, marketplaces, functional sewers, bath complexes complete with libraries and shops, and fountains with fresh drinking water supplied by hundreds of miles of aqueducts. Throughout the territory under the control of ancient Rome, residential architecture ranged from modest houses to country villas.
In the capital city of Rome, there were imperial residences on the elegant Palatine Hill, from which the word palace derives. The low plebeian and middle equestrian classes lived in the city center, packed into apartments, or insulae, which were almost like modern ghettos. These areas, often built by upper class property owners to rent, were often centred upon collegia or taberna. These people, provided with a free supply of grain, and entertained by gladiatorial games, were enrolled as clients of patrons among the upper class patricians, whose assistance they sought and whose interests they upheld.
Language
[edit]The native language of the Romans was Latin, an Italic language the grammar of which relies little on word order, conveying meaning through a system of affixes attached to word stems.[178] Its alphabet was based on the Etruscan alphabet, which was in turn based on the Greek alphabet.[179] Although surviving Latin literature consists almost entirely of Classical Latin, an artificial and highly stylised and polished literary language from the 1st century BC, the spoken language of the Roman Empire was Vulgar Latin, which significantly differed from Classical Latin in grammar and vocabulary, and eventually in pronunciation.[180] Speakers of Latin could understand both until the 7th century when spoken Latin began to diverge so much that 'Classical' or 'Good Latin' had to be learned as a second language.[181]
While Latin remained the main written language of the Roman Empire, Greek came to be the language spoken by the well-educated elite, as most of the literature studied by Romans was written in Greek. Most of the emperors were bilingual but had a preference for Latin in the public sphere for political reasons, a practice that first started during the punic wars.[182] In the eastern part of the Roman Empire (and later the Eastern Roman Empire), Latin was never able to replace Greek, a legacy of the Hellenistic period.[183] Justinian would be the last emperor to use Latin in government and marks when Greek officially took over.[184] The expansion of the Roman Empire spread Latin throughout Europe, and Vulgar Latin evolved into many distinct Romance languages.
Religion
[edit]
Archaic Roman religion, at least concerning the gods, was made up not of written narratives, but rather of complex interrelations between gods and humans.[185] Unlike in Greek mythology, the gods were not personified, but were vaguely defined sacred spirits called numina. Romans also believed that every person, place or thing had its own genius, or divine soul. During the Roman Republic, Roman religion was organised under a strict system of priestly offices, which were held by men of senatorial rank. The College of Pontifices was uppermost body in this hierarchy, and its chief priest, the Pontifex Maximus, was the head of the state religion. Flamens took care of the cults of various gods, while augurs were trusted with taking the auspices. The sacred king took on the religious responsibilities of the deposed kings. In the Roman Empire, deceased emperors who had ruled well were deified by their successors and the Senate.[186] and the formalised imperial cult became increasingly prominent.
As contact with the Greeks increased, the old Roman gods became increasingly associated with Greek gods.[187] Under the Empire, the Romans absorbed the mythologies of their conquered subjects, often leading to situations in which the temples and priests of traditional Italian deities existed side by side with those of foreign gods.[188]
Beginning with Emperor Nero in the 1st century AD, Roman official policy towards Christianity was negative, and at some point, being a Christian could be punishable by death. Under Emperor Diocletian, the persecution of Christians reached its peak. However, it became an officially supported religion in the Roman state under Diocletian's successor, Constantine I, with the signing of the Edict of Milan in 313, and quickly became dominant. All religions except Christianity were prohibited in 391 AD by an edict of Emperor Theodosius I.[189]
Ethics and morality
[edit]Like many ancient cultures, concepts of ethics and morality, while sharing some commonalities with modern society, differed greatly in several important ways. Because ancient civilisations like Rome were under constant threat of attack from marauding tribes, their culture was necessarily militaristic with martial skills being a prized attribute.[190] Whereas modern societies consider compassion a virtue, Roman society considered compassion a vice, a moral defect. Indeed, one of the primary purposes of the gladiatorial games was to inoculate Roman citizens from this weakness.[191][190][192] Romans instead prized virtues such as courage and conviction (virtus), a sense of duty to one's people, moderation and avoiding excess (moderatio), forgiveness and understanding (clementia), fairness (severitas), and loyalty (pietas).[193]
Roman society had well-established and restrictive norms related to sexuality, though as with many societies, the lion's share of the responsibilities fell on women. Women were generally expected to be monogamous having only a single husband during their life (univira), though this was much less regarded by the elite, especially under the empire. Women were expected to be modest in public avoiding any provocative appearance and to demonstrate absolute fidelity to their husbands (pudicitia). Indeed, wearing a veil was a common expectation to preserve modesty. Sex outside of marriage was generally frowned upon for men and women and indeed was made illegal during the imperial period.[194] Nevertheless, prostitution was an accepted and regulated practice.[195]
Public demonstrations of death, violence, and brutality were used as a source of entertainment in Roman communities; however it was also a way to maintain social order, demonstrate power, and signify communal unity.
Art, music and literature
[edit]

Roman painting styles show Greek influences, and surviving examples are primarily frescoes used to adorn the walls and ceilings of country villas, though Roman literature includes mentions of paintings on wood, ivory, and other materials.[196][197] Several examples of Roman painting have been found at Pompeii, and from these art historians divide the history of Roman painting into four periods.
The first style of Roman painting was practised from the early 2nd century BC to the early- or mid-1st century BC. It was mainly composed of imitations of marble and masonry, though sometimes including depictions of mythological characters.The second style began during the early 1st century BC and attempted to depict realistically three-dimensional architectural features and landscapes. The third style occurred during the reign of Augustus (27 BC – 14 AD), and rejected the realism of the second style in favour of simple ornamentation. A small architectural scene, landscape, or abstract design was placed in the center with a monochrome background. The fourth style, which began in the 1st century AD, depicted scenes from mythology, while retaining architectural details and abstract patterns.
Portrait sculpture used youthful and classical proportions, evolving later into a mixture of realism and idealism. During the Antonine and Severan periods, ornate hair and bearding, with deep cutting and drilling, became popular. Advancements were also made in relief sculptures, usually depicting Roman victories.
Roman music was largely based on Greek music, and played an important part in many aspects of Roman life.[198] In the Roman military, musical instruments such as the tuba (a long trumpet) or the cornu were used to give various commands, while the buccina (possibly a trumpet or horn) and the lituus (probably an elongated J-shaped instrument), were used in ceremonial capacities.[199] Music was used in the Roman amphitheatres between fights and in the odea, and in these settings is known to have featured the cornu and the hydraulis (a type of water organ).[200] Most religious rituals featured musical performances.[201] Some music historians believe that music was used at almost all public ceremonies.[198]
The graffiti, brothels, paintings, and sculptures found in Pompeii and Herculaneum suggest that the Romans had a sex-saturated culture.[202]
Literature and Libraries
[edit]Latin literature was, from its start, influenced heavily by Greek authors. Some of the earliest extant works are of historical epics telling the early military history of Rome. As the Republic expanded, authors began to produce poetry, comedy, history, and tragedy.
Ancient Rome's literary contributions are still recognized today and the works by ancient Roman authors were available in bookshops as well as in public and private libraries. Many scholars and statesmen of ancient Rome cultivated private libraries that were used both as demonstrations of knowledge and displays of wealth and power.[203] Private libraries were so commonly encountered that Vitruvius wrote about where libraries should be situated within a villa.[204] In addition to numerous private libraries, the Roman Empire saw the establishment of early public libraries.
Although Julius Caesar had intended to establish public libraries to further establish Rome as a great cultural center like Athens and Alexandria, he died before this was accomplished. Caesar's former lieutenant, Gaius Asinius Pollio, took up the project and opened the first public library in Rome in the Atrium Libertatis.[205] Emperors Augustus, Tiberius, Vespasian, Domitian, and Trajan also founded or expanded public libraries in Rome during their reigns.[206][207][208] These included the Ulpian Library in Trajan's Forum and libraries in the Temple of Apollo Palatinus, the Temple of Peace in the Roman Forum, the Temple of Divus Augustus, which was dedicated to Minerva when it was rebuilt under Emperor Domitian's orders.[209] Some of these, including the library at the Temple of Divus Augustus also served as archives.[209] By the fall of the Western Roman Empire, the city of Rome had more than two dozen public libraries.[210] Rome was not the only city to benefit from such institutions. As the Roman Empire spread, public libraries were established in other major cities and cultural centers including Ephesos, Athens, and Timgad.[211][212]
Most public libraries of this time were not built expressly for that purpose, instead sharing space in temples, baths, and other community buildings. In addition to serving as repositories for books, public libraries hosted orations by authors.[203] These recitations served as social gatherings and allowed those who may not be literate to be entertained by poetry, epics, philosophical treatises, and other works.
Cuisine
[edit]
Ancient Roman cuisine changed over the long duration of this ancient civilisation. Dietary habits were affected by the influence of Greek culture, the political changes from Kingdom to Republic to Empire, and the Empire's enormous expansion, which exposed Romans to many new, provincial culinary habits and cooking techniques. In the beginning the differences between social classes were relatively small, but disparities evolved with the Empire's growth. Men and women drank wine with their meals.[214]
The ancient Roman diet included many items that are staples of modern Italian cooking. Pliny the Elder discussed more than 30 varieties of olive, 40 kinds of pear, figs (native and imported from Africa and the eastern provinces), and a wide variety of vegetables, including carrots (of different colours, but not orange[215]) as well as celery, garlic, some flower bulbs, cabbage and other brassicas (such as kale and broccoli), lettuce, endive, onion, leek, asparagus, radishes, turnips, parsnips, beets, green peas, chard, cardoons, olives, and cucumber.[216]
However, some foods now considered characteristic of modern Italian cuisine were not used.[217] In particular, spinach and eggplant (aubergine) were introduced later from the Arab world, and tomatoes, potatoes, capsicum peppers, and maize (the modern source of polenta)[216] only appeared in Europe following the discovery of the New World and the Columbian Exchange.[217] The Romans knew of rice, but it was very rarely available to them. There were also few citrus fruits.[217]
Butcher's meat such as beef was an uncommon luxury. The most popular meat was pork, especially sausages.[218] Fish was more common than meat, with a sophisticated aquaculture and large-scale industries devoted to oyster farming. The Romans also engaged in snail farming and oak grub farming. Some fish were greatly esteemed and fetched high prices, such as mullet raised in the fishery at Cosa, and "elaborate means were invented to assure its freshness".[219]
Traditionally, a breakfast called ientaculum[220] was served at dawn. At mid-day to early afternoon, Romans ate cena,[220] the main meal of the day, and at nightfall a light supper called vesperna.[221] With the increased importation of foreign foods, the cena grew larger in size and included a wider range of foods. Thus, it gradually shifted to the evening, while the vesperna[221] was abandoned completely over the course of the years. The mid-day meal prandium became a light meal to hold one over until cena.[220]
Fashion
[edit]
, От тоги распространенной одежды в эпоху Юлия Цезаря, постепенно отказались все социальные классы Империи. В начале IV века тога стала просто одеждой, которую сенаторы носили в Сенате и на церемониальных мероприятиях. В IV веке на смену тоге пришла паэнула ( одежда, похожая на пончо) как повседневная одежда римлян, от низших классов до высших. Еще одной одеждой, которая была популярна среди римлян в последние годы существования Западной Римской империи, был паллий , который в основном носили философы и ученые в целом. Из-за внешних влияний, главным образом со стороны германских народов, римляне переняли туники, очень похожие на те, что использовались германскими народами, с которыми они взаимодействовали в последние годы Западной империи, а также переняли брюки и шляпы типа Pileus Pannonicus . В Поздней Империи палудаментум (вид военной одежды) использовался только императором Рима (со времен правления Августа , первого императора), тогда как далматик (также используемый христианским духовенством) начал распространяться по всей империи. [222]
Игры и отдых
[ редактировать ]

Молодежь Рима имела несколько форм спортивных игр и упражнений. Игра для мальчиков должна была подготовить их к активной военной службе, например, к прыжкам , борьбе , боксу , скачкам . [223] В сельской местности развлечением богатых также была рыбалка и охота. [224] У римлян также было несколько форм игры с мячом, в том числе одна, напоминающая гандбол . [223] Игры в кости , настольные игры и азартные игры были популярными развлечениями. [223] Для богатых званые обеды представляли собой возможность развлечений, иногда с музыкой, танцами и чтением стихов. [196] Большинство, менее обеспеченное, иногда устраивало подобные вечеринки в клубах или ассоциациях, но для большинства римлян развлекательная трапеза обычно означала посещение таверн . [196] Дети развлекали себя игрушками и такими играми, как чехарда . [224] [196]
Публичные игры и зрелища спонсировались ведущими римлянами, которые хотели продемонстрировать свою щедрость и завоевать одобрение народа; в Риме или его провинциях это обычно означало императора или его наместников. Площадки в Риме и провинциях были построены специально для публичных игр. Римский Колизей был построен в 70 году нашей эры при римском императоре Веспасиане и открыт в 80 году нашей эры для проведения других мероприятий и гладиаторских боев. Гладиаторы обладали экзотическим и изобретательным разнообразием оружия и доспехов. Иногда они сражались насмерть, но чаще до окончательной победы, обычно в соответствии с настроением наблюдающей толпы. Шоу экзотических животных были популярны сами по себе; но иногда животных натравливали на людей, будь то вооруженные профессионалы или безоружные преступники, приговоренные к публичной смерти.
Гонки на колесницах были чрезвычайно популярны среди всех сословий. В Риме эти скачки обычно проводились в Большом цирке , который был специально построен для скачек на колесницах и скачках и, как крупнейшее общественное место Рима, также использовался для фестивалей и представлений животных. [225] Он мог вместить около 150 000 человек; [226] Возничие мчались группами, обозначенными по цвету; некоторые поклонники были членами чрезвычайно, даже крайне партийных цирковых группировок.
Технология
[ редактировать ]
Древний Рим мог похвастаться впечатляющими технологическими достижениями, используя многие достижения, которые были утеряны в средние века и не имели соперников до XIX и XX веков. Примером этого является изолированное остекление , которое не было изобретено до 1930-х годов. Многие практические римские инновации были заимствованы из более ранних греческих проектов. Достижения часто были разделены и основаны на ремесле. Ремесленники охраняли технологии как коммерческую тайну . [227]
Римское гражданское и военное строительство составляло значительную часть технологического превосходства и наследия Рима и способствовало строительству сотен дорог , мостов , акведуков , общественных бань , театров и арен . Многие памятники, такие как Колизей , Пон-дю-Гар и Пантеон , остаются свидетельствами римской инженерии и культуры.
Римляне были известны своей архитектурой , которая сгруппирована с греческими традициями в « классическую архитектуру ». Хотя существовало много отличий от греческой архитектуры , Рим в значительной степени заимствовал у Греции строгие, шаблонные конструкции и пропорции зданий. Если не считать двух новых порядков колонн, композитных и тосканских , а также купола , который произошел от этрусской арки , в Риме до конца республики было относительно мало архитектурных нововведений.
В I веке до нашей эры римляне начали широко использовать римский бетон . Бетон был изобретен в конце III века до нашей эры. Это был мощный цемент, полученный из пуццолана , который вскоре вытеснил мрамор в качестве основного строительного материала Рима и позволил создать множество смелых архитектурных форм. [228] Также в I веке до нашей эры Витрувий написал «О архитектуре» , возможно, первый полный трактат по архитектуре в истории. В конце I века до нашей эры Рим также начал использовать стеклодувное дело вскоре после его изобретения в Сирии около 50 г. до н.э. Мозаика покорила Империю после того, как образцы были собраны во время Луция Корнелия Суллы кампании в Греции.
Римляне также в основном строили из древесины, что привело к быстрому упадку лесных массивов вокруг Рима и на большей части Апеннинских гор из-за спроса на древесину для строительства, судостроения и пожаротушения. Первые свидетельства торговли древесиной на большие расстояния связаны с обнаружением деревянных досок, срубленных между 40 и 60 годами нашей эры, доставленных из гор Юра на северо-востоке Франции и оказавшихся на расстоянии более 1055 миль (1700 км) в фундаменте роскошный портик, который был частью огромной виллы богатого патриция в центре Рима. Предполагается, что древесина длиной около 4 метров (13 футов) попала в Рим по реке Тибр на кораблях, следовавших через Средиземное море от места слияния рек Сона и Рона находится город Лион в месте, где сейчас . день Франции. [229]

С прочным фундаментом и хорошим дренажем. [230] Римские дороги были известны своей долговечностью, и многие сегменты римской дорожной системы все еще использовались спустя тысячу лет после падения Рима. Строительство обширной и эффективной туристической сети по всей Империи резко увеличило мощь и влияние Рима. Они позволяли римские легионы с предсказуемым временем марша между ключевыми точками империи, независимо от времени года. быстро развертывать [231] Эти автомагистрали также имели огромное экономическое значение, укрепляя роль Рима как торгового перекрестка - откуда пошла поговорка «все дороги ведут в Рим». Римское правительство поддерживало систему промежуточных станций, известную как cursus publicus , и установило систему конных эстафет, позволяющую отправкам преодолевать расстояние до 80 км (50 миль) в день.
Римляне построили многочисленные акведуки для снабжения водой городов и промышленных объектов, а также для помощи в сельском хозяйстве . К третьему веку город Рим снабжался 11 акведуками общей длиной 450 км (280 миль). Римляне также добились значительных успехов в области санитарии . Римляне были особенно известны своими общественными банями , называемыми парилками , которые использовались как для гигиенических, так и для социальных целей. Во многих римских домах были туалеты со смывом и внутренняя водопроводная система , а сложная канализационная система, Большая Клоака , использовалась для осушения местных болот и сброса отходов в Тибр. Некоторые историки предполагают, что свинцовые трубы в канализационных и водопроводных системах привели к повсеместному отравлению свинцом , что способствовало падению Рима ; однако содержание свинца было бы сведено к минимуму. [232] [233]
Наследие
[ редактировать ]Древний Рим – прародитель западной цивилизации . [234] Обычаи . , религия , право , технологии , архитектура , политическая система , армия , литература , языки , алфавит , правительство и многие факторы и аспекты западной цивилизации — все это унаследовано от римских достижений Повторное открытие римской культуры оживило западную цивилизацию, сыграв роль в эпоху Возрождения и эпохи Просвещения . [235]
Историография
[ редактировать ]Первичные и вторичные источники
[ редактировать ]Два самых длинных древних отчета по римской истории, истории Ливия и Дионисия Галикарнасского, были составлены на 500 лет позже даты основания республики и на 200 лет после поражения Ганнибала. [236] Хотя по истории Древнего Рима существовало множество работ, многие из них утеряны. В результате этой утраты в римской истории образовались пробелы, которые заполнены ненадежными произведениями, такими как « История Августы» и другими книгами малоизвестных авторов. Историки использовали свои работы для восхваления римской культуры и обычаев, а также для того, чтобы льстить своим покровителям. [237] Цезарь написал свои собственные отчеты о своих военных кампаниях в Галлии и во время Гражданской войны, отчасти для того, чтобы произвести впечатление на своих современников. [238]
В Империи процветали биографии знаменитых людей и первых императоров, примерами которых являются «Двенадцать цезарей Плутарха » Светония и «Параллельные жизни» . Другими крупными произведениями имперских времен были работы Ливия и Тацита.
- Полибий – Истории
- Саллюстий - Катилинская война и Югуртинская война.
- Юлий Цезарь – Галльская война и Гражданская война
- Ливи – основан городом
- Дионисий Галикарнасский – Римские древности
- Плиний Старший – Naturalis Historia
- Иосиф Флавий – Иудейская война
- Светоний – Двенадцать Цезарей
- Тацит – Анналы и истории
- Плутарх – Параллельные жизни (серия биографий знаменитых римлян и греков)
- Кассий Дион - Римская история
- Иродиан - История Римской империи со времен Марка Аврелия
- Аммиан Марцеллин - Res Gestae
Интерес к изучению и идеализации Древнего Рима стал преобладать в эпоху итальянского Возрождения . Книга Эдварда Гиббона «История упадка и падения Римской империи » «начала современное изучение римской истории в англоязычном мире». [239] Бартольд Георг Нибур был основоположником изучения древнеримской истории и написал «Римскую историю» , прослеживая период до Первой Пунической войны . Во времена « Наполеона История римлян» Виктора Дюрюи подчеркнула кесарева сечения популярный в то время период . История Рима , римское конституционное право и Corpus Inscriptionum Latinarum , все Теодор Моммзен , [240] стали вехами.
- Эдвард Гиббон – История упадка и разрушения Римской империи
- Джон Бэгналл Бери – История Поздней Римской империи
- Майкл Грант – Римский мир [241]
- Барбара Левик — Клавдий [242]
- Бартольд Георг Нибур
- Михаил Ростовцев
- Говард Хейс Скаллард – История римского мира [243]
- Рональд Сайм – Римская революция [244]
- Адриан Голдсуорси – Цезарь: жизнь колосса и как пал Рим
- Мэри Бирд - SPQR: История Древнего Рима
См. также
[ редактировать ]- Очерк классических исследований
- Регионы греко-римской древности
- Список древних римлян
- Список римских императоров
- Список римских гражданских войн и восстаний
- Византийская империя
- Римская армия
- Список археологически подтвержденных женщин из древнего Средиземноморья
Примечания
[ редактировать ]- ^ Конкретные даты различаются в зависимости от того, следует ли кто-то римской традиции, современной археологии или конкурирующим взглядам на то, какие конкретные события отмечают конечные точки.
- ↑ Существует несколько разных оценок численности населения Римской империи.
- Шайдель, Саллер и Моррис 2007 , с. 2 оценивает в 60 миллионов.
- Голдсмит, Раймонд В. (сентябрь 1984 г.). «Оценка размера и структуры национального продукта ранней Римской империи». Обзор доходов и богатства . 30 (3): 263. doi : 10.1111/j.1475-4991.1984.tb00552.x . оценки 55.
- Белох, Карл Юлиус (1886). Население греко-римского мира (на немецком языке). Дункер. п. 507. оценки 54.
- Мэддисон, Ангус (2007). Контуры мировой экономики, 1–2030 гг. нашей эры. Очерки макроэкономической истории . Издательство Оксфордского университета. стр. 51, 120. ISBN. 978-0-1992-2721-1 . оценки 48.
- Население Римской империи оценивается в 65 человек (при упоминании нескольких других оценок от 55 до 120 человек).
- Маклинн, Фрэнк (2011). Марк Аврелий: воин, философ, император . Случайный дом. п. 3. ISBN 978-1-4464-4933-2 .
[T] Наиболее вероятная оценка правления Марка Аврелия составляет где-то от семидесяти до восьмидесяти миллионов.
- МакЭведи, Колин; Джонс, Ричард (1978). Атлас истории населения мира . Нью-Йорк: Пингвин. ISBN 0-1405-1076-1 . OCLC 4150954 . ОЛ 4292284М .
- Бюро переписи населения США. среднее значение цифр из разных источников, перечисленных в исторических оценках мирового населения Архивировано 13 октября 2013 года в Wayback Machine.
- Кремер, Майкл (1993). «Рост населения и технологические изменения: от одного миллиона до нашей эры до 1990 года» в Ежеквартальном журнале экономики 108 (3): 681–716.
- ^ Между 343 и 241 годами до нашей эры римская армия сражалась каждый год, кроме пяти. [153]
- ^ Позже в христианской литургии слово «полдень» стало обозначать ноны , время молитвы первоначально в 15:00, но позже в полдень, поэтому «полдень» стал синонимом полудня.
Ссылки
[ редактировать ]- ^ «Древний Рим | Факты, карты и история» . Британская энциклопедия . Проверено 5 сентября 2017 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Таагепера, Рейн (1979). «Размер и продолжительность империй: кривые роста-упадка, с 600 г. до н.э. по 600 г. н.э.». История социальных наук . 3 (3/4): 125. дои : 10.2307/1170959 . ISSN 0145-5532 . JSTOR 1170959 .
Турчин, Петр; Адамс, Джонатан М.; Холл, Томас Д. (декабрь 2006 г.). «Ориентация исторических империй Восток-Запад» . Журнал исследований мировых систем . 12 (2): 222. doi : 10.5195/JWSR.2006.369 . ISSN 1076-156X . - ^ Фюре, Франсуа; Озуф, Мона, ред. (1989). Критический словарь Французской революции . Издательство Гарвардского университета. п. 793. ИСБН 978-0-6741-7728-4 . ; Лакхэм, Робин; Уайт, Гордон (1996). Демократизация на Юге: зубчатая волна . Издательство Манчестерского университета. п. 11. ISBN 978-0-7190-4942-2 . ; Селлерс, Мортимер Н. (1994). Американский республиканизм: римская идеология в конституции Соединенных Штатов . Нью-Йоркский университет Пресс. п. 90. ИСБН 978-0-8147-8005-3 .
- ^ Боутрайт 2012 , с. 519.
- ^ Боутрайт 2012 , с. 29.
- ^ Боутрайт 2012 , с. 31.
- ^ Боутрайт 2012 , стр. 31–32.
- ^ Боутрайт 2012 , с. 32.
- ^ Меллор, Рональд и МакГи Марни, Древний римский мир , с. 15 (цитировано 15 марта 2009 г.).
- ^ Боутрайт 2012 , с. 35. « Рекс» , латинское слово, обозначающее «король», появляется в двух фрагментарных текстах шестого века: один — в надписи из святилища Вулкана , а другой — в глиняном черепке, найденном в Регии ».
- ^ Jump up to: а б с Боутрайт 2012 , с. 36.
- ^ Боутрайт 2012 , с. 37.
- ^ Боутрайт 2012 , с. 39.
- ^ Боутрайт 2012 , с. 40.
- ^ Боутрайт 2012 , с. 42.
- ^ Боутрайт 2012 , с. 43.
- ^ Корнелл 1995 , стр. 215 и последующие.
- ^ Матышак 2003 , стр. 43–44.
- ^ Адкинс и Адкинс 1998 , стр. 41–42.
- ^ Хукер, Ричард (6 июня 1999 г.). «Рим: Римская республика» . Университет штата Вашингтон. Архивировано из оригинала 14 мая 2011 года.
- ^ Магистрат Джорджа Лонга, Массачусетс. Появляется на стр. 723–724 Словаря греческих и римских древностей Уильяма Смита, DCL, LL.D. Опубликовано Джоном Мюрреем, Лондон, 1875 г. Веб-сайт, 8 декабря 2006 г. Проверено 24 марта 2007 г.
- ^ Ливий, Тит (Ливий) (1998). «Книга II» . Возвышение Рима, книги 1–5 . Перевод Люси, TJ Oxford World's Classics. ISBN 978-0-1928-2296-3 .
- ^ Адкинс и Адкинс 1998 , стр. 39.
- ^ Это буквально римские либры , от которых произошел фунт.
- ^ [1] Плутарх, Параллельные жизни , Жизнь Камилла , XXIX, 2.
- ^ Jump up to: а б с Хейвуд 1971 , стр. 350–358 .
- ^ Пирр Эпирский (2). Архивировано 14 апреля 2016 года в Wayback Machine и Пирр Эпирский (3). Архивировано 3 марта 2016 года в Wayback Machine Джона Лендеринга. Ливиус.орг. Проверено 21 марта 2007 г.
- ^ Беннетт, Мэтью; Доусон, Дойн; Филд, Рон; Хоторнвейт, Филип; Лоудс, Майк (2016). История войн: полное наглядное руководство по истории войн от Древнего мира до Гражданской войны в США . п. 61.
- ^ Голдсуорси 2006 , стр. 25–26; Майлз, 2011 г. , стр. 175–176.
- ^ «Кассий Дион – Фрагменты книги 11» . penelope.uchicago.edu . Проверено 6 сентября 2022 г.
- ^ Лаббертон, Роберт Хенлопен. Новый исторический атлас и всеобщая история . п. 35.
- ^ Каспари, Максимилиан Отто Бисмарк (1911). . В Чисхолме, Хью (ред.). Британская энциклопедия . Том. 22 (11-е изд.). Издательство Кембриджского университета. п. 850.
- ^ Хейвуд 1971 , стр. 376–393 ; Хукер, Ричард (6 июня 1999 г.). «Рим: Пунические войны» . Университет штата Вашингтон . Проверено 22 марта 2007 г.
- ^ Бери, Джон Багнелл (1889). История Поздней Римской империи . Макмиллан и компания ; Рим: Завоевание эллинистических империй. Архивировано 1 мая 2011 года в Wayback Machine Ричардом Хукером. Университет штата Вашингтон. 6 июня 1999 г. Проверено 22 марта 2007 г.
- ^ Duiker & Spielvogel 2001 , стр. 136–137 ; Падение Римской республики, 133–27 до н.э. Университет Пердью . Проверено 24 марта 2007 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Eques (Рыцарь). Архивировано 7 августа 2014 года в Wayback Machine Джона Лендеринга. Ливиус.орг. Проверено 24 марта 2007 г.
- ^ Адкинс и Адкинс 1998 , стр. 38.
- ^ Тума, Элиас Х. (1965). Двадцать шесть веков аграрной реформы: сравнительный анализ . Издательство Калифорнийского университета. п. 34.
- ^ Jump up to: а б с Уильям Харрисон Де Пюи (1893). Британская энциклопедия: словарь искусств, наук и общей литературы; переиздание Р.С. Пила с новыми картами и оригинальными американскими статьями . Вернер Ко.п. 760.
- ^ Генри Джордж Лидделл (1855 г.). История Рима до основания империи . п. 305.
- ^ Юлий Цезарь (100–44 до н.э.) . Би-би-си. Проверено 21 марта 2007 г.
- ^ [2] Плутарх, Жизнь Цезаря. Проверено 1 октября 2011 г.
- ^ Август (31 г. до н. э. – 14 г. н. э.), автор Гарретт Г. Фэган. Императорибус Романис 5 июля 2004 г. Проверено 21 марта 2007 г.
- ↑ Монеты императора Августа. Архивировано 25 мая 2009 г. в Wayback Machine ; примерами являются монета 38 г. до н. э. с надписью «Divi Iuli filius» и еще одна монета 31 г. до н. э. с надписью «Divi filius» ( Auguste vu par lui-même et par les autres, автор: Джульетта Рид. Архивировано 19 марта 2009 г. в Wayback Machine ).
- ^ [3] Светоний, Двенадцать Цезарей , Август , XV.
- ^ [4] Плутарх, Параллельные жизни , Жизнь Антония , LXXI, 3–5.
- ^ Август (63 г. до н. э. – 14 г. н. э.) с bbc.co.uk. сайта Проверено 12 марта 2007 г.; Лэнгли, Эндрю; Соуза, де Филип (1996). Римские времена . Пресс для фитиля свечей. п. 14.
- ^ Династия Юлиев-Клавдиев (27 г. до н.э. – 68 г. н.э.) . Отделом греческого и римского искусства Метрополитен -музея . Октябрь 2000 г. Проверено 18 марта 2007 г.
- ^ Орр, Джеймс (1915). Международная стандартная библейская энциклопедия . Компания Говард-Северанс. п. 2598 .
- ^ Шерман, Чарльз Финеас (1917). Римское право в современном мире . Бостонская книжная компания. п. 50 .
- ^ Вернер Эк, Эпоха Августа
- ^ Пелхэм, Генри Фрэнсис (1911). . В Чисхолме, Хью (ред.). Британская энциклопедия . Том. 2 (11-е изд.). Издательство Кембриджского университета. п. 912.
- ^ [5] Светоний, Двенадцать Цезарей , Август , XXI, 1.
- ^ [6] Светоний, Двенадцать Цезарей , Август , XXI.
- ^ Дуикер и Шпильвогель 2001 , с. 140 .
- ^ [7] Светоний, Двенадцать Цезарей , Август , 63.
- ^ [8] Кассий Дион, Римская история , LVII, 12.
- ^ Джон Чарльз Тарвер (1902). Тиберий, тиран . А. Констебль. стр. 342–428 .
- ^ Иоганн Якоб Херцог; Джон Генри Огастес Бомбергер (1858). Протестантская теологическая и церковная энциклопедия: сокращенный перевод настоящей энциклопедии Герцога . Линдси и Блейкистон. п. 99 . ; Чаутокуан . М. Бэйли. 1881. с. 445 .
- ^ Компендиум (1858 г.). Сборник всеобщей истории. Древнее и современное, автора «Двух тысяч вопросов по Ветхому и Новому Заветам» . п. 109 .
- ^ Сэр Уильям Смит (1890). Абей-Диспонтей . Дж. Мюррей. п. 776 .
- ^ [9] Светоний, Двенадцать Цезарей , Клавдий , XVII.
- ^ Клавдий Барбары Левик. п. 77.
- ^ Краткая история: Краткая история Великобритании . Издательство информационной базы. 2009. с. 34.
- ^ Англия вторглась . Эмберли Паблишинг Лимитед. 2014. с. 27.
- ^ Во имя Рима: Люди, которые завоевали Римскую империю . Хачетт Великобритания. 2010. с. 30.
- ^ «Гай Светоний Паулин» . 27 сентября 2016 г. Архивировано из оригинала 13 июля 2021 г. Проверено 21 февраля 2023 г.
- ^ Создание Европы: история Запада, том I до 1790 года . 2013. с. 162.
- ^ [10] Светоний, Двенадцать Цезарей , Нерон , XVI.; [11] Тацит, Анналы , 38.
- ^ Нерон (54–68 гг. Н.э.) , Герберт В. Бенарио. О римских императорах. 10 ноября 2006 г. Проверено 18 марта 2007 г.
- ^ А. Страх; П. Лиддел, ред. (2010). «Слава Италии и всеобщая судьба Рима в «Географике» Страбона» . Historiae Mundi. Исследования по всеобщей истории . Лондон: Дакворт. стр. 87–101 . Проверено 20 ноября 2021 г.
- ^ Кивени, Артур (январь 1987 г.). Артур Кивени: Рим и объединение Италии . Крумский шлем. ISBN 9780709931218 . Проверено 20 ноября 2021 г.
- ^ Билланович, Джозеф (2008). Libreria Universitaria Hoepli, Lezioni di philologia, Джузеппе Билланович и Роберто Пеше: Corpus Iuris Civilis, Italia non erat provinciale, sed domina provincialum , Feltrinelli, стр.363 (на итальянском языке). Роберто Пеше. ISBN 9788896543092 . Проверено 20 ноября 2021 г.
- ^ Бляйкен, Йохен (15 октября 2015 г.). Италия: абсолютный центр республики и Римской империи . Пингвин Великобритания. ISBN 9780241003909 . Проверено 20 ноября 2021 г.
- ^ Морсильо, Марта Гарсиа (2010). «Римская Италия: правительница мира и прародительница всех земель » . В А. Страх; П. Лидделл (ред.). История мира Исследования по всеобщей истории Лондон: Блумсбери. ISBN 9781472519801 . Проверено 20 ноября 2021 г.
- ^ Другие имена и наименования, связанные со статусом Италии в римские времена (на итальянском языке). Блумсбери. 20 ноября 2013 г. ISBN. 9781472519801 . Проверено 20 ноября 2021 г.
- ^ «Antico appellativo dell'Italia romana: Италия — прародительница всех земель » (на итальянском языке) . Проверено 20 ноября 2021 г.
- ^ Светоний
- ^ О'Коннелл 1989 , с. 81 ; Крейс, Стивен. «Август Цезарь и Pax Romana» . Путеводитель по истории . Проверено 21 марта 2007 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Скарр, 1995 год .
- ^ Иосиф Флавий, Иудейские войны VI.9.3
- ^ Jump up to: а б Светоний . Двенадцать Цезарей: Веспасиан .
- ^ [12] Кассий Дион, Римская история , LXVI.; [13] Светоний, Двенадцать цезарей , Тит , VII, 3.
- ^ [14] Светоний, Двенадцать Цезарей , Домициан , X.
- ^ Тит Флавий Домициан Проверено 29 октября 2011 г.
- ^ «Кассий Дион - Краткое изложение книги 68» . ; Кассий Дион, Римская история , 68, 1.
- ^ Энциклопедия европейских народов . Издательство информационной базы. 2006. с. 406.
- ^ [15] Кассий Дион, Римская история , 68, 6.
- ^ [16] Кассий Дион, Римская история , 68, 13.
- ^ [17] Кассий Дион, Римская история , 68, 17–30.
- ^ Императоры Рима: История императорского Рима от Юлия Цезаря до Последнего императора . Хачетт Великобритания. 2014. с. 64.
- ^ Энциклопедия христианства, том 4 . Вм. Издательство Б. Эрдманс. 2005. с. 15 . ISBN 978-0-8028-2416-5 .
- ^ [18] Historia Augusta, Жизнь Адриана .
- ^ [19] Historia Augusta , Жизнь Антонина Пия , V, 4.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Кассий Дион , «Воплощение книги LXXII» , Римская история.
- ^ Прошлые пандемии, опустошившие Европу , Верити Мерфи. Новости Би-би-си . 7 ноября 2005 г.
- ^ Гиббон, Эдвард (1906). «Глава I» . В Бери, Дж. Б. (ред.). История упадка и разрушения Римской империи . Фред де Фау и Ко.
- ^ Пять хороших императоров из истории UNRV. Проверено 12 марта 2007 г.
- ^ Кэри 1967 , с. 704.
- ^ [20] Кассий Дион, Римская история , 76, 7.
- ^ [21] Кассий Дион, Римская история , 76, 9–12.
- ^ [22] Кассий Дион, Римская история , LXXVIII, 22–23.; [23] Historia Augusta , Жизнь Каракаллы , VI.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Гиссенский папирус, 40, 7–9 «Я дарую всем жителям Империи римское гражданство, и никто не остается вне civitas, за исключением dediticii»
- ^ Борода, Мэри (20 октября 2015 г.). SPQR: История Древнего Рима . Профиль. стр. 529–530. ISBN 978-1-8476-5441-0 .
- ^ Хейвуд 1971 , стр. 376–393 .
- ^ [24] Historia Augusta , Жизнь Александра Севера , LIX.
- ^ Скип Нокс, Э. Л. «Кризис третьего века (235–285)» . История западной цивилизации . Государственный университет Бойсе. Архивировано из оригинала 3 мая 2007 года. ; Хейвуд 1971 , стр. 376–393 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б Гиббон, Эдвард (1906). «Глава X» (Онлайн-версия) . В Бери, Дж. Б. (ред.). История упадка и разрушения Римской империи . Фред де Фау и Ко.
- ^ [25] Historia Augusta , Жизни тридцати претендентов , III и XXX.
- ^ [26] Historia Augusta , Жизнь Аврелиана , XXXII; [27] Historia Augusta , Жизнь Клавдия , I.
- ^ Лактанций, «VII» , О смерти преследователей.
- ↑ Иоанн Зонарас, Краткое содержание: От Диоклетиана до смерти Галерия.
- ^ Диоклетиан (284–305 гг. Н.э.), автор Ральф В. Матисен. О римских императорах. 17 марта 1997 г. Проверено 20 марта 2007 г.
- ^ Уорд-Перкинс 1994 .
- ^ Лактанций, «X-XVI» , О смерти гонителей.
- ^ Гиббон, Эдвард (1906). «Глава ХХ». В Бери, Дж. Б. (ред.). История упадка и разрушения Римской империи . Фред де Фау и Ко.
- ^ Гиббон, Эдвард (1906). «Глава XVII» (Онлайн-версия) . В Бери, Дж. Б. (ред.). История упадка и разрушения Римской империи . Фред де Фау и компания ; Константин I (306–337 гг. Н.э.) Ганса А. Польсандера. Де Императорибус Романис. 8 января 2004 г. Проверено 20 марта 2007 г.
- ^ Гонорий (395–423 гг. Н.э.), автор Ральф В. Матисен. О римских императорах. 2 июня 1999 г. Проверено 21 марта 2007 г.
- ^ Дуикер и Шпильвогель 2001 , стр. 155 .
- ^ Гиббон, Эдвард (1906). «Глава XXVI» (Онлайн-версия) . В Бери, Дж. Б. (ред.). История упадка и разрушения Римской империи . Фред де Фау и Ко.
- ^ «Императорский диптих: Восток и Запад после 395 года» (на итальянском языке) . Проверено 12 августа 2023 г.
- ^ Лэфэм, Льюис (1997). Конец Света. Нью-Йорк: Книги Томаса Данна. ISBN 0-3122-5264-1 . стр. 47–50.
- ^ [28] Бери, Дж. Б.: История Поздней Римской империи , 8, §2.; [29] Бери, Дж. Б.: История Поздней Римской империи , 6, §4.; [30] Бери, Дж. Б.: История Поздней Римской империи , 6, §3.; [31] Бери, Дж. Б.: История Поздней Римской империи , 9.; «Германские вторжения в Западную Европу» . Университет Калгари . Август 1996 года. Архивировано из оригинала 12 августа 2013 года . Проверено 22 марта 2007 г. ; Дукер и Шпильвогель 2001 , с. 157
- ^ «Римские императоры – ДИР Ромул Августул» . www.roman-emperors.org . 23 июля 2022 г .; Ромул Августул (475–476 гг. Н.э.) - Два взгляда Ральфа В. Матисена и Джеффри С. Натана. Де Императорибус Романис. 26 августа 1997 г. Проверено 22 марта 2007 г.
- ^ Матисен, Ральф А. (8 февраля 1998 г.). «Римские императоры – ДИР Непот» .
- ^ Дюрант и Дюрант 1944 , с. 670.
- ^ Дуикер и Шпильвогель 2001 , с. 347 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б с Хукер, Ричард (6 июня 1999 г.). «Византийская империя» . Университет штата Вашингтон . Архивировано из оригинала 24 февраля 1999 года.
- ^ Брей, Р.С. (2004). Армии чумы . Джеймс Кларк и Ко. р. 26. ISBN 978-0-2271-7240-7 .
- ^ Крейц, Барбара М. (1996). До норманнов: Южная Италия в девятом и десятом веках . Издательство Пенсильванского университета. ISBN 978-0-8122-1587-8 .
- ^ Дуикер и Шпильвогель 2001 , с. 349 .
- ^ Василий II (976–1025 гг. Н. Э.) Кэтрин Холмс. О римских императорах. 1 апреля 2003 г. Проверено 22 марта 2007 г.
- ^ Гиббон, Эдвард (1906). «Глава LXI» (Онлайн-версия) . В Бери, Дж. Б. (ред.). История упадка и разрушения Римской империи . Фред де Фау и Ко.
- ^ Мехмет II в Коркуте-Озгене. Theottomans.org. Проверено 3 апреля 2007 г.
- ^ Дуикер и Шпильвогель 2001 , с. 149 ; Аннотация к книге «Население Древнего Рима». Гленн Р. Стори. Исследования дальнего света. 1 декабря 1997 г. Проверено 22 апреля 2007 г.; Население Рима Уитни Дж. Оутс. Первоначально опубликовано в журнале «Классическая филология» .Том. 29, № 2 (апрель 1934 г.), стр. 101–116. Проверено 22 апреля 2007 г.
- ^ Н.Морли, Метрополис и внутренние районы (Кембридж, 1996) 174–183.
- ^ Гаванде, Атул (2014). Быть смертным . Профильные книги. п. 32. ISBN 978-1-8466-8582-8 .
- ^ Росси, Лино (1981). Каменные журналы. Знаки и рисунки времени на триумфальных памятниках Римской империи (на итальянском языке). Книга Хака. п. 59. ИСБН 978-8-8164-0071-9 .
- ^ Адкинс и Адкинс 1998 , стр. 46.
- ^ Jump up to: а б с Дукер и Шпильвогель 2001 , с. 146 .
- ^ Фрэнк Фрост Эбботт, Общество и политика в Древнем Риме , BiblioBazaar, LLC, 2009, с. 41
- ^ Jump up to: а б Лекция 13: Краткая социальная история Римской империи Стивена Крейса. 11 октября 2006 г. Проверено 2 апреля 2007 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б с д и ж г час Адкинс и Адкинс 1998 , с. 211.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Вернер 1978 , с. 31.
- ^ Дуикер и Шпильвогель 2001 , стр. 143 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б с Римское образование . Подготовка к латинскому экзамену ExCET. Техасская классическая ассоциация, Джинни Линдзи, сентябрь 1998 г. Проверено 27 марта 2007 г.
- ^ Матышак 2003 , стр. 16–42.
- ^ Jump up to: а б с д Киган 1993 , стр. 263–264 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б с Поттер, Дэвид (2004). Римская армия и флот . стр. 67–70 . в цветке 2004 г.
- ^ Обсуждение тактики гоплитов и их социокультурной среды см. Хэнсон, Виктор Дэвис (1989). Западный путь войны: пехотный бой в классической Греции . Нью-Йорк: Альфред А. Кнопф. ISBN 0-3945-7188-6 .
- ^ Голдсуорси 1996 , с. 33.
- ^ Шелтон, Джо-Энн, изд. (1998). Как это делали римляне: справочник по римской социальной истории . Нью-Йорк: Издательство Оксфордского университета. стр. 245–249. ISBN 0-1950-8974-Х .
- ^ Окли, Стивен П. (2004). Ранняя республика . п. 27 . в цветке 2004 г.
- ^ Mackay 2004 , стр. 249–250 Маккей указывает, что количество легионов выросло до 30 к 125 году нашей эры и до 33 в период Севера (200–235 нашей эры).
- ^ Голдсуорси 1996 , стр. 36–37.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Элтон 1996 , стр. 89–96.
- ^ Бреннан, Корри Т. (2004). Власть и процесс в соответствии с республиканской «конституцией» . стр. 66–68 . в цветке 2004 г.
- ^ Голдсуорси 1996 , стр. 121–125.
- ^ Маккей 2004 , стр. 245–252.
- ^ Mackay 2004 , стр. 295–296. Также главы 23–24.
- ^ Саддингтон, Д.Б. (2011) [2007]. «Классы: эволюция римского императорского флота». В Эрдкампе, Пол (ред.). Товарищ римской армии . Уайли-Блэквелл. стр. 201–217 (табл. 12.2 на стр. 204). ISBN 978-1-4051-2153-8 .
- ^ Коарелли, Филиппо (1987), Святилища Лацио в эпоху республиканцев . НИС, Рим, стр. 35–84.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Этот абзац основан на Поттере, 2004 г. , стр. 76–78.
- ^ Элтон 1996 , стр. 99–101.
- ^ Сабин, Филип; ван Вис, Ганс; Уитби, Майкл, ред. (2007). Кембриджская история греческих и римских войн . Издательство Кембриджского университета. п. 231. ИСБН 978-0-5217-8274-6 .
- ^ Хезелтайн, Джон (2005). Дороги в Рим . Музей Дж. Пола Гетти. п. 11. ISBN 978-0-7112-2552-7 .
- ^ Темин, Петр (2001). «Рыночная экономика в ранней Римской империи» . Абстрактные архивы . Услуги истории экономики. Архивировано из оригинала 15 июня 2010 года.
- ^ См. «Шедевры. Крест Дезидерия» . Fondazione Brescia Musei . Архивировано из оригинала 19 октября 2021 года . Проверено 2 октября 2016 г. . Описание научных исследований Медальона Брешии см. в книге Дэниела Томаса Хауэллса (2015). « Каталог позднеантичного золотого стекла в Британском музее (PDF) ». Лондон: Британский музей (Совет по исследованиям в области искусств и гуманитарных наук), с. 7. По состоянию на 2 октября 2016 г. Портрет из золотого стекла (скорее всего, сделанный александрийским греком из-за египетского диалекта надписи ), датированный III веком нашей эры; Беквит, Джон, Раннехристианское и византийское искусство, История искусства Пингвина (ныне Йельский университет), 2-е изд. 1979, ISBN 0-1405-6033-5 , с. 25; Бордман, редактор Джона, Оксфордская история классического искусства, 1993, OUP, ISBN 0-1981-4386-9 , стр. 338–340; Григ, Люси, «Портреты, понтифики и христианизация Рима четвертого века», Документы британской школы в Риме , Vol. 72, (2004), стр. 203–230, JSTOR 40311081 , стр. 207; Яс Эльснер (2007). «Изменяющаяся природа римского искусства и искусствоведческая проблема стиля», в Еве Р. Хоффман (редактор), Позднеантичное и средневековое искусство средневекового мира , 11–18. Оксфорд, Молден и Карлтон: Blackwell Publishing. ISBN 978-1-4051-2071-5 , с. 17, рисунок 1.3 на с. 18.
- ^ Паркин, Тим, и Помрой, Артур, Социальная история Рима, справочник, Routledge, 2007, стр. 72. ISBN 978-0-4154-2675-6
- ^ Босуэлл, Джон Истберн, «Expositio и Oblatio: отказ от детей и древняя и средневековая семья», American Historical Review , 89 , 1984, стр. 12
- ^ Кассон 1998 , стр. 10–11 , 24–32.
- ^ Кассон 1998 , стр. 10–11, 24–32 .
- ^ Семейные ценности в Древнем Риме Ричарда Саллера. Цифровые коллекции библиотеки Чикагского университета: Архив Fathom. 2001 г. Посещено 14 апреля 2007 г.
- ^ Адкинс и Адкинс 1998 , стр. 39–40.
- ^ Роусон, Берил (1987). Семья в Древнем Риме: новые перспективы . Издательство Корнельского университета. п. 7. ISBN 978-0-8014-9460-4 .
- ^ Фриер, Брюс В. и Макгинн, Томас А.Дж. Сборник примеров по римскому семейному праву , Oxford University Press: Американская филологическая ассоциация, 2004, стр. 20
- ^ Роусон, Берил, «Римская семья», в книге «Семья в Древнем Риме: новые перспективы» , Cornell University Press, 1986, стр. 30, 40–41; Галинский, Карл, Культура Августа: интерпретативное введение , Princeton University Press, 1998, стр. 130–132, ISBN 978-0-6910-5890-0
- ^ Latin Online: Введение в серию. Архивировано 29 апреля 2015 года в Wayback Machine Уинфредом П. Леманном и Джонатаном Слокамом. Центр лингвистических исследований. Техасский университет в Остине. 15 февраля 2007 г. Проверено 1 апреля 2007 г.
- ^ Калверт, Дж. Б. (8 августа 1999 г.). «Латинский алфавит» . Денверский университет . Архивировано из оригинала 3 апреля 2007 года.
- ^ Классическое латинское приложение . п. 2. Проверено 2 апреля 2007 г.
- ^ Йожеф Герман, Вульгарная латынь , английский перевод 2000, стр. 109–114 ISBN 978-0-2710-2001-3
- ^ Рошетт 2023 , с. 263 268; Рошетт 2018 , с. 114-115,118.
- ^ Рошетт 2018 , стр. 108.
- ^ Адкинс и Адкинс 1998 , стр. 203; Калделлис 2023 , с. 289; Рошетт 2011 , с. 562; Рошетт 2023 , с. 283.
- ^ Матышак 2003 , с. 24.
- ^ Эдвард Гиббон (1787). История упадка и падения Римской империи . напечатано для JJ Tourneisen. п. 91. ; Американская энциклопедия: библиотека универсальных знаний . Энциклопедия Американской корпорации. 1919. с. 644.
- ^ Уиллис 2000 , стр. 166–168.
- ^ Уиллис 2000 .
- ^ Феодосий I (379–395 гг. Н.э.) , Дэвид Вудс. О римских императорах. 2 февраля 1999 г. Проверено 4 апреля 2007 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Астор, Уильям. «Хлеб и зрелища в Риме и Америке» . Проверено 11 августа 2017 г.
- ^ Ежегодные издания: Западная цивилизация . Том. 1 (12-е изд.). МакГроу-Хилл/Душкин. 2002. с. 68.
...где сострадание рассматривалось как моральный недостаток...
- ^ Джексон, Майкл Энтони (2004). Оглянитесь назад, чтобы идти вперед: жизненные уроки героев истории . Аркадное издательство. п. 174. ИСБН 978-1-5597-0727-5 .
Гладаторские игры были популярны, потому что римляне действительно считали сострадание пороком и слабостью.
- ^ Харви, Брайан К., изд. (2016). Повседневная жизнь в Древнем Риме: Справочник . Издательская компания Хакетт. стр. 21–28. ISBN 978-1-5851-0796-4 .
- ^ Ленглендс, Ребекка (2006). Сексуальная мораль в Древнем Риме . Издательство Кембриджского университета. стр. 3–20. ISBN 978-0-5218-5943-1 .
- ^ Мэтью Диллон и Линда Гарланд (2005). Древний Рим: от ранней республики до убийства Юлия Цезаря . Тейлор и Фрэнсис. п. 382. ИСБН 978-0-4152-2459-8 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б с д Адкинс и Адкинс 1998 , стр. 350–352.
- ^ Римская живопись из хронологии истории искусств. Отдел греческого и римского искусства Метрополитен-музея. 2004–10. Проверено 22 апреля 2007 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Граут, Дональд Джей; Палиска, Клод В. (1988). История западной музыки . Нортон. ISBN 978-0-3939-5627-6 . Проверено 31 мая 2012 г.
- ^ Адкинс и Адкинс 1998 , стр. 89.
- ^ Адкинс и Адкинс 1998 , стр. 349–350.
- ^ Адкинс и Адкинс 1998 , стр. 300.
- ^ Грант 2005 , стр. 130–134.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Дикс, Т. Кейт (1994). « Публичные библиотеки» в Древнем Риме: идеология и реальность» . Библиотеки и культура . 29 (3): 282–296. ISSN 0894-8631 . JSTOR 25542662 .
- ^ «Витрувий Поллион, Десять книг по архитектуре, КНИГА VI, ГЛАВА IV: ПРАВИЛЬНОЕ ОБСЛУЖИВАНИЕ РАЗНЫХ КОМНАТ, раздел 1» . www.perseus.tufts.edu . Проверено 29 ноября 2023 г.
- ^ «Плиний Старший, Естественная история, КНИГА XXXV. ОТЧЕТ КАРТИН И ЦВЕТОВ. ГЛАВА 2. (2) — ЧЕСТЬ, ОТДАВАЕМАЯ ПОРТРЕТАМ» . www.perseus.tufts.edu . Проверено 29 ноября 2023 г.
- ^ «Библиотека — Древний Рим, Коллекции, Архивы | Британника» . www.britanica.com . Проверено 29 ноября 2023 г.
- ^ Хьюстон, Джордж У. (2008). «Тиберий и библиотеки: собрания публичных книг и библиотечные здания в ранней Римской империи» . Библиотеки и культурные записи . 43 (3): 247–269. дои : 10.1353/lac.0.0032 . ISSN 2166-3033 . S2CID 161471143 .
- ^ Стаикос, Константинос Сп (25 октября 2021 г.), «История библиотеки в западной цивилизации, том II: от Цицерона до Адриана: римский мир от истоков латинской литературы до монументальных и частных библиотек Империи» , История Библиотеки западной цивилизации, том II , Брилл, doi : 10.1163/9789004473508 , ISBN 978-9-0044-7350-8 , получено 29 ноября 2023 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б «Римский форум: его история и его памятники / Ч. Хюльсен; перевод Джесси Бенедикта Картера» . ХатиТраст . hdl : 2027/njp.32101076187390 . Проверено 29 ноября 2023 г.
- ^ Бойд, CE (1915). Публичные библиотеки и литературная культура Древнего Рима . Издательство Чикагского университета. ISBN 978-1-1648-3397-0 .
- ^ Картрайт, Марк. «Библиотеки древнего мира» . Энциклопедия всемирной истории . Проверено 29 ноября 2023 г.
- ^ Пфайффер, Гомер Ф. (1931). «Римская библиотека в Тимгаде» . Мемуары Американской академии в Риме . 9 : 157–165. дои : 10.2307/4238558 . ISSN 0065-6801 . JSTOR 4238558 .
- ^ Дж. Карсон Вебстер, Месячные труды в античном и средневековом искусстве до конца двенадцатого века, Исследования в области гуманитарных наук 4 (Northwestern University Press, 1938), с. 128. В собраниях Эрмитажа .
- ^ Чивителло, Линда (2011). Кухня и культура: история еды и людей . Джон Уайли и сыновья. ISBN 978-0-4704-0371-6 .
- ^ Филлис Прей Бобер, Искусство, культура и кухня: древняя и средневековая гастрономия , University of Chicago Press (2001), стр. 188.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Патрик Фаас, За римским столом: еда и пиршества в Древнем Риме , University of Chicago Press (2005), стр. 209.
- ^ Jump up to: а б с Филлис Прей Бобер, Искусство, культура и кухня: древняя и средневековая гастрономия , University of Chicago Press (2001), с. 187.
- ^ Магелонн Туссен-Самат, История еды , John Wiley & Sons (2009), стр. 93.
- ^ Джон Э. Стамбо, Древний римский город , JHU Press (1988), стр. 148.
- ^ Jump up to: а б с Артман, Джон: «Древний Рим – независимый учебный блок», стр. 26, Good Apple, 1991.
- ^ Jump up to: а б Артман, Джон:: «Древний Рим - Независимый учебный блок», с. 26, Доброе яблоко, 1991.
- ^ «Далматика» (на итальянском языке ) Проверено 12 августа 2023 г.
- ^ Jump up to: а б с Кассон 1998 , стр. 98–108 .
- ^ Jump up to: а б «Повседневная жизнь: Развлечения» . SPQR онлайн . 1998. Архивировано из оригинала 30 апреля 2007 года.
- ^ Большой цирк . Энциклопедия Романа. Чикагский университет. Проверено 19 апреля 2007 г.
- ^ Джон Хамфри, Римские цирки: арены для гонок на колесницах , University of California Press, 1986, стр. 216.
- ^ Древнеримские законы защищали от развращения рабов с целью получения секретов искусства хозяина. Зейдман, Боб (2011). Справочник программного IP-детектива: Измерение, сравнение и обнаружение нарушений . Прентис Холл. п. 103 . ISBN 978-0-1370-3533-5 .
- ^ Зима, Томас Нельсон (1979). «Римский бетон: восхождение, вершина и упадок искусства» . Труды Академии наук Небраски . 7 : 137–143.
- ↑ Чой, Чарльз К. (4 декабря 2019 г.). «Грязная находка показывает, как иностранная древесина помогла построить Древний Рим». InsideScience.org . Проверено 22 мая 2020 г.
- ^ «Римская дорожная система» . Britannica.com . Британская энциклопедия, Inc. Проверено 19 августа 2017 г.
- ^ Киган 1993 , с. 303 .
- ^ Ходж, AT (1992). Римские акведуки и водоснабжение . Дакворт. ISBN 9780715621943 .
- ^ Граут, Джеймс. «Отравление свинцом и Рим» . Чикагский университет. Архивировано из оригинала 26 мая 2012 года . Проверено 22 июля 2011 г.
- ^ Джейкоб Дорси Форрест (1906). Развитие западной цивилизации: исследование этической, экономической и политической эволюции . Издательство Чикагского университета. ; Уильям Каннингем (1900). Очерк западной цивилизации в ее экономических аспектах: Средневековье и современность . Университетское издательство . Проверено 31 мая 2012 г. ; Эндрю Флеминг Уэст , Ценность классики . 1917. с. 185
- ^ Куно Фишер (1887). История современной философии . Сыновья К. Скрибнера. п. 85. ; Майкл Бургер (2008). Формирование западной цивилизации: от античности к эпохе Просвещения . Университет Торонто Пресс. п. 203. ИСБН 978-1-5511-1432-3 .
- ^ Финли, Мичиган (2008). Древняя история: доказательства и модели . История АКЛС. п. 9. ISBN 978-1-5974-0534-8 .
К сожалению, два самых длинных древних отчета об истории Римской Республики, области, в которой проблемы в настоящее время стоят наиболее остро и наиболее широко обсуждаются, истории Ливия и Дионисия Галикарнасского, были составлены на 500 лет (в очень круглых цифрах) позже. чем традиционная дата основания республики, на 200 лет со дня разгрома Ганнибала.
- ^ [32] Плутарх, Параллельные жизни , Жизнь Мариуса , XI, 5–7.
- ^ Хэндфорд, ЮАР (1951). Цезарь: Завоевание Галлии . Хармондсворт: Пингвин. п. 24.
- ^ Борода, Мэри (20 октября 2015 г.). SPQR: История Древнего Рима . Профиль. стр. 15–16. ISBN 978-1-8476-5441-0 .
- ^ Люкконен, Петри. «Теодор Моммзен» . Книги и писатели (kirjasto.sci.fi) . Куусанкоски Публичная библиотека . Архивировано из оригинала 24 августа 2014 года.
- ^ Грант, Майкл (1987). Мир Рима . Пингвин. ISBN 9780452008496 .
- ^ Левик, Барбара (1993). Клавдий . Издательство Йельского университета. ISBN 978-0-3000-5831-4 .
- ^ см . онлайн-издание
- ^ Сайм, Рональд (2002). Римская революция . Издательство Оксфордского университета. ISBN 978-0-1928-0320-7 .
Цитируемые работы
[ редактировать ]- Адкинс, Лесли ; Адкинс, Рой А. (1998). Руководство к жизни в Древнем Риме . Издательство Оксфордского университета. ISBN 978-0-1951-2332-6 .
- Боутрайт, Мэри Т.; и др. (2012). Римляне: от деревни к империи (2-е изд.). Издательство Оксфордского университета. ISBN 978-0-1997-3057-5 . ОЛ 25033142М .
- Кэри, Макс (1967). История Рима вплоть до правления Константина (2-е изд.). Пресса Святого Мартина.
- Кассон, Лайонел (1998). Повседневная жизнь в Древнем Риме . Издательство Университета Джонса Хопкинса. ISBN 978-0-8018-5992-2 .
- Корнелл, Тим Дж . (1995). Начало Рима: Италия и Рим от бронзового века до Пунических войн (ок. 1000–264 до н.э.) . Рутледж. OCLC 31515793 .
- Дуйкер, Уильям ; Шпильфогель, Джексон (2001). Всемирная история (3-е изд.). Уодсворт. ISBN 978-0-5345-7168-9 . ОЛ 6786176М .
- Дюрант, Уилл; Дюрант, Ариэль (1944). История цивилизации . Том. III: Цезарь и Христос. Саймон и Шустер. ISBN 978-1-5673-1023-8 .
- Элтон, Хью (1996). Война в римской Европе 350–425 гг . н.э. Издательство Оксфордского университета. ISBN 978-0-1981-5241-5 .
- Флауэр, Харриет И., изд. (2004). Кембриджский компаньон Римской республики . Издательство Кембриджского университета. ISBN 978-0-5210-0390-2 .
- Голдсуорси, Адриан Кейт (1996). Римская армия на войне: 100 г. до н. э. – 200 г. н. э . Издательство Оксфордского университета. ISBN 978-0-1981-5057-2 .
- Голдсуорси, Адриан Кейт (2006). Падение Карфагена: Пунические войны 265–146 гг . до н.э. Феникс. ISBN 978-0-3043-6642-2 .
- Грант, Майкл (2005). Города Везувия: Помпеи и Геркуланум . Феникс Пресс. ISBN 978-1-8988-0045-3 .
- Хейвуд, Ричард (1971). Древний мир . Компания Дэвида Маккея, Inc.
- Калделлис, Энтони (2023). Новая Римская империя: История Византии . Нью-Йорк: Издательство Оксфордского университета . дои : 10.1093/bear/9780197549322.001.0001 . ISBN 978-0-1975-4932-2 .
- Киган, Джон (1993). История войны . Альфред А. Кнопф. ISBN 978-0-3945-8801-8 .
- Ливи . Возвышение Рима, книги 1–5, перевод с латыни Т. Дж. Люса, 1998. Oxford World's Classics. Оксфорд: Издательство Оксфордского университета. ISBN 0-1928-2296-9 .
- Маккей, Кристофер С. (2004). Древний Рим: Военная и политическая история . Издательство Кембриджского университета. ISBN 978-0-5218-0918-4 .
- Матышак, Филипп (2003). Хроника Римской республики . компании Thames & Hudson, Ltd. ISBN 978-0-5000-5121-4 .
- Майлз, Ричард (2011). Карфаген должен быть разрушен . Пингвин. ISBN 978-0-1410-1809-6 .
- О'Коннелл, Роберт (1989). Об оружии и людях: история войны, оружия и агрессии . Издательство Оксфордского университета. ISBN 978-0-1950-5359-3 .
- Рошетт, Бруно (2011). «Языковая политика в Римской республике и империи» . Товарищ по латинскому языку : 549–563. дои : 10.1002/9781444343397.ch30 . hdl : 2268/35932 . ISBN 978-1-4051-8605-6 .
- Рошетт, Бруно (2018). «Существовал ли римский лингвистический империализм во времена республики и раннего принципата?» . Lingue e Linguaggio (1/2018): 107–128. дои : 10.1418/90426 . ISSN 1720-9331 .
- Рошетт, Бруно (2023). Маллен, Алекс (ред.). «Отношение римских императоров к языковой практике» . Социальные факторы в латинизации римского Запада (1-е изд.). Оксфорд: Oxford Academic: 258–285. дои : 10.1093/oso/9780198887294.003.0012 . ISBN 978-0-1988-8729-4 . Проверено 22 декабря 2023 г.
- Скарр, Крис (1995). Исторический атлас Древнего Рима пингвинов . Книги о пингвинах. ISBN 978-0-1405-1329-5 .
- Шайдель, Уолтер ; Саллер, Ричард П.; Моррис, Ян (2007). Кембриджская экономическая история греко-римского мира . Издательство Кембриджского университета. ISBN 978-0-5217-8053-7 . ОЛ 16929915W .
- Уорд-Перкинс, Джон Брайан (1994). Римская имперская архитектура . Издательство Йельского университета. ISBN 978-0-3000-5292-3 .
- Вернер, Пол (1978). Жизнь в Риме в древние времена . перевод Дэвида Макрея. Редакции Минерва SA
- Уиллис, Рой (2000). Мировая мифология: Иллюстрированное руководство . Книги Кена Фина. ISBN 978-1-8645-8089-1 .
Дальнейшее чтение
[ редактировать ]- Антонио, Маргарет Л.; и др. (8 ноября 2019 г.). «Древний Рим: генетический перекресток Европы и Средиземноморья» . Наука . 366 (6466). Американская ассоциация содействия развитию науки : 708–714. Бибкод : 2019Sci...366..708A . дои : 10.1126/science.aay6826 . ПМК 7093155 . ПМИД 31699931 .
- Кассий Дион (январь 2004 г.). Рим Диона, том V, книги 61–76 (54–211 гг. Н. Э.) . Проверено 17 декабря 2006 г.
- Коарелли, Филиппо (2007). Рим и окрестности: Археологический справочник . Издательство Калифорнийского университета.
- Коулстон, Дж. К.; Додж, Хейзел, ред. (2000). Древний Рим: Археология вечного города . Школа археологии Оксфордского университета.
- Форсайт, Гэри (2005). Критическая история раннего Рима . Издательство Калифорнийского университета.
- Фокс, Мэтью (1996). Римские исторические мифы: Царственный период в литературе Августа . Издательство Оксфордского университета.
- Габба, Эмилио (1991). Дионисий и история архаического Рима . Издательство Калифорнийского университета.
- Гиббон, Эдвард (1776–1789). История упадка и разрушения Римской империи .
- Голдсуорси, Адриан Кейт (2003). Полная римская армия . Темза и Гудзон. ISBN 978-0-5000-5124-5 .
- Голдсуорси, Адриан Кейт (2008). Цезарь: Жизнь колосса . Издательство Йельского университета. ISBN 978-0-3001-2689-1 .
- Холлоуэй, Р. Росс (1994). Археология раннего Рима и Лациума . Рутледж.
- Кивени, Артур (2005). Рим и объединение Италии (2-е изд.). Бристоль Феникс.
- Краус, Кристина Шаттлворт; Вудман, Эй Джей (1997). Латинские историки . Издательство Оксфордского университета.
- Митчелл, Ричард Э. (1990). Патриции и плебеи: Возникновение Римского государства . Издательство Корнельского университета.
- Поттер, ТВ (1987). Римская Италия . Издательство Калифорнийского университета.
- Раафлауб, Курт А., изд. (2004). Социальная борьба в архаическом Риме: новые взгляды на конфликт орденов (2-е изд.). Блэквелл.
- Розенштейн, Натан С.; Морштейн-Маркс, Роберт, ред. (2006). Спутник Римской республики . Блэквелл.
- Скаллард, Х.Х. (1982). От Гракхов до Нерона (5-е изд.). Рутледж. ISBN 978-0-4150-2527-0 .
- Смит, Кристофер Дж. (1996). Ранний Рим и Лациум: экономика и общество ок. 1000–500 гг . до н.э. Издательство Оксфордского университета.
- Стюарт, Роберта (1998). Государственная должность в раннем Риме: ритуальная процедура и политическая практика . Издательство Мичиганского университета.
- Уэйд, Лиззи (8 ноября 2019 г.). «Иммигранты с Ближнего Востока сформировали Рим». Наука . 366 (6466). Американская ассоциация содействия развитию науки : 673. Бибкод : 2019Sci...366..673W . дои : 10.1126/science.366.6466.673 . ПМИД 31699914 . S2CID 207965960 .
- Вульф, Грег (2012). Рим: История Империи . Издательство Оксфордского университета.
- Вайк, Мария (1997). Проецирование прошлого: Древний Рим, кино и история . Рутледж.
Внешние ссылки
[ редактировать ]- Ресурсы по Древнему Риму для учащихся библиотеки средней школы Куртенэ.
- История древнего Рима OpenCourseWare от Университета Нотр-Дам предоставляет бесплатные ресурсы, включая лекции, вопросы для обсуждения, задания и экзамены.
- Галерея древнего искусства: Древний Рим